Configurar a redistribuição de rotas BGP internas no IGP
Opções de download
Linguagem imparcial
O conjunto de documentação deste produto faz o possível para usar uma linguagem imparcial. Para os fins deste conjunto de documentação, a imparcialidade é definida como uma linguagem que não implica em discriminação baseada em idade, deficiência, gênero, identidade racial, identidade étnica, orientação sexual, status socioeconômico e interseccionalidade. Pode haver exceções na documentação devido à linguagem codificada nas interfaces de usuário do software do produto, linguagem usada com base na documentação de RFP ou linguagem usada por um produto de terceiros referenciado. Saiba mais sobre como a Cisco está usando a linguagem inclusiva.
Sobre esta tradução
A Cisco traduziu este documento com a ajuda de tecnologias de tradução automática e humana para oferecer conteúdo de suporte aos seus usuários no seu próprio idioma, independentemente da localização. Observe que mesmo a melhor tradução automática não será tão precisa quanto as realizadas por um tradutor profissional. A Cisco Systems, Inc. não se responsabiliza pela precisão destas traduções e recomenda que o documento original em inglês (link fornecido) seja sempre consultado.
Contents
Introduction
Este documento descreve como redistribuir rotas do protocolo BGP no processo Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
Prerequisites
Requirements
A Cisco recomenda que você tenha conhecimento da configuração básica do BGP e compreenda os protocolos de roteamento de:
- BGP
- OSPF
- Protocolo de Roteamento IGRP Melhorado (EIGRP)
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Para obter mais informações, consulte Estudos de Caso BGP e Configuração do BGP.
Componentes Utilizados
As informações neste documento são baseadas no software Cisco IOS® versão 15.1(4)M5.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. Se a rede estiver ativa, certifique-se de que você entenda o impacto potencial de qualquer comando.
Informações de Apoio
Como em outro IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) para redistribuição de IGP, o comportamento é diferente quando o BGP (IBGP) interno é redistribuído no OSPF. As rotas aprendidas de IBGP não são encaminhadas para um protocolo de roteamento IGP através do comando redistribute. Use o comando bgp redistribute-internal no processo BGP no roteador que redistribui.
Configurar
Diagrama de Rede
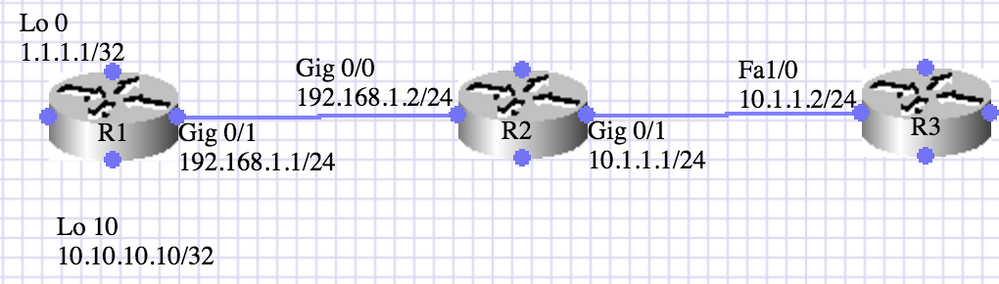
Configurar o OSPF entre R2 e R3
No cenário descrito aqui, os roteadores R1 e R2 executam o IBGP e os roteadores R2 ou R3 executam a área 0 do OSPF. O R1 anuncia duas rotas (1.1.1.1 /32 e 10.10.10.10/32) através do comando network.
R2 redistribui o BGP na área 0 do OSPF. É necessário redistribuir as rotas internas selecionadas (10.10.10.10/32).
A tarefa é realizada com o uso de lista de prefixos e mapa de rotas.
R1:
interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback10 ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 10 no synchronization bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 1.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 network 10.10.10.10 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 192.168.1.2 remote-as 100 no auto-summary
R1#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 10.10.10.10, local AS number 10 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using 296 bytes of memory 2 path entries using 128 bytes of memory 1/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 136 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 560 total bytes of memory BGP activity 2/0 prefixes, 2/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.1.2 4 10 6 7 3 0 0 00:03:10 0
R2:
interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto !
