Introduzione
Questo documento descrive il processo di configurazione di WAN Media Access Control Security (MACsec) sulle piattaforme Cisco Catalyst 8500 con sottointerfacce.
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Cisco raccomanda la conoscenza dei seguenti argomenti:
- Concetti di rete avanzati, tra cui WAN, VLAN e crittografia
- Informazioni su MACsec (IEEE 802.1AE) e gestione chiavi (IEEE 802.1X-2010)
- Familiarità con Cisco IOS® XE Command Line Interface (CLI)
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
- Cisco Catalyst serie 8500 Edge Platform
- Cisco IOS XE versione 17.14.01a
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Premesse
WAN MACsec è una soluzione di sicurezza progettata per proteggere il traffico di rete attraverso le reti WAN utilizzando le funzionalità di MACsec. Quando si utilizza una rete di provider di servizi per lo scambio di dati, è importante crittografare i dati in transito per evitare manomissioni. La tecnologia WAN MACsec è facile da installare e gestire e rappresenta la soluzione ideale per le organizzazioni che devono proteggere il traffico di rete dalla manipolazione dei dati, come le intercettazioni e gli attacchi man-in-the-middle. Fornisce una crittografia continua e con velocità di linea, garantendo che i dati rimangano sicuri e senza compromessi mentre attraversano diverse infrastrutture di rete, tra cui reti di provider di servizi, ambienti cloud e reti aziendali.
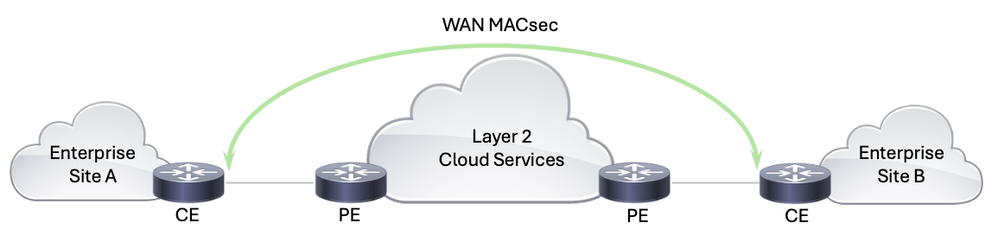 Soluzione WAN MACsec
Soluzione WAN MACsec
Per condividere un po' di storia, MACsec, definito dallo standard IEEE 802.1AE, fornisce comunicazioni sicure sulle reti Ethernet garantendo riservatezza, integrità e autenticità dei dati per i frame Ethernet. Operando al livello di collegamento dati (livello 2) del modello OSI (Open Systems Interconnection), MACsec cripta e autentica i frame Ethernet per proteggere la comunicazione tra i nodi. Originariamente progettato per le LAN, MACsec è stato sviluppato anche per supportare le installazioni WAN. Offre la crittografia della velocità di linea, che assicura una latenza e un sovraccarico minimi, fondamentali per le reti ad alta velocità.
IEEE 802.1X-2010 è una modifica allo standard IEEE 802.1X originale, che definisce il controllo degli accessi alla rete basato sulle porte. La revisione del 2010 introduce il protocollo MACsec Key Agreement (MKA), che è essenziale per la gestione delle chiavi di crittografia nelle implementazioni MACsec. MKA gestisce la distribuzione e la gestione delle chiavi crittografiche utilizzate da MACsec per crittografare e decrittografare i dati. MKA è uno standard che contribuisce all'interoperabilità multivendor per le distribuzioni MACsec, supportando scambi di chiave sicuri e meccanismi di rigenerazione delle chiavi, fondamentali per mantenere la sicurezza continua in ambienti WAN dinamici.
Nelle distribuzioni MACsec WAN, IEEE 802.1AE (MACsec) fornisce i meccanismi fondamentali di crittografia e sicurezza a livello di collegamento dati, garantendo che tutti i frame Ethernet siano protetti mentre attraversano la rete. IEEE 802.1X-2010 con il protocollo MKA, gestisce l'attività critica di distribuzione e gestione delle chiavi di crittografia necessarie per il funzionamento di MACsec. Insieme, questi standard garantiscono che il MACsec WAN sia in grado di fornire una crittografia solida e ad alta velocità su reti WAN, fornendo protezione completa per i dati in transito, mantenendo al contempo l'interoperabilità e la facilità di gestione.
Per risolvere le problematiche specifiche degli ambienti WAN, sono stati apportati alcuni miglioramenti alle implementazioni MACsec tradizionali:
- Tag 802.1Q in the Clear: questa funzione consente al tag VLAN 802.1Q di essere esposto all'esterno dell'intestazione MACsec crittografata, facilitando la progettazione di reti più flessibili, soprattutto in ambienti di trasporto pubblico Ethernet. Questa funzionalità è essenziale per l'integrazione di MACsec con i servizi Carrier Ethernet, in quanto consente la coesistenza di traffico crittografato e non crittografato sulla stessa rete, semplificando l'architettura di rete e riducendo i costi.
- Adattabilità su Public Carrier Ethernet: le moderne implementazioni MACsec WAN possono adattarsi ai servizi Ethernet di un vettore pubblico. Questa adattabilità include la modifica dell'indirizzo di destinazione EAPoL (Ethernet Authentication Protocol over LAN) e di EtherType, che consentono a MACsec di funzionare senza problemi sulle reti Carrier Ethernet, che possono altrimenti utilizzare o bloccare questi frame.
