Cisco Aironet Directional Hyperlocation Antenna (AIR-ANT25-LOC-02=) Installation Guide
Available Languages
Table of Contents
Cisco Aironet Directional Hyperlocation Antenna (AIR-ANT25-LOC-02=)
2.4 GHz WiFi Antenna Radiation Patterns
5GHz WiFi Antenna Radiation Patterns
Choosing the Mounting Location and Brackets
Flush-Mounting the Antenna on a Wall
Mounting using Short-Link Mount Assembly
Mounting using Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket Assembly
Obtain Documentation and Submit a Service Request
Cisco Aironet Directional Hyperlocation Antenna (AIR-ANT25-LOC-02=)
This document describes the AIR-ANT25-LOC-02= antenna and provides electrical specifications and mounting instructions.
The antenna is a four-port polarization-diverse patch array that operates over the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz Wi-Fi bands. The antenna provides both location-based services and Wi-Fi coverage over wide, open areas. The antenna may be mounted on a wall or mounted using an articulating mount. The location array in the antenna services a wide coverage area (±55º left and right of the boresight).
The antenna ships with an articulating mount for use on flat surfaces and masts and is adjustable in both the horizontal and vertical planes. The antenna radome can be painted using commonly available non-conductive spray paints, such as Krylon or Rust-Oleum. The antenna is designed for use in indoor or outdoor environments. The antenna is designed for use with the Cisco Aironet AP3702E and AP3702P access points along with the Cisco Hyperlocation module (AIR-RM3010L-x-K9=).
The following information is provided in this document:
Technical Specifications
Figure 1 Antenna Dimensions (in inches)

What’s in the Box
■![]() AIR-ANT25-LOC-02= directional hyperlocation antenna with directional WiFi, with five attached cables. See the Parts of the Antenna.
AIR-ANT25-LOC-02= directional hyperlocation antenna with directional WiFi, with five attached cables. See the Parts of the Antenna.
■![]() Mounting bracket assembly parts and hardware. See the Mounting Bracket Hardware Kit.
Mounting bracket assembly parts and hardware. See the Mounting Bracket Hardware Kit.
Parts of the Antenna
Figure 6 Face view of the antenna

Four coaxial cables with RP-TNC (plug) connectors that attach to the AP’s antenna connectors. |
|||
One cable with a rectangular (DART) connector that attaches to the Hyperlocation module |
Arrow denoting the direction for Hyperlocation. This arrow is present on the top (as shown), base, and the sides of the antenna. For information on orienting the antenna for Hyperlocation to work, see the Hyperlocation Deployment Guide at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/technotes/8-1/Halo-DG/b_hyperlocation-deployment-guide.html |
Figure 7 Back view of the antenna

