Configuring Indoor Deployment for -E Domain
IW9167EH supports indoor deployment for -E domain.
By default, indoor deployment is disabled, and the 5G radio supports channels 100, 104, 108, 112, 116, 120, 124, 128, 132, 136, 140. After factory reset, indoor deployment configuration is reset to default, which is disabled.
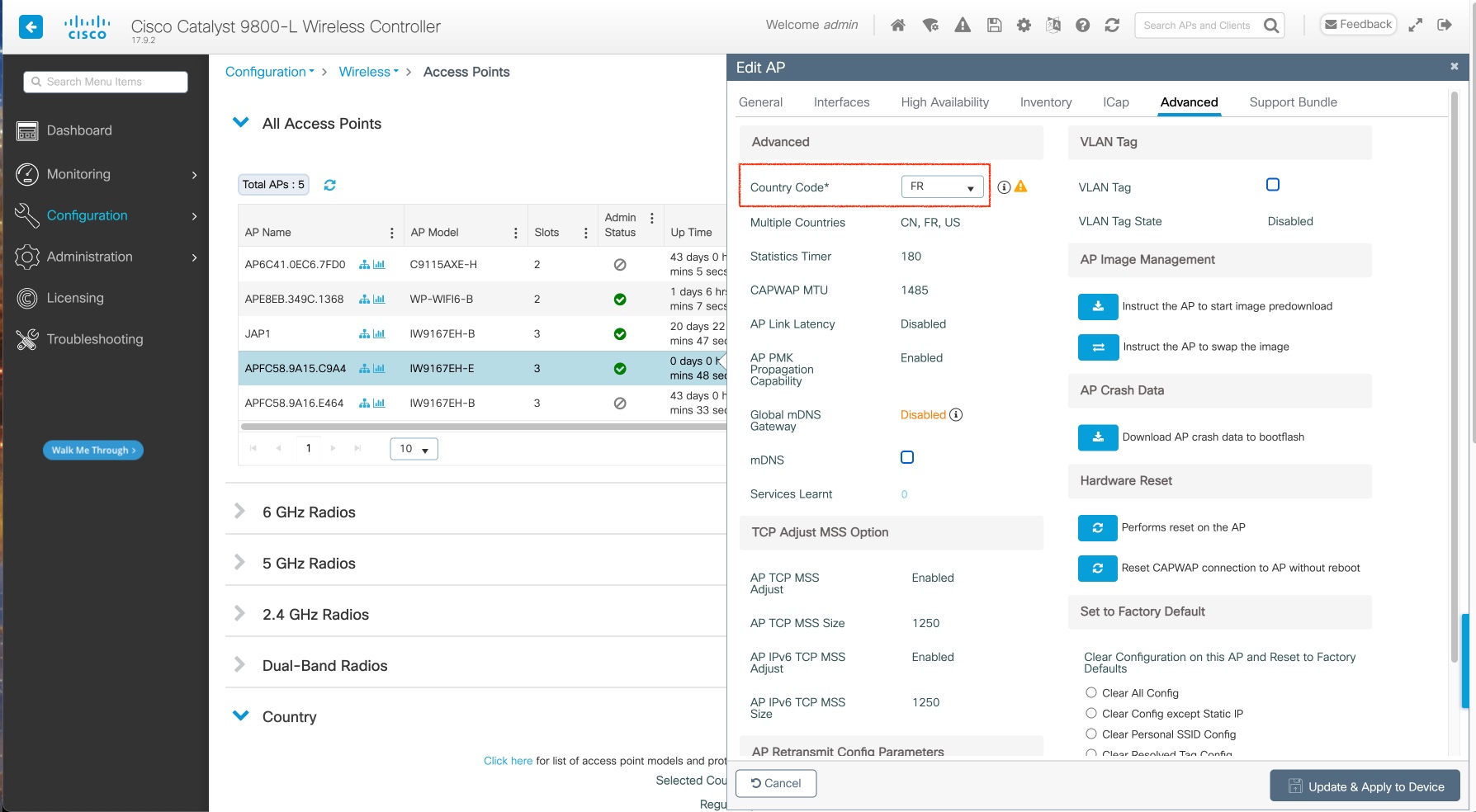
You can check AP mode by using the show ap name <ap-name> config general | section Indoor command. In the command output, "Enabled" means AP is in indoor mode, and "Disabled" means AP is in outdoor mode, as shown in the following example.
#show ap name APFC58.9A15.C9A4 config general | inc Indoor
AP Indoor Mode : Disabled
To configure the AP to indoor mode, use the ap name <ap-name > indoor command from wireless LAN controller. This command triggers an AP rebooting. After AP registers to the wireless LAN controller after rebooting, you need to assign corresponding country code to the AP. When indoor deployment is enabled, 5G radio supports channels 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64, 100, 104, 108, 112, 116, 120, 124, 128, 132, 136, 140.
 Note |
To disable indoor deployment, use the ap name <ap-name > no indoor command. |

 Note |
Channel list extends from U-NII-2c to U-NII-1, U-NII-2a, U-NII-2c (channel 144 is excluded). |




 Feedback
Feedback