WAN MACsec rappresenta un progresso significativo nella crittografia Ethernet, rispondendo alla crescente esigenza di connessioni WAN sicure ad alta velocità. La sua capacità di fornire crittografia con velocità di linea, il supporto per progetti di rete flessibili e l'adattabilità ai servizi di trasporto pubblico lo rendono un componente critico delle moderne architetture di sicurezza di rete. Sfruttando WAN MACsec, le organizzazioni possono ottenere una sicurezza solida per i collegamenti WAN ad alta velocità, semplificando al contempo le architetture di rete e riducendo la complessità operativa.
Configurazione
Esempio di rete
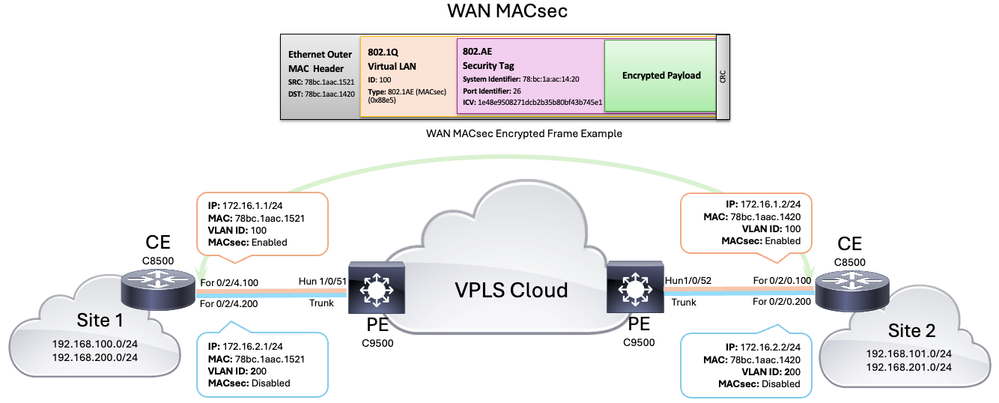 Topologia WAN MACsec
Topologia WAN MACsec
Configurazioni
Fase 1: Configurazione di base del dispositivo
Per avviare la configurazione, è necessario innanzitutto definire le sottointerfacce da utilizzare per la segmentazione del traffico e la connessione al provider di servizi. Per questo scenario, vengono definite due sottointerfacce per la VLAN 100 associata alla subnet 172.16.1.0/24 e la VLAN 200 associata alla subnet 172.16.2.0/24 (successivamente, solo una sottointerfaccia verrà configurata con MACsec).
| CE 8500-1 |
CE 8500-2 |
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.100
encapsulation dot1Q 100 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.200
encapsulation dot1Q 200 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0
|
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.100
encapsulation dot1Q 100 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.200
encapsulation dot1Q 200 ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0
|
Passaggio 2: configurare la catena di chiavi MACsec
Tenere presente che lo standard IEEE 802.1X-2010 specifica che le chiavi di crittografia MACsec possono essere derivate da una chiave già condivisa (PSK), da un protocollo EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) 802.1X o scelte e distribuite da un server di chiavi MKA. In questo esempio le chiavi PSK vengono utilizzate e configurate manualmente tramite la catena di chiavi MACsec e corrispondono alla chiave di associazione di connettività (CAK), ovvero la chiave primaria utilizzata per derivare tutte le altre chiavi di crittografia utilizzate in MACsec.
| CE 8500-1 |
CE 8500-2 |
8500-1#configure terminal
8500-1(config)#key chain keychain_vlan100 macsec
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec)#key 01
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#key-string a5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e1
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#lifetime 00:00:00 Jun 1 2024 duration 864000
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#key 02
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#key-string b5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e2
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#lifetime 23:00:00 Jun 1 2024 infinite
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec-key)#exit
8500-1(config-keychain-macsec)#exit
|
8500-2#configure terminal
8500-2(config)#key chain keychain_vlan100 macsec
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec)#key 01
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#key-string a5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e1
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#lifetime 00:00:00 Jun 1 2024 duration 864000
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#key 02
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#key-string b5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e2
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#lifetime 23:00:00 Jun 1 2024 infinite
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec-key)#exit
8500-2(config-keychain-macsec)#exit
|

Nota: durante la configurazione della catena di chiavi MACsec, tenere presente che la stringa della chiave deve essere costituita solo da cifre esadecimali. L'algoritmo di crittografia aes-128-cmac richiede una chiave di 32 cifre esadecimali, mentre l'algoritmo di crittografia aes-256-cmac richiede una chiave di 64 cifre esadecimali.

Nota: quando si utilizzano più chiavi, è necessario un periodo di tempo sovrapposto tra di esse per ottenere un rollover della chiave senza hit dopo la scadenza della durata della chiave specificata.

Avviso: è importante verificare che gli orologi di entrambi i router siano sincronizzati, pertanto si consiglia di utilizzare il protocollo NTP (Network Time Protocol). In caso contrario, si potrebbe impedire la creazione di sessioni MKA o causarne il fallimento in futuro.
Passaggio 3: Configurare i criteri MKA
Mentre il criterio MKA predefinito può essere utile per la configurazione iniziale e per le reti semplici, la configurazione di un criterio MKA personalizzato per MACsec WAN è generalmente consigliata per soddisfare specifici requisiti di sicurezza, conformità e prestazioni. I criteri personalizzati offrono maggiore flessibilità e controllo, garantendo una sicurezza di rete solida e personalizzata in base alle esigenze.