Mounting Bracket Hardware Kit
Antenna Mounting Bracket Kit Contents shows the parts of the antenna bracket kit that is factory-shipped with the antenna.
Figure 8 Antenna Mounting Bracket Kit Contents
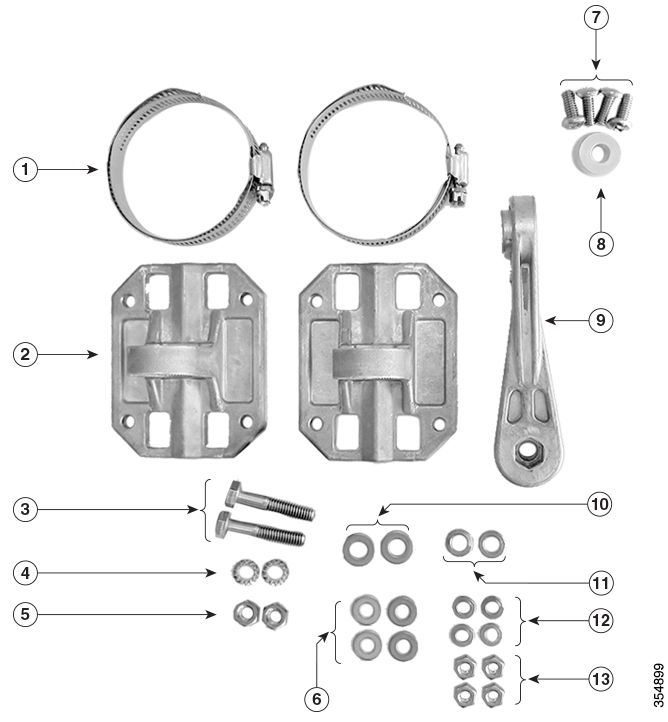
Worm-gear type hose clamp (50-135mm), 2 nos, used only when mounting the antenna on a pole. |
Spacer1 for attaching Female-Female mount flanges. |
||
| Both mount flanges are identical. Each can be attached to the back of the antenna, a wall, or a pole. |
|||
Mounting the Antenna
Follow these steps for installing the antenna:
■![]() Read the Safety Instructions and Installation Guidelines thoroughly.
Read the Safety Instructions and Installation Guidelines thoroughly.
■![]() Familiarize yourself with theParts of the Antenna and Mounting Bracket Hardware Kit.
Familiarize yourself with theParts of the Antenna and Mounting Bracket Hardware Kit.
■![]() Proceed with Choosing the Mounting Location and Brackets and then following the different deployment scenarios provided therein.
Proceed with Choosing the Mounting Location and Brackets and then following the different deployment scenarios provided therein.
–![]() Flush-Mounting the Antenna on a Wall
Flush-Mounting the Antenna on a Wall
–![]() Mounting using Short-Link Mount Assembly
Mounting using Short-Link Mount Assembly
–![]() Mounting using Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket Assembly
Mounting using Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket Assembly
Safety Instructions
- IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device. Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS - Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Statement 1030
Follow these safety instructions when installing your antenna.
■![]() Plan your installation procedure carefully and completely before you begin.
Plan your installation procedure carefully and completely before you begin.
■![]() If you are installing an antenna for the first time, for your own safety as well as others, seek professional assistance. Consult your dealer, who can explain which mounting method to use for the location where you intend to install the antenna.
If you are installing an antenna for the first time, for your own safety as well as others, seek professional assistance. Consult your dealer, who can explain which mounting method to use for the location where you intend to install the antenna.
■![]() Select your installation site with safety, as well as performance, in mind. Remember that electric power cables and telephone lines look alike. For your safety, assume that any line is an electric power line until determined otherwise.
Select your installation site with safety, as well as performance, in mind. Remember that electric power cables and telephone lines look alike. For your safety, assume that any line is an electric power line until determined otherwise.
■![]() Call your local power company or building maintenance organization if you are unsure about cables close to your mounting location.
Call your local power company or building maintenance organization if you are unsure about cables close to your mounting location.
■![]() When installing your antenna, do not use a metal ladder. Do dress properly: shoes with rubber soles and heels, rubber gloves, and a long sleeved shirt or jacket.
When installing your antenna, do not use a metal ladder. Do dress properly: shoes with rubber soles and heels, rubber gloves, and a long sleeved shirt or jacket.
■![]() If an accident or emergency occurs with the power lines, call for qualified emergency help immediately.
If an accident or emergency occurs with the power lines, call for qualified emergency help immediately.
Installation Guidelines
As antennas transmit and receive radio signals, they are susceptible to RF obstructions and common sources of interference that can reduce throughput and range of the device to which they are connected. Follow these guidelines to ensure the best possible performance:
■![]() Mount the antenna to utilize its propagation characteristics. This antenna is designed to radiate energy in a somewhat narrow beam from the front of the antenna. It should be aimed into the intended coverage area.
Mount the antenna to utilize its propagation characteristics. This antenna is designed to radiate energy in a somewhat narrow beam from the front of the antenna. It should be aimed into the intended coverage area.
■![]() Keep the antenna away from metal obstructions such as heating and air-conditioning ducts, large ceiling trusses, building superstructures, and major power cabling runs. If necessary, use a rigid conduit to lower the antenna away from these obstructions.
Keep the antenna away from metal obstructions such as heating and air-conditioning ducts, large ceiling trusses, building superstructures, and major power cabling runs. If necessary, use a rigid conduit to lower the antenna away from these obstructions.
■![]() The density of the materials used in a building’s construction determines the number of walls the signal must pass through and still maintain adequate coverage. Consider the following before choosing the location to install your antenna:
The density of the materials used in a building’s construction determines the number of walls the signal must pass through and still maintain adequate coverage. Consider the following before choosing the location to install your antenna:
–![]() Signals penetrate paper, vinyl and drywall the easiest. A signal can penetrate five or six walls constructed of drywall or wood.
Signals penetrate paper, vinyl and drywall the easiest. A signal can penetrate five or six walls constructed of drywall or wood.
–![]() Signals are more heavily attenuated passing through concrete and solid-wood walls.
Signals are more heavily attenuated passing through concrete and solid-wood walls.
–![]() Signals often reflect off thick metal walls and may not penetrate at all.
Signals often reflect off thick metal walls and may not penetrate at all.
■![]() Install the antenna away from microwave ovens and 2 GHz cordless phones. These products can cause signal interference because they operate in the same frequency range as the access point to which your antenna is connected.
Install the antenna away from microwave ovens and 2 GHz cordless phones. These products can cause signal interference because they operate in the same frequency range as the access point to which your antenna is connected.
Choosing the Mounting Location and Brackets
The antenna is designed for use with the Cisco Aironet AP3702E and AP3702P access points along with the Cisco Hyperlocation module (AIR-RM3010L-x-K9=). The antenna can be mounted only vertically, on a wall, or on a pole. For pole-mounting, the pole should have a minimum diameter of 2 inches and a maximum diameter of 5 inches (50mm - 135mm).
The antenna is designed for both indoor and outdoor deployments. You can deploy it in large halls, warehouses, and atriums having high ceilings.
When mounting the antenna you need to assemble the bracket hardware, mount the antenna using the bracket, and adjust the antenna orientation.
The antenna should be mounted clear of any obstructions to the side or front of the antenna enclosure. Note that this antenna should be aimed into the intended coverage area, and so you should mount the antenna so as to achieve the required mechanical tilt. Mount the antenna as close to the access point so that the access point is within the range of the connecting cables.
Depending on where you are mounting the antenna, there are multiple mounting and bracket assembly options available. See .
Mounting Bracket Assemblies and Dimensions
Figure 9 Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)

