Traffic Decryption Explained
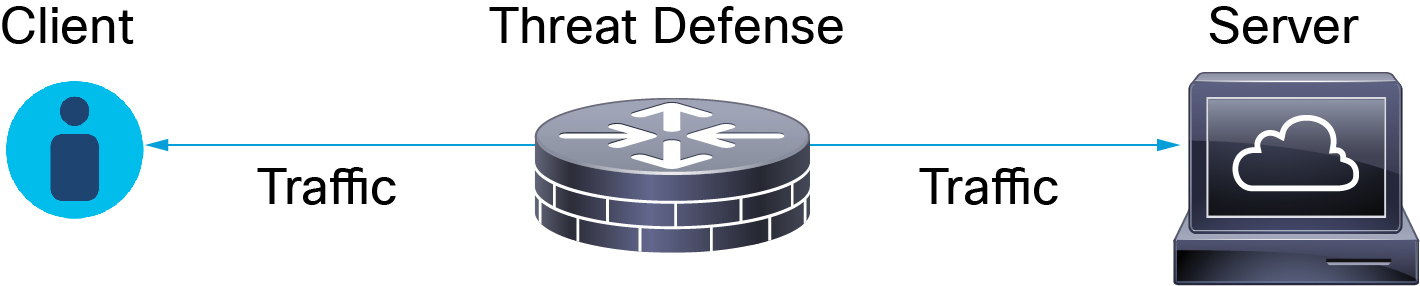
Most traffic on the internet is encrypted and in most cases, you don't want to decrypt it; even if you don't, you can still glean some information about it and block it from your network if necessary.
Your choices are:
-
Decrypt the traffic and subject it to the full array of deep inspection:
-
Advanced Malware Protection
-
Security intelligence
-
Threat Intelligence Director
-
Application detectors
-
URL and category filtering
-
-
Leave the traffic encrypted and set up your access control and decryption policy to look for and potentially block:
-
Old protocol versions (such as Secure Sockets Layer)
-
Unsecure cipher suites
-
Applications with high risk and low business relevance
-
Untrusted issuer Distinguished Names
-
Access control policy
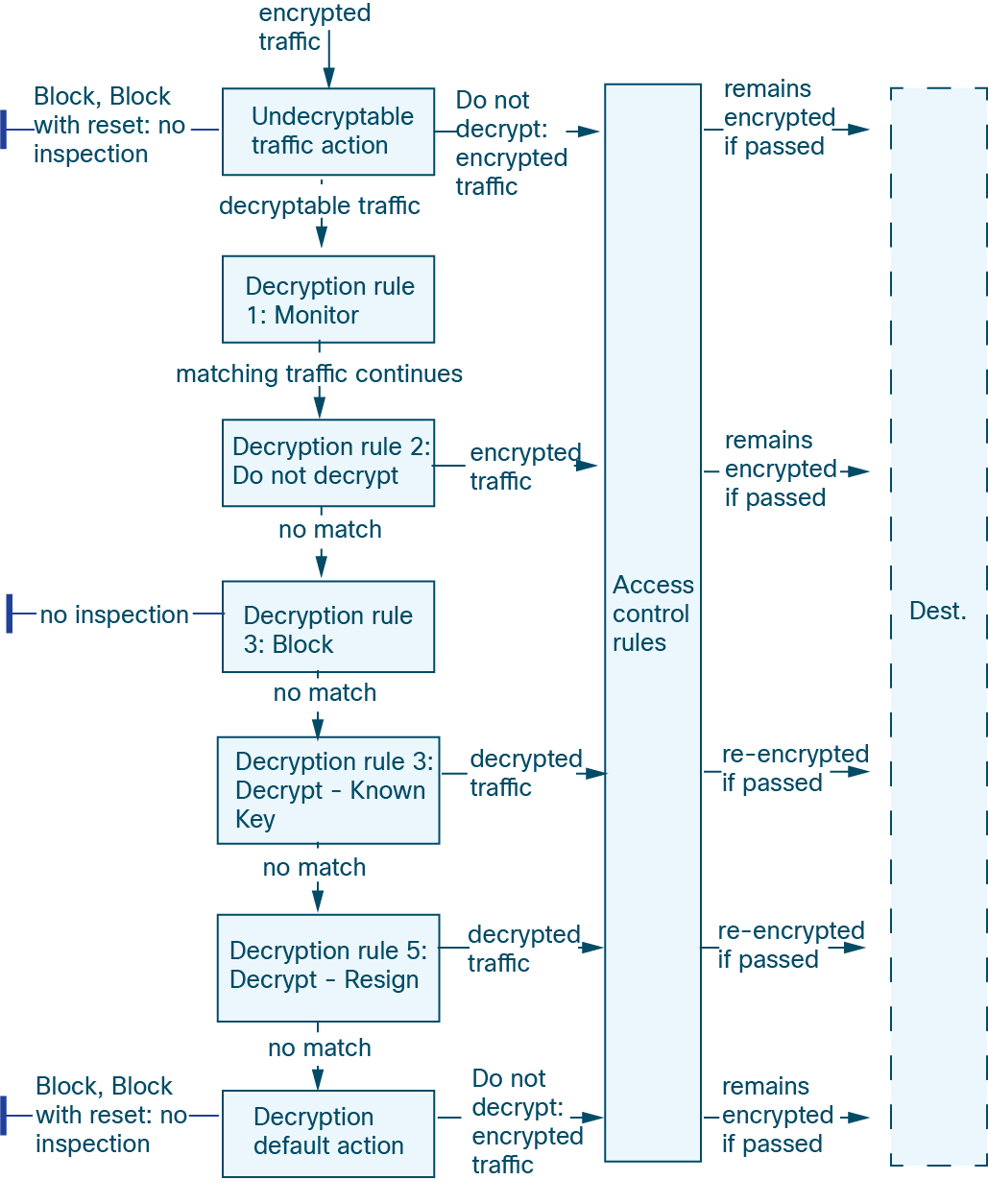
An access control policy is the main configuration that invokes subpolicies and other configurations, including a decryption policy. If you associate a decryption policy with access control, the system uses that decryption policy to handle encrypted sessions before it evaluates the sessions with access control rules. If you do not configure TLS/SSL inspection, or your devices do not support it, access control rules handle all encrypted traffic.
Access control rules also handle encrypted traffic when your TLS/SSL inspection configuration allows the traffic to pass. However, some access control rule conditions require unencrypted traffic, so encrypted traffic might match fewer rules. Also, by default, the system disables intrusion and file inspection of encrypted payloads. This helps reduce false positives and improves performance when an encrypted connection matches an access control rule that has intrusion and file inspection configured.