Quando si configura il criterio MKA, è possibile selezionare diversi elementi, ad esempio Priorità server chiavi, Ritardo protezione per MACsec Key Agreement Packet Data Unit (MKPDU), Cipher Suite e così via. In questa piattaforma e nelle versioni software è possibile utilizzare le seguenti cifrature:
| Cifratura MACsec |
Descrizione |
| gcm-aes-128 |
GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) con AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) che utilizza una chiave a 128 bit |
| gcm-aes-256 |
GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) con AES che utilizza una chiave a 256 bit (maggiore capacità di crittografia) |
| gcm-aes-xpn-128 |
GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) con AES che utilizza una chiave a 128 bit, con XPN (Extended Packet Numbering) |
| gcm-aes-xpn-256 |
GCM (Galois/Counter Mode) con AES che utilizza una chiave a 256 bit, con XPN (maggiore capacità di crittografia) |

Nota: XPN migliora la cifratura GCM-AES supportando la numerazione dei pacchetti più lunga, che migliora la sicurezza per le sessioni a lunga durata o per gli ambienti ad alta velocità di trasmissione. L'uso di collegamenti ad alta velocità, ad esempio 40 Gb/s o 100 Gb/s, può causare tempi di rollover delle chiavi molto brevi perché il numero di pacchetto (PN) all'interno del frame MACsec, in genere basato sul numero di pacchetti inviati, potrebbe esaurirsi rapidamente a queste velocità. XPN estende la sequenza di numerazione dei pacchetti ed elimina la necessità di reimpostare frequentemente le chiavi SAK (Security Association Key) che possono verificarsi nei collegamenti ad alta capacità.
In questo esempio, la cifratura selezionata per il criterio MKA è gcm-aes-xpn-256 e ad altri elementi verrà assegnato il valore predefinito:
| CE 8500-1 |
CE 8500-2 |
8500-1#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
8500-1(config)#mka policy subint100
8500-1(config-mka-policy)#macsec-cipher-suite gcm-aes-xpn-256
8500-1(config-mka-policy)#end
|
8500-2#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
8500-2(config)#mka policy subint100
8500-2(config-mka-policy)#macsec-cipher-suite gcm-aes-xpn-256
8500-2(config-mka-policy)#end
|
Passaggio 4: Configurare MACsec a livello di interfaccia e sottointerfaccia
In questo scenario, anche se l'interfaccia fisica non è configurata con un indirizzo IP, alcuni comandi macsec devono essere applicati a questo livello affinché la soluzione funzioni. I criteri MACsec e la catena di chiavi vengono applicati a livello di sottointerfaccia (vedere l'esempio di configurazione):
| CE 8500-1 |
CE 8500-2 |
8500-1#configure terminal
8500-1(config)#interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4
8500-1(config-if)#mtu 9216
8500-1(config-if)#cdp enable
8500-1(config-if)#macsec dot1q-in-clear 1
8500-1(config-if)#macsec access-control should-secure
8500-1(config-if)#exit
8500-1(config)#interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.100
8500-1(config-if)#eapol destination-address broadcast-address
8500-1(config-if)#eapol eth-type 876F
8500-1(config-if)#mka policy subint100
8500-1(config-if)#mka pre-shared-key key-chain keychain_vlan100
8500-1(config-if)#macsec
8500-2(config-if)#end
|
8500-2#configure terminal
8500-2(config)#interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0
8500-2(config-if)#mtu 9216
8500-2(config-if)#cdp enable
8500-2(config-if)#macsec dot1q-in-clear 1
8500-2(config-if)#macsec access-control should-secure
8500-2(config-if)#exit
8500-1(config)#interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.100
8500-2(config-if)#eapol destination-address broadcast-address
8500-2(config-if)#eapol eth-type 876F
8500-2(config-if)#mka policy subint100
8500-2(config-if)#mka pre-shared-key key-chain keychain_vlan100
8500-2(config-if)#macsec
8500-2(config-if)#end
|
Comandi applicati a livello di interfaccia fisica
a. L'MTU è impostata su 9216 in quanto il provider di servizi utilizzato nella topologia consente i frame jumbo, ma questo non è un requisito
b. Il comando macsec dot1q-in-clear consente di deselezionare (non crittografato) il tag VLAN (dot1q)
c. Il comando macsec access-control should-secure consente di inviare o ricevere pacchetti non crittografati dall'interfaccia fisica o dall'interfaccia secondaria (questo comando è necessario se alcune sottointerfacce richiedono la crittografia e altre no, a causa del comportamento MACsec predefinito che non consente di trasmettere o ricevere pacchetti non crittografati dalla stessa interfaccia fisica su cui è abilitato MACsec)
Comandi applicati a livello di sottointerfaccia
a. A questo punto, il comando eapol destination-address broadcast-address è necessario per modificare l'indirizzo MAC di destinazione dei frame EAPoL (che per impostazione predefinita è un indirizzo MAC multicast 01:80:C2:00:00:03) in un indirizzo MAC di trasmissione per essere certi che il provider di servizi li inonda e non li scarichi o li consumi.
b. Il comando eapol eth-type 876F viene usato anche per modificare il tipo ethernet predefinito del frame EAPoL (che per impostazione predefinita è 0x888E) e cambiarlo in 0x876F. Anche in questo caso, è necessario impedire al provider di servizi di eliminare o utilizzare questi frame.
c. I comandi mka policy <nome criterio> e mka pre-shared-key-chain <nome catena di chiavi> vengono utilizzati per applicare il criterio personalizzato e la catena di chiavi alla sottointerfaccia.
d. Infine, ma non per importanza, il comando macsec abilita MACsec a livello di sottointerfaccia.