Slotted holes for steel band clamps, for pole-mounting only. |
Screw holes for fastening flange to the antenna or to a wall. |
Figure 10 Length of Short Link Mount – in inches (and millimeters)

| Mount flanges. One flange attaches to the mounting surface—a wall or a pole. The other flange attaches to the antenna. |
|||
Figure 11 Assembling the Short Link Mount

Figure 12 Length of Fully Assembled Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket – in inches (and millimeters)

Figure 13 Assembling the Full Mount Arm–Flanges Bracket

Flush-Mounting the Antenna on a Wall
You can mount the antenna directly on a wall, vertically, without using any mounting bracket assembly, allowing the antenna to be flush against the wall (see Flush-mounting the Antenna on a Wall). The cables, at the back of the antenna, will need to be routed through a hole in the wall.
The following table lists the materials needed for this installation:
To flush-mount the antenna on a wall, follow these steps:
Determine the mounting location for the antenna.
Note![]() The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
- Use the antenna as a template and mark the positions of the holes for flushing-mounting the antenna, on the wall. Drill holes into this marked positions and insert wall anchors as required.
- Cut a hole in the wall, for passing the antenna cables through.
- Hold up the antenna against the wall and pass the antenna cables through the hole in the wall. Make sure you orient the antenna correctly (note the arrow on the back of the antenna that indicates the top of the antenna).
- Align the antenna’s wall-mount screw holes with the holes in the wall, and then fasten the antenna to the wall using the fasteners which you have procured.
- Optionally, seal the hole for the cables using a cable sealing system, such as the Roxtec Multidiameter™ cable sealing system. Visit http://www.roxtec.com/ for information on how to install the cable sealing system.
- Connect the antenna cables to the access point.
Figure 14 Flush-mounting the Antenna on a Wall
Hole in the wall through which the cables are routed. Optionally, you can seel this hole using a cable sealing system, such as the Roxtec Multidiameter™ cable sealing system. Visit http://www.roxtec.com/ for information on how to install the cable sealing system. |
Mounting using Short-Link Mount Assembly
You can mount the antenna on a wall or a pole, vertically, using the Short-Link mount bracket assembly. See Short-Link Mount Assembly.
Figure 15 Short-Link Mount Assembly