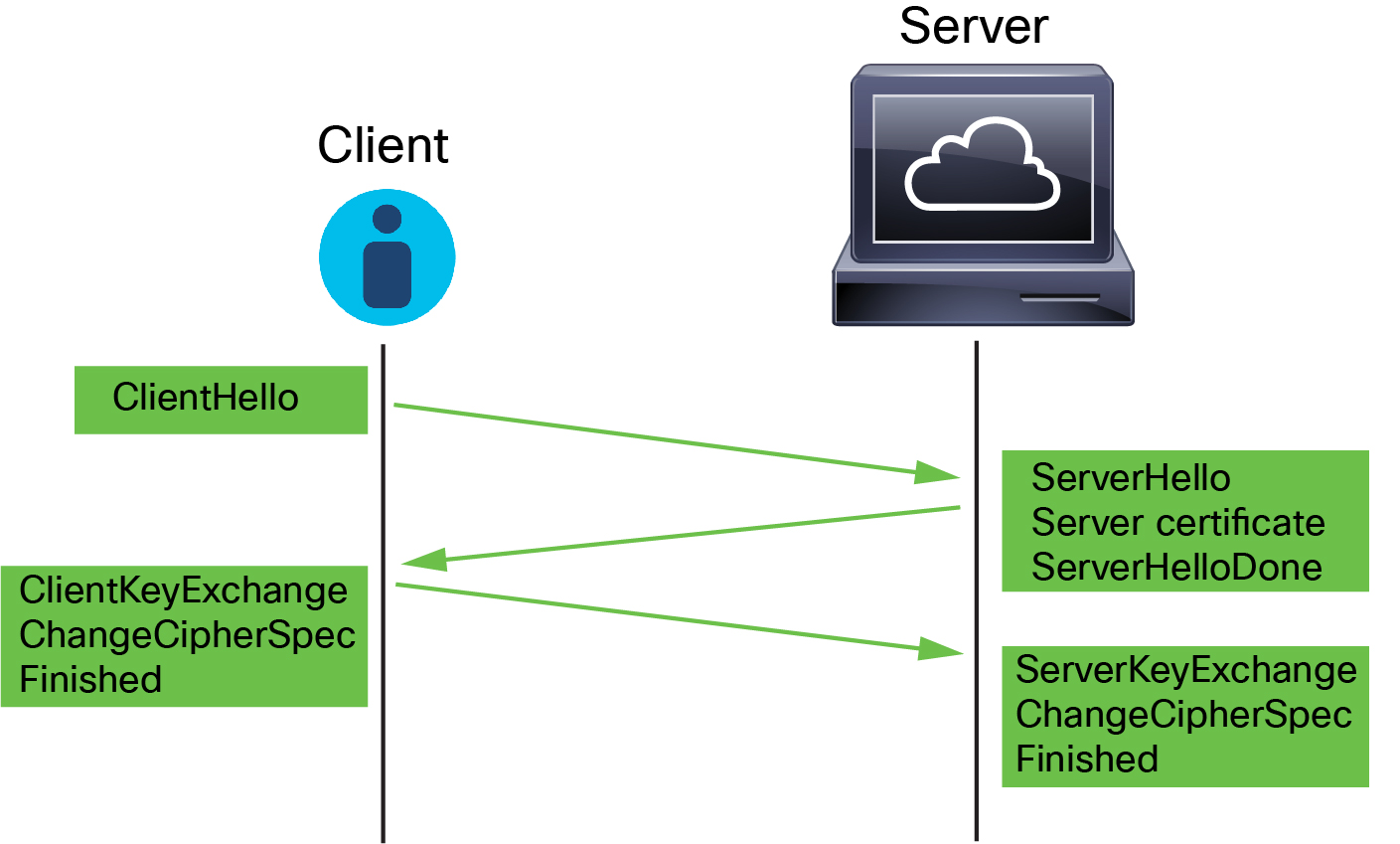
Among protocols decrypted
Among the protocols we decrypt:
-
TLS versions up to 1.3 (if Snort 3 is enabled)
-
DNS over HTTPS
-
DNS over TLS (RFC 7858)
-
FTPS, SMTPS, IMAPS, POP3S
Notes
Decryption ruless require processing overhead that can impact performance. Before you decide to decrypt traffic, see When to Decrypt Traffic, When Not to Decrypt.
As long as your managed devices have Snort 3 enabled, the system supports decrypting TLS 1.3 traffic. You can enable TLS 1.3 decryption in an decryption policy's advanced options; for more information, see Decryption Policy Advanced Options.
The Firepower System does not support mutual authentication; that is, you cannot upload a client certificate to the Secure Firewall Management Center and use it for either Decrypt - Resign or Decrypt - Known Key decryption rule actions. For more information, see Decrypt and Resign (Outgoing Traffic). and Known Key Decryption (Incoming Traffic).
If you set the value of TCP maximum segment size (MSS) using FlexConfig, the observed MSS could be less than your setting. For more information, see About the TCP MSS.


 Feedback
Feedback