Nella configurazione corrente, senza le precedenti modifiche EAPoL, gli switch 9500 sul lato del provider di servizi non inoltravano i frame EAPoL.

Nota: i comandi MACsec come dot1q-in-clear e should-secure vengono ereditati dalle sottointerfacce. Inoltre, i comandi EAPoL possono essere impostati a livello di interfaccia fisica e in questi casi, vengono ereditati anche dalle sottointerfacce. Tuttavia, la configurazione esplicita dei comandi EAPoL sull'interfaccia secondaria ha la precedenza sul valore o sul criterio ereditato per tale interfaccia secondaria.
Verifica
Dopo aver applicato la configurazione, l'output successivo mostra la configurazione in esecuzione rilevante da ciascun router Customer Edge (CE) C8500 (alcune configurazioni sono state omesse):
| CE 8500-1 |
CE 8500-2 |
8500-1#show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 8792 bytes
!
!
version 17.14
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service call-home
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
!
hostname 8500-1
!
boot-start-marker
boot system flash bootflash:c8000aep-universalk9.17.14.01a.SPA.bin
boot-end-marker
!
!
no logging console
no aaa new-model
!
!
key chain keychain_vlan100 macsec key 01 cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac key-string a5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e1 lifetime 00:00:00 Jun 1 2024 duration 864000 key 02 cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac key-string b5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e2 lifetime 23:00:00 Jun 1 2024 infinite
!
!
!
!
!
!
license boot level network-premier addon dna-premier
!
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
mka policy subint100 macsec-cipher-suite gcm-aes-xpn-256
!
!
!
!
!
!
cdp run
!
!
!
!
interface Loopback100
ip address 192.168.100.10 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback200
ip address 192.168.200.10 255.255.255.0
!
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4
mtu 9216
no ip address
no negotiation auto
cdp enable
macsec dot1q-in-clear 1 macsec access-control should-secure
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.100
encapsulation dot1Q 100
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip mtu 9184
eapol destination-address broadcast-address eapol eth-type 876F mka policy subint100 mka pre-shared-key key-chain keychain_vlan100 macsec
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.200
encapsulation dot1Q 200
ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0
!
!
router eigrp 100
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
!
control-plane
!
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
stopbits 1
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
transport input ssh
!
!
!
!
!
!
end
8500-1#
|
8500-2#show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 8525 bytes
!
!
version 17.14
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service call-home
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
!
hostname 8500-2
!
boot-start-marker
boot system flash bootflash:c8000aep-universalk9.17.14.01a.SPA.bin
boot-end-marker
!
!
no logging console
no aaa new-model
!
!
key chain keychain_vlan100 macsec key 01 cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac key-string a5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e1 lifetime 00:00:00 Jun 1 2024 duration 864000 key 02 cryptographic-algorithm aes-256-cmac key-string b5b2df4657bd8c02fcdaaf1212fe27ccc54626ad12d7c3b64c7a93e0113011e2 lifetime 23:00:00 Jun 1 2024 infinite
!
!
!
!
!
!
license boot level network-premier addon dna-premier
!
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
mka policy subint100 macsec-cipher-suite gcm-aes-xpn-256
!
!
!
!
!
!
cdp run
!
!
!
!
interface Loopback101
ip address 192.168.101.10 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback201
ip address 192.168.201.10 255.255.255.0
!
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0
mtu 9216
no ip address
no negotiation auto
cdp enable
macsec dot1q-in-clear 1 macsec access-control should-secure
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.100
encapsulation dot1Q 100
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
ip mtu 9184
eapol destination-address broadcast-address eapol eth-type 876F mka policy subint100 mka pre-shared-key key-chain keychain_vlan100 macsec
!
interface FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.200
encapsulation dot1Q 200
ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
!
router eigrp 100
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
!
control-plane
!
!
!
!
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
stopbits 1
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
transport input ssh
!
!
!
!
!
!
end
8500-2#
|

Nota: dopo aver abilitato MACsec, applicando il comando macsec, l'MTU di quell'interfaccia viene regolata automaticamente e ridotta di 32 byte per tenere conto del sovraccarico di MACsec.
Successivamente, è possibile trovare un elenco di comandi essenziali che possono essere utilizzati per controllare e verificare lo stato di MACsec tra peer. Questi comandi forniscono informazioni dettagliate sulle sessioni MACsec correnti, le catene di chiavi, i criteri e le statistiche:
show mka sessions - Questo comando visualizza lo stato corrente delle sessioni MKA.
show mka sessions detail - Questo comando fornisce informazioni dettagliate su ciascuna sessione MKA.
show mka keychains: questo comando mostra le keychains utilizzate per MACsec e l'interfaccia assegnata.
show mka policy - Questo comando visualizza i criteri applicati, le interfacce e la suite di cifratura utilizzata.
show mka summary - Questo comando fornisce un riepilogo delle sessioni e delle statistiche MKA.
show macsec statistics interface <nome interfaccia> - Questo comando visualizza le statistiche MACsec per un'interfaccia specificata e consente di identificare se il traffico crittografato viene inviato e ricevuto.
| CE 8500-1 |
CE 8500-2 |
8500-1#show mka sessions
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Fo0/2/4.100 78bc.1aac.1521/001a subint100 NO NO
26 78bc.1aac.1420/001a 1 Secured 02
8500-1#show mka sessions detail
MKA Detailed Status for MKA Session
===================================
Status: SECURED - Secured MKA Session with MACsec
TX-SSCI.................. 2
Local Tx-SCI............. 78bc.1aac.1521/001a
Interface MAC Address.... 78bc.1aac.1521
MKA Port Identifier...... 26
Interface Name........... FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.100
Audit Session ID.........
