VLAN Mapping
In a typical deployment of VLAN mapping, you want the service provider to provide a transparent switching infrastructure that includes customers’ switches at the remote location as a part of the local site. This allows customers to use the same VLAN ID space and run Layer 2 control protocols seamlessly across the provider network. In such scenarios, we recommend that service providers do not impose their VLAN IDs on their customers.
One way to establish translated VLAN IDs (S-VLANs) is to map customer VLANs to service-provider VLANs (called VLAN ID mapping) on trunk ports connected to a customer network. Packets entering the port are mapped to a service provider VLAN (S-VLAN) based on the port number and the packet’s original customer VLAN-ID (C-VLAN).
Service providers’s internal assignments might conflict with a customer’s VLAN. To isolate customer traffic, a service provider could decide to map a specific VLAN into another one while the traffic is in its cloud.
Switch Support
VLAN Mapping is supported on all models of Cisco Catalyst IE9300 Rugged Series Switches. The feature is available with a Network Essentials or Network Advantage license.
Deployment Example
All forwarding operations on the switch are performed using S-VLAN and not C-VLAN information because the VLAN ID is mapped to the S-VLAN on ingress.
 Note |
When you configure features on a port configured for VLAN mapping, you always use the S-VLAN rather than the customer VLAN-ID (C-VLAN). One-to-one VLAN mapping is not supported at this time. |
On an interface configured for VLAN mapping, the specified C-VLAN packets are mapped to the specified S-VLAN when they enter the port. Symmetrical mapping to the customer C-VLAN occurs when packets exit the port.
The switch supports the following types of VLAN mapping on trunk ports:
Mapping Customer VLANs to Service-Provider VLANs
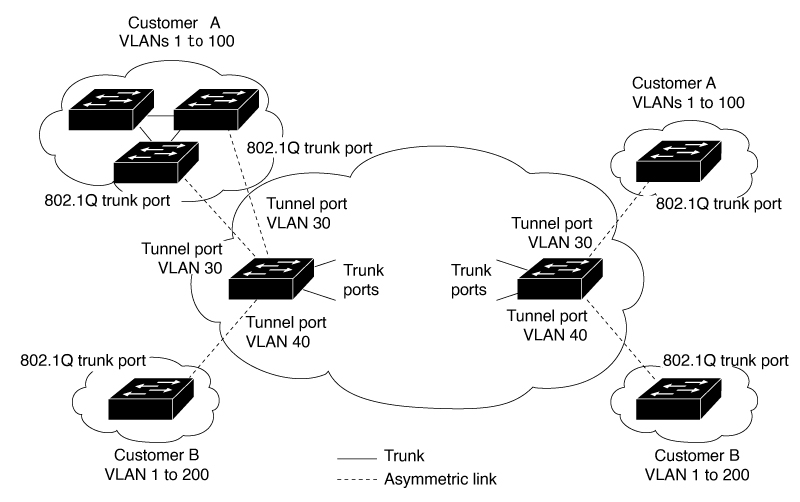
The preceding illustration shows a topology where Customer A and Customer B use the same VLANs in multiple sites on different sides of a service-provider network. You map the customer VLAN IDs to service-provider VLAN IDs for packet travel across the service-provider backbone. The customer VLAN IDs are retrieved at the other side of the service-provider backbone for use in the other customer site. Configure the same set of VLAN mappings at a customer-connected port on each side of the service-provider network.
Selective QnQ
Selective QnQ maps the specified customer VLANs entering the UNI to the specified S-VLAN ID. The S-VLAN ID is added to the incoming unmodified C-VLAN and the packet travels the service provider network double-tagged. At the egress, the S-VLAN ID is removed and the customer VLAN-ID is retained on the packet. By default, packets that do not match the specified customer VLANs are dropped.
QnQ on a Trunk Port
QnQ on a trunk port maps all the customer VLANs entering the UNI to the specified S-VLAN ID. Similar to Selective QnQ, the packet is double-tagged and at the egress, the S-VLAN ID is removed.
 Feedback
Feedback