The following table lists the materials needed for this installation:
Short-Link mount bracket assembly parts, as shown in Length of Short Link Mount – in inches (and millimeters). |
|
| Four mounting screws and wall anchors (Used for mounting the antenna and bracket assembly on a wall. These fasteners should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna and bracket, plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.) |
|
(Optional, and for wall mounting only) |
|
Mounting the Antenna on a Wall
To mount the antenna on a wall using the short-link mount bracket assembly, follow these steps:
Familiarize yourself with:
- Length of Short Link Mount – in inches (and millimeters)
- Assembling the Short Link Mount
- Determine the mounting location for the antenna.
Note![]() The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
- Use the mount flange as a template (see Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)) and mark the positions of the holes for mounting the antenna-bracket assembly on the wall. Drill holes into this marked positions, insert wall anchors as required, and attach the flange to the wall using four screws.
- (Optional) Cut a hole in the wall, for passing the antenna cables through.
- Attach the other mount flange to the back of the antenna.
- Hold up the antenna–mount flange assembly against the wall and pass the antenna cables through the hole in the wall. Make sure you orient the antenna correctly (note the arrow on the back of the antenna that indicates the top of the antenna).
- Mount the antenna–mount flange assembly on to the flange mount on the wall. For guidance, see the short-link mount bracket assembly in Assembling the Short Link Mount.
- (Optional) Seal the hole for the cables using a cable sealing system, such as the Roxtec Multidiameter™ cable sealing system. Visit http://www.roxtec.com/ for information on how to install the cable sealing system.
- Connect the antenna cables to the access point.
Mounting the Antenna on a Pole
You can mount the antenna on poles that have diameters ranging from 2 to 5 inches (50mm - 135mm).
Note![]() The pole or mast must be rigid enough to hold the weight of the antenna plus the associated forces produced by wind loads. In addition, the pole or mast must be structurally strong enough to withstand the clamping force of the hose clamps.
The pole or mast must be rigid enough to hold the weight of the antenna plus the associated forces produced by wind loads. In addition, the pole or mast must be structurally strong enough to withstand the clamping force of the hose clamps.
To mount the antenna on a pole using the short-link mount bracket assembly, follow these steps:
Familiarize yourself with:
- Length of Short Link Mount – in inches (and millimeters)
- Assembling the Short Link Mount
- Determine the mounting location on the pole.
Note![]() The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
- Position and mount a mounting flange (Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)) onto the pole using the hose clamps provided in the kit. The hose clamps should pass through the slots on the mounting flange (Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)).
- Tighten the clamps only enough such that the flange and antenna can be held in place until the antenna is positioned to its final position.
- Attach the other mount flange to the back of the antenna.
- Hold up the antenna–mount flange assembly against the pole-mounted flange. Make sure you orient the antenna correctly (note the arrow on the back of the antenna that indicates the top of the antenna).
- Mount the antenna–mount flange assembly on to the flange mount on the pole. For guidance, see the short-link mount bracket assembly in Assembling the Short Link Mount.
- Tighten the hose clamps until the antenna is fully secure on the mast. Ensure that the antenna cannot rotate about the mast.
- Connect the antenna cables to the access point.
Mounting using Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket Assembly
You can mount the antenna on a wall or a pole, vertically, with both azimuth and elevation adjustment. For this you will need to use the full bracket assembly which includes the mount arm and the mount flanges. See Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket Assembly.
Figure 16 Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket Assembly