CAK Name (CKN)........... 02
Member Identifier (MI)... 8387013B6C4D6106D4443285
Message Number (MN)...... 439243
EAP Role................. NA
Key Server............... NO
MKA Cipher Suite......... AES-256-CMAC
Latest SAK Status........ Rx & Tx
Latest SAK AN............ 0
Latest SAK KI (KN)....... F5720CC2E83183F1E673DACD00000001 (1)
Old SAK Status........... FIRST-SAK
Old SAK AN............... 0
Old SAK KI (KN).......... FIRST-SAK (0)
SAK Transmit Wait Time... 0s (Not waiting for any peers to respond)
SAK Retire Time.......... 0s (No Old SAK to retire)
SAK Rekey Time........... 0s (SAK Rekey interval not applicable)
MKA Policy Name.......... subint100
Key Server Priority...... 0
Delay Protection......... NO
Delay Protection Timer.......... 0s (Not enabled)
Confidentiality Offset... 0
Algorithm Agility........ 80C201
SAK Rekey On Live Peer Loss........ NO
Send Secure Announcement.. DISABLED
SCI Based SSCI Computation.... NO
SAK Cipher Suite......... 0080C20001000004 (GCM-AES-XPN-256)
MACsec Capability........ 3 (MACsec Integrity, Confidentiality, & Offset)
MACsec Desired........... YES
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers............ 1
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers Responded.. 0
Live Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS RxSA SSCI
Priority Installed
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
F5720CC2E83183F1E673DACD 439222 78bc.1aac.1420/001a 0 YES 1
Potential Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS RxSA SSCI
Priority Installed
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8500-1#show mka keychains
MKA PSK Keychain(s) Summary...
Keychain Latest CKN Interface(s)
Name Latest CAK Applied
===============================================================================================
keychain_vlan100 02 Fo0/2/4.100
<HIDDEN>
8500-1#show mka policy
MKA Policy defaults :
Send-Secure-Announcements: DISABLED
MKA Policy Summary...
Codes : CO - Confidentiality Offset, ICVIND - Include ICV-Indicator,
SAKR OLPL - SAK-Rekey On-Live-Peer-Loss,
DP - Delay Protect, KS Prio - Key Server Priority
Policy KS DP CO SAKR ICVIND Cipher Interfaces
Name Prio OLPL Suite(s) Applied
===============================================================================
*DEFAULT POLICY* 0 FALSE 0 FALSE TRUE GCM-AES-128
GCM-AES-256
subint100 0 FALSE 0 FALSE TRUE GCM-AES-XPN-256 Fo0/2/4.100
8500-1#show mka summary
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Fo0/2/4.100 78bc.1aac.1521/001a subint100 NO NO
26 78bc.1aac.1420/001a 1 Secured 02
MKA Global Statistics
=====================
MKA Session Totals
Secured.................... 14
Fallback Secured........... 0
Reauthentication Attempts.. 0
Deleted (Secured).......... 13
Keepalive Timeouts......... 0
CA Statistics
Pairwise CAKs Derived...... 0
Pairwise CAK Rekeys........ 0
Group CAKs Generated....... 0
Group CAKs Received........ 0
SA Statistics
SAKs Generated.............. 0
SAKs Rekeyed................ 2
SAKs Received............... 18
SAK Responses Received...... 0
SAK Rekeyed as KN Mismatch.. 0
MKPDU Statistics
MKPDUs Validated & Rx...... 737255
"Distributed SAK"..... 18
"Distributed CAK"..... 0
MKPDUs Transmitted......... 738485
"Distributed SAK"..... 0
"Distributed CAK"..... 0
MKA Error Counter Totals
========================
Session Failures
Bring-up Failures................ 0
Reauthentication Failures........ 0
Duplicate Auth-Mgr Handle........ 0
SAK Failures
SAK Generation................... 0
Hash Key Generation.............. 0
SAK Encryption/Wrap.............. 0
SAK Decryption/Unwrap............ 0
SAK Cipher Mismatch.............. 0
CA Failures
Group CAK Generation............. 0
Group CAK Encryption/Wrap........ 0
Group CAK Decryption/Unwrap...... 0
Pairwise CAK Derivation.......... 0
CKN Derivation................... 0
ICK Derivation................... 0
KEK Derivation................... 0
Invalid Peer MACsec Capability... 0
MACsec Failures
Rx SC Creation................... 0