router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 log-adjacency-changes redistribute bgp 100 metric 100 metric-type 1 subnets route-map BGP-To_OSPF network 10.1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
R2#show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 3.3.3.3 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:38 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1
router bgp 10 no synchronization bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp redistribute-internal neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 10 no auto-summary ! ip prefix-list BGP-to-ospf seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/16 ! route-map BGP-To_OSPF permit 10 match ip address prefix-list BGP-to-ospf
R2#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 192.168.1.2, local AS number 10 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using 272 bytes of memory 2 path entries using 112 bytes of memory 1/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 128 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 512 total bytes of memory BGP activity 2/0 prefixes, 2/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.1.1 4 10 8 7 3 0 0 00:03:52 2 R2#show ip bgp BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 192.168.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i1.1.1.1/32 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 i *>i10.10.10.10/32 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 i
R2#show ip route 1.1.1.1 Routing entry for 1.1.1.1/32 Known via "bgp 10", distance 200, metric 0, type internal Last update from 192.168.1.1 00:04:53 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.1.1, from 192.168.1.1, 00:04:53 ago Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 0 MPLS label: none R2#show ip route 10.10.10.10 Routing entry for 10.10.10.10/32 Known via "bgp 10", distance 200, metric 0, type internal Last update from 192.168.1.1 00:04:56 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.1.1, from 192.168.1.1, 00:04:56 ago Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 0 MPLS label: none
R3:
interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto
router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 10.1.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
R3#show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.1.2 1 FULL/DR 00:00:36 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1
A tabela de roteamento em R3 antes da redistribuição do BGP - internal é adicionada em R2 no roteador BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2:
router bgp 10 bgp redistribute-internal
Verificar
R3:
A tabela de roteamento para R3 após a redistribuição do BGP - internal é adicionada em R2 no roteador BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 O E1 10.10.10.10/32 [110/11] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:06, GigabitEthernet0/1
Configurar o EIGRP entre R2 e R3:
No cenário descrito aqui, os roteadores R1 e R2 executam o IBGP e os roteadores R2 ou R3 executam o EIGRP Autonomous System (AS) 1. O R1 anuncia duas rotas (1.1.1.1 /32 e 10.10.10.10/32) através do comando network.
R2 redistribui o BGP no EIGRP AS 1. É necessário redistribuir as rotas internas selecionadas (10.10.10.10/32).
A tarefa é realizada com o uso de lista de prefixos e mapa de rotas.
R2:
router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 redistribute bgp 10 metric 1544 10 255 1 1500 route-map BGP_To_EIGRP eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2
route-map BGP_To_EIGRP, permit, sequence 10 Match clauses: ip address prefix-lists: BGP-to-eigrp Set clauses: Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes
ip prefix-list BGP-to-eigrp: 1 entries
seq 1 permit 10.10.10.10/32
R3:
router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3
A saída do comando show IP route em R3 antes da redistribuição do BGP - internal é adicionada em R2 no roteador BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2:
router bgp 10 bgp redistribute-internal
Verificar
A saída do comando show IP route em R3 após o BGP redistribute-internal é adicionada em R2 no roteador BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 D EX 10.10.10.10/32 [170/1660672] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:04, GigabitEthernet0/1
Configurar o RIP entre R2 e R3:
No cenário descrito aqui, os roteadores R1 e R2 executam o IBGP e os roteadores R2 ou R3 executam o RIPv2.
O R1 anuncia duas rotas (1.1.1.1 /32 e 10.10.10.10/32) através do comando network.
R2 redistribui o BGP em RIPv2. É necessário redistribuir as rotas internas selecionadas (10.10.10.10/32).
A tarefa é realizada com o uso de lista de prefixos e mapa de rotas.
R2:
router rip version 2 redistribute bgp 10 metric 1 route-map BGP_To_RIP network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
route-map BGP_To_RIP, permit, sequence 10 Match clauses: ip address prefix-lists: BGP-to-rip Set clauses: Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes ip prefix-list BGP-to-rip: 1 entries seq 1 permit 10.10.10.10/32
R3:
router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
Saída em R3 antes de ativar o bgp redistribute-internal em R2 no roteador bgp 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2:
router bgp 10 bgp redistribute-internal
Verificar
Saída em R3 depois de habilitar a redistribuição BGP - interno em R2 no roteador BGP 10:
R3#sh ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 R 10.10.10.10/32 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1
Troubleshoot
Atualmente, não há informações específicas de solução de problemas disponíveis para esta configuração.
Histórico de revisões
| Revisão | Data de publicação | Comentários |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Oct-2016 |
Versão inicial |
Colaborado por engenheiros da Cisco
- Gaurav MahajanEngenheiro do TAC da Cisco
Contate a Cisco
- Abrir um caso de suporte

- (É necessário um Contrato de Serviço da Cisco)
 Feedback
Feedback