Configurazione di esempio: EtherChannel tra gli switch Catalyst con software CatOS e Cisco IOS
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritta la configurazione di EtherChannel tra uno switch Catalyst 5