Tx SC Creation................... 0
Rx SA Installation............... 0
Tx SA Installation............... 0
MKPDU Failures
MKPDU Tx............................... 0
MKPDU Rx ICV Verification.............. 0
MKPDU Rx Fallback ICV Verification..... 0
MKPDU Rx Validation.................... 0
MKPDU Rx Bad Peer MN................... 0
MKPDU Rx Non-recent Peerlist MN........ 0
SAK USE Failures
SAK USE Latest KN Mismatch............. 0
SAK USE Latest AN not in USE........... 0
8500-1#show macsec statistics interface Fo0/2/4.100
MACsec Statistics for FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/4.100
SecY Counters
Ingress Untag Pkts: 0
Ingress No Tag Pkts: 0
Ingress Bad Tag Pkts: 0
Ingress Unknown SCI Pkts: 0
Ingress No SCI Pkts: 0
Ingress Overrun Pkts: 0
Ingress Validated Octets: 0
Ingress Decrypted Octets: 11853398
Egress Untag Pkts: 0
Egress Too Long Pkts: 0
Egress Protected Octets: 0
Egress Encrypted Octets: 11782598
Controlled Port Counters
IF In Octets: 14146226
IF In Packets: 191065
IF In Discard: 0
IF In Errors: 0
IF Out Octets: 14063174
IF Out Packets: 190042
IF Out Errors: 0
Transmit SC Counters (SCI: 78BC1AAC1521001A)
Out Pkts Protected: 0
Out Pkts Encrypted: 190048
Transmit SA Counters (AN 0)
Out Pkts Protected: 0
Out Pkts Encrypted: 190048
Receive SA Counters (SCI: 78BC1AAC1420001A AN 0)
In Pkts Unchecked: 0
In Pkts Delayed: 0
In Pkts OK: 191069
In Pkts Invalid: 0
In Pkts Not Valid: 0
In Pkts Not using SA: 0
In Pkts Unused SA: 0
In Pkts Late: 0
|
8500-2#show mka sessions
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Fo0/2/0.100 78bc.1aac.1420/001a subint100 NO YES
26 78bc.1aac.1521/001a 1 Secured 02
8500-2#show mka sessions detail
MKA Detailed Status for MKA Session
===================================
Status: SECURED - Secured MKA Session with MACsec
TX-SSCI.................. 1
Local Tx-SCI............. 78bc.1aac.1420/001a
Interface MAC Address.... 78bc.1aac.1420
MKA Port Identifier...... 26
Interface Name........... FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.100
Audit Session ID.........
CAK Name (CKN)........... 02
Member Identifier (MI)... F5720CC2E83183F1E673DACD
Message Number (MN)...... 438678
EAP Role................. NA
Key Server............... YES
MKA Cipher Suite......... AES-256-CMAC
Latest SAK Status........ Rx & Tx
Latest SAK AN............ 0
Latest SAK KI (KN)....... F5720CC2E83183F1E673DACD00000001 (1)
Old SAK Status........... FIRST-SAK
Old SAK AN............... 0
Old SAK KI (KN).......... FIRST-SAK (0)
SAK Transmit Wait Time... 0s (Not waiting for any peers to respond)
SAK Retire Time.......... 0s (No Old SAK to retire)
SAK Rekey Time........... 0s (SAK Rekey interval not applicable)
MKA Policy Name.......... subint100
Key Server Priority...... 0
Delay Protection......... NO
Delay Protection Timer.......... 0s (Not enabled)
Confidentiality Offset... 0
Algorithm Agility........ 80C201
SAK Rekey On Live Peer Loss........ NO
Send Secure Announcement.. DISABLED
SCI Based SSCI Computation.... NO
SAK Cipher Suite......... 0080C20001000004 (GCM-AES-XPN-256)
MACsec Capability........ 3 (MACsec Integrity, Confidentiality, & Offset)
MACsec Desired........... YES
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers............ 1
# of MACsec Capable Live Peers Responded.. 1
Live Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS RxSA SSCI
Priority Installed
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8387013B6C4D6106D4443285 438697 78bc.1aac.1521/001a 0 YES 2
Potential Peers List:
MI MN Rx-SCI (Peer) KS RxSA SSCI
Priority Installed
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8500-2#show mka keychains
MKA PSK Keychain(s) Summary...
Keychain Latest CKN Interface(s)
Name Latest CAK Applied
===============================================================================================
keychain_vlan100 02 Fo0/2/0.100
<HIDDEN>
8500-2#show mka policy
MKA Policy defaults :
Send-Secure-Announcements: DISABLED
MKA Policy Summary...