The following table lists the materials needed for this installation:
Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket assembly as shown in Assembling the Full Mount Arm–Flanges Bracket. |
|
| Four mounting screws and wall anchors (Used for mounting the antenna and bracket assembly on a wall. These fasteners should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna and bracket, plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.) |
|
(Optional, and for wall mounting only) |
|
Mounting the Antenna on a Wall
To mount the antenna on a wall using the full bracket assembly, follow these steps:
Familiarize yourself with:
- Length of Fully Assembled Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket – in inches (and millimeters)
- Assembling the Full Mount Arm–Flanges Bracket
- Determine the mounting location for the antenna.
Note![]() The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
- Use the mount flange as a template (see Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)) and mark the positions of the holes for mounting the antenna-bracket assembly on the wall. Drill holes into this marked positions, insert wall anchors as required, and attach the flange to the wall using four screws.
- (Optional) Cut a hole in the wall, for passing the antenna cables through.
- Attach the other mount flange to the back of the antenna.
- Hold up the antenna–mount flange assembly against the wall and pass the antenna cables through the hole in the wall. Make sure you orient the antenna correctly (note the arrow on the back of the antenna that indicates the top of the antenna).
- Mount the antenna–mount flange assembly on to the flange mount on the wall, using the mount arm. For guidance, see the full mount arm–flanges bracket assembly in Assembling the Full Mount Arm–Flanges Bracket. Do not fully tighten the pivot adjustment screws.
- Adjust the azimuth (side-to-side position) and elevation (up-and-down position) of the antenna (see Antenna Azimuth Adjustment and Antenna Elevation Adjustment). Loosen the adjustment screws slightly to allow for adjustment. Azimuth angle can be adjusted ±25 degrees and elevation can be adjusted ±60 degrees. You can use the azimuth and elevation markings on the mounting arm and the flanges as a guide.
- After you adjust the antenna position, tighten the adjustment screws to 18.7 +/- 5 lb-ft (25.4 Nm).
- (Optional) Seal the hole for the cables using a cable sealing system, such as the Roxtec Multidiameter™ cable sealing system. Visit http://www.roxtec.com/ for information on how to install the cable sealing system.
- Connect the antenna cables to the access point.
Mounting the Antenna on a Pole
You can mount the antenna on poles that have diameters ranging from 2 to 5 inches (50mm - 135mm).
Note![]() The pole or mast must be rigid enough to hold the weight of the antenna plus the associated forces produced by wind loads. In addition, the pole or mast must be structurally strong enough to withstand the clamping force of the hose clamps.
The pole or mast must be rigid enough to hold the weight of the antenna plus the associated forces produced by wind loads. In addition, the pole or mast must be structurally strong enough to withstand the clamping force of the hose clamps.
To mount the antenna on a pole using the full bracket assembly, follow these steps:
Familiarize yourself with:
- Length of Fully Assembled Mount Arm-Flanges Bracket – in inches (and millimeters)
- Assembling the Full Mount Arm–Flanges Bracket
- Determine the mounting location on the pole.
Note![]() The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
The fasteners and mounting surface should be capable of maintaining a minimum pullout force of 150 pounds (68 kg) to support the weight of the antenna plus the potential wind loading on the antenna.
- Position and mount a mounting flange (Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)) onto the pole using the hose clamps provided in the kit. The hose clamps should pass through the slots on the mounting flange (Mount Flange Parts and Dimensions (in millimeters)).
- Tighten the clamps only enough such that the flange and antenna can be held in place until the antenna is positioned to its final position.
- Attach the other mount flange to the back of the antenna.
- Hold up the antenna–mount flange assembly against the pole-mounted flange. Make sure you orient the antenna correctly (note the arrow on the back of the antenna that indicates the top of the antenna).
- Mount the antenna–mount flange assembly on to the flange mount on the wall, using the mount arm. For guidance, see the full mount arm–flanges bracket assembly in Assembling the Full Mount Arm–Flanges Bracket. Do not fully tighten the pivot adjustment screws.
- Adjust the azimuth (side-to-side position) and elevation (up-and-down position) of the antenna. Loosen the adjustment screws slightly to allow for adjustment. Azimuth angle can be adjusted ±25 degrees and elevation can be adjusted ±60 degrees. You can use the azimuth and elevation markings on the mounting arm and the flanges as a guide.
- After you adjust the antenna position, tighten the adjustment screws to 18.7 +/- 5 lb-ft (25.4 Nm).
- Tighten the hose clamps until the antenna is fully secure on the mast. Ensure that the antenna cannot rotate about the mast.
- Connect the antenna cables to the access point.
Painting the Antenna
Painting the antenna and the bracket does not affect its performance if you use standard exterior-grade, oil-based or latex paint. Do not use metallic or metallic-flake paints, which will degrade antenna performance.
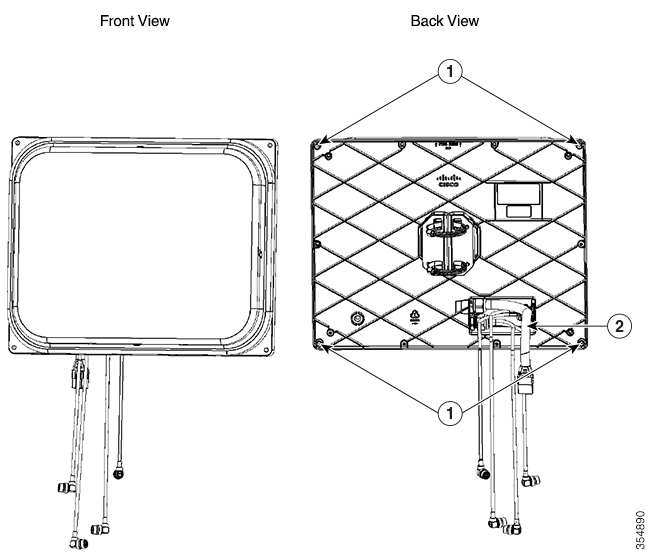
Note![]() Before painting the antenna, cover the pressure-release vent on the rear, lower-left of the antenna with masking tape to prevent clogging (Back view of the antenna).
Before painting the antenna, cover the pressure-release vent on the rear, lower-left of the antenna with masking tape to prevent clogging (Back view of the antenna).
Cisco recommends Krylon Fusion for Plastic or Rust-Oleum for Plastic (which might require a primer coat). For best results, follow the surface preparation suggestions from the paint manufacturer.
Obtain Documentation and Submit a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation.
To receive new and revised Cisco technical content directly to your desktop, you can subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation RSS feed. The RSS feeds are a free service.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1721R)
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)







 Feedback
Feedback