Codes : CO - Confidentiality Offset, ICVIND - Include ICV-Indicator,
SAKR OLPL - SAK-Rekey On-Live-Peer-Loss,
DP - Delay Protect, KS Prio - Key Server Priority
Policy KS DP CO SAKR ICVIND Cipher Interfaces
Name Prio OLPL Suite(s) Applied
===============================================================================
*DEFAULT POLICY* 0 FALSE 0 FALSE TRUE GCM-AES-128
GCM-AES-256
subint100 0 FALSE 0 FALSE TRUE GCM-AES-XPN-256 Fo0/2/0.100
8500-2#show mka summary
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Fo0/2/0.100 78bc.1aac.1420/001a subint100 NO YES
26 78bc.1aac.1521/001a 1 Secured 02
MKA Global Statistics
=====================
MKA Session Totals
Secured.................... 8
Fallback Secured........... 0
Reauthentication Attempts.. 0
Deleted (Secured).......... 7
Keepalive Timeouts......... 0
CA Statistics
Pairwise CAKs Derived...... 0
Pairwise CAK Rekeys........ 0
Group CAKs Generated....... 0
Group CAKs Received........ 0
SA Statistics
SAKs Generated.............. 13
SAKs Rekeyed................ 4
SAKs Received............... 0
SAK Responses Received...... 12
SAK Rekeyed as KN Mismatch.. 0
MKPDU Statistics
MKPDUs Validated & Rx...... 524753
"Distributed SAK"..... 0
"Distributed CAK"..... 0
MKPDUs Transmitted......... 524796
"Distributed SAK"..... 12
"Distributed CAK"..... 0
MKA Error Counter Totals
========================
Session Failures
Bring-up Failures................ 0
Reauthentication Failures........ 0
Duplicate Auth-Mgr Handle........ 0
SAK Failures
SAK Generation................... 0
Hash Key Generation.............. 0
SAK Encryption/Wrap.............. 0
SAK Decryption/Unwrap............ 0
SAK Cipher Mismatch.............. 0
CA Failures
Group CAK Generation............. 0
Group CAK Encryption/Wrap........ 0
Group CAK Decryption/Unwrap...... 0
Pairwise CAK Derivation.......... 0
CKN Derivation................... 0
ICK Derivation................... 0
KEK Derivation................... 0
Invalid Peer MACsec Capability... 0
MACsec Failures
Rx SC Creation................... 0
Tx SC Creation................... 0
Rx SA Installation............... 1
Tx SA Installation............... 0
MKPDU Failures
MKPDU Tx............................... 0
MKPDU Rx ICV Verification.............. 0
MKPDU Rx Fallback ICV Verification..... 0
MKPDU Rx Validation.................... 0
MKPDU Rx Bad Peer MN................... 0
MKPDU Rx Non-recent Peerlist MN........ 0
SAK USE Failures
SAK USE Latest KN Mismatch............. 0
SAK USE Latest AN not in USE........... 0
8500-2#show macsec statistics interface Fo0/2/0.100
MACsec Statistics for FortyGigabitEthernet0/2/0.100
SecY Counters
Ingress Untag Pkts: 0
Ingress No Tag Pkts: 0
Ingress Bad Tag Pkts: 0
Ingress Unknown SCI Pkts: 0
Ingress No SCI Pkts: 0
Ingress Overrun Pkts: 0
Ingress Validated Octets: 0
Ingress Decrypted Octets: 11767966
Egress Untag Pkts: 0
Egress Too Long Pkts: 0
Egress Protected Octets: 0
Egress Encrypted Octets: 11838828
Controlled Port Counters
IF In Octets: 14045710
IF In Packets: 189805
IF In Discard: 0
IF In Errors: 0
IF Out Octets: 14128836
IF Out Packets: 190832
IF Out Errors: 0
Transmit SC Counters (SCI: 78BC1AAC1420001A)
Out Pkts Protected: 0
Out Pkts Encrypted: 190834
Transmit SA Counters (AN 0)
Out Pkts Protected: 0
Out Pkts Encrypted: 190834
Receive SA Counters (SCI: 78BC1AAC1521001A AN 0)
In Pkts Unchecked: 0
In Pkts Delayed: 0
In Pkts OK: 189812
In Pkts Invalid: 0
In Pkts Not Valid: 0
In Pkts Not using SA: 0
In Pkts Unused SA: 0
In Pkts Late: 0
|
La raggiungibilità dalle diverse sottointerfacce ha esito positivo, così come la raggiungibilità tra le subnet 192.168.0.0/16. I prossimi test ping dimostrano che la connettività è riuscita:
8500-1#ping 172.16.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
8500-1#ping 172.16.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
8500-1#ping 192.168.101.10 source 192.168.100.10
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.101.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.100.10
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
8500-1#
Dopo aver acquisito i pacchetti da un test ICMP sul dispositivo Provider Edge (PE), è possibile confrontare i frame crittografati e non. Si noti che l'intestazione MAC esterna Ethernet è la stessa su entrambi i frame, con il tag dot1q visibile. Tuttavia, il frame crittografato mostra un EtherType pari a 0x88E5 (MACsec), mentre il frame non crittografato visualizza un EtherType pari a 0x0800 (IPv4) insieme alle informazioni del protocollo ICMP:
| Encrypted Frame VLAN 100 |
Unencrypted Frame VLAN 200 |
F241.03.03-9500-1#show monitor capture cap buffer detail | begin Frame 80
Frame 80: 150 bytes on wire (1200 bits), 150 bytes captured (1200 bits) on interface /tmp/epc_ws/wif_to_ts_pipe, id 0
Interface id: 0 (/tmp/epc_ws/wif_to_ts_pipe)
Interface name: /tmp/epc_ws/wif_to_ts_pipe
Encapsulation type: Ethernet (1)
Arrival Time: Jul 29, 2024 23:50:16.528191000 UTC
[Time shift for this packet: 0.000000000 seconds]
Epoch Time: 1722297016.528191000 seconds
[Time delta from previous captured frame: 0.224363000 seconds]
[Time delta from previous displayed frame: 0.224363000 seconds]
[Time since reference or first frame: 21.989269000 seconds]
Frame Number: 80
Frame Length: 150 bytes (1200 bits)
Capture Length: 150 bytes (1200 bits)
[Frame is marked: False]
[Frame is ignored: False]
[Protocols in frame: eth:ethertype:vlan:ethertype:macsec:data]
Ethernet II, Src: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21), Dst: 78:bc:1a:ac:14:20 (78:bc:1a:ac:14:20)
Destination: 78:bc:1a:ac:14:20 (78:bc:1a:ac:14:20)
Address: 78:bc:1a:ac:14:20 (78:bc:1a:ac:14:20)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Source: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21)
Address: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Type: 802.1Q Virtual LAN (0x8100) 802.1Q Virtual LAN, PRI: 0, DEI: 0, ID: 100
000. .... .... .... = Priority: Best Effort (default) (0)
...0 .... .... .... = DEI: Ineligible
.... 0000 0110 0100 = ID: 100
Type: 802.1AE (MACsec) (0x88e5) 802.1AE Security tag
0010 11.. = TCI: 0x0b, VER: 0x0, SC, E, C
0... .... = VER: 0x0
.0.. .... = ES: Not set
..1. .... = SC: Set
...0 .... = SCB: Not set
.... 1... = E: Set
.... .1.. = C: Set
.... ..00 = AN: 0x0
Short length: 0
Packet number: 147 System Identifier: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21) Port Identifier: 26 ICV: 2b80cff435c7ef5a8d21b473b998cfb4
Data (102 bytes)
0000 99 53 71 3e f6 c7 9b bb 00 21 68 48 d6 ca 26 af .Sq>.....!hH..&.
0010 80 a5 76 40 19 c9 45 97 b3 5a 48 d3 2d 30 72 a6 ..v@..E..ZH.-0r.
0020 96 47 6e a7 4c 30 90 e5 70 10 80 e8 68 00 5f ad .Gn.L0..p...h._.
0030 7f dd 4a 70 a8 46 00 ef 7d 56 fe e2 66 ba 6c 1b ..Jp.F..}V..f.l.
0040 3a 07 44 4e 5e e7 04 cb cb f4 03 71 8d 40 da 55 :.DN^......q.@.U
0050 9f 1b ef a6 3a 1e 42 c7 05 e6 9e d0 39 6e b7 3f ....:.B.....9n.?
0060 f2 82 cf 66 f2 5b ...f.[
Data: 9953713ef6c79bbb00216848d6ca26af80a5764019c94597b^@&
[Length: 102]
|
F241.03.03-9500-1#show monitor capture cap buff detail | begin Frame 126
Frame 126: 118 bytes on wire (944 bits), 118 bytes captured (944 bits) on interface /tmp/epc_ws/wif_to_ts_pipe, id 0
Interface id: 0 (/tmp/epc_ws/wif_to_ts_pipe)
Interface name: /tmp/epc_ws/wif_to_ts_pipe
Encapsulation type: Ethernet (1)
Arrival Time: Jul 29, 2024 23:50:26.198492000 UTC
[Time shift for this packet: 0.000000000 seconds]
Epoch Time: 1722297026.198492000 seconds
[Time delta from previous captured frame: 0.280042000 seconds]
[Time delta from previous displayed frame: 0.280042000 seconds]
[Time since reference or first frame: 31.659570000 seconds]
Frame Number: 126
Frame Length: 118 bytes (944 bits)
Capture Length: 118 bytes (944 bits)
[Frame is marked: False]
[Frame is ignored: False]
[Protocols in frame: eth:ethertype:vlan:ethertype:ip:icmp:data]
Ethernet II, Src: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21), Dst: 78:bc:1a:ac:14:20 (78:bc:1a:ac:14:20)
Destination: 78:bc:1a:ac:14:20 (78:bc:1a:ac:14:20)
Address: 78:bc:1a:ac:14:20 (78:bc:1a:ac:14:20)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Source: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21)
Address: 78:bc:1a:ac:15:21 (78:bc:1a:ac:15:21)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Type: 802.1Q Virtual LAN (0x8100) 802.1Q Virtual LAN, PRI: 0, DEI: 0, ID: 200
000. .... .... .... = Priority: Best Effort (default) (0)
...0 .... .... .... = DEI: Ineligible
.... 0000 1100 1000 = ID: 200
Type: IPv4 (0x0800)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 172.16.2.1, Dst: 172.16.2.2
0100 .... = Version: 4
.... 0101 = Header Length: 20 bytes (5)
Differentiated Services Field: 0x00 (DSCP: CS0, ECN: Not-ECT)
0000 00.. = Differentiated Services Codepoint: Default (0)
.... ..00 = Explicit Congestion Notification: Not ECN-Capable Transport (0)
Total Length: 100
Identification: 0x0055 (85)
Flags: 0x0000
0... .... .... .... = Reserved bit: Not set
.0.. .... .... .... = Don't fragment: Not set
..0. .... .... .... = More fragments: Not set
Fragment offset: 0
Time to live: 255
Protocol: ICMP (1)
Header checksum: 0x5f20 [validation disabled]
[Header checksum status: Unverified]
Source: 172.16.2.1 Destination: 172.16.2.2
Internet Control Message Protocol
Type: 8 (Echo (ping) request)
Code: 0
Checksum: 0x6a4e [correct]
[Checksum Status: Good]
Identifier (BE): 17 (0x0011)
Identifier (LE): 4352 (0x1100)
Sequence number (BE): 0 (0x0000)
Sequence number (LE): 0 (0x0000)
Data (72 bytes)
0000 00 00 00 00 00 25 13 c6 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd .....%..........
0010 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0020 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0030 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ................
0040 ab cd ab cd ab cd ab cd ........
Data: 00000000002513c6abcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdb^@&
[Length: 72]
|
Informazioni correlate
 Soluzione WAN MACsec
Soluzione WAN MACsec Topologia WAN MACsec
Topologia WAN MACsec





 Feedback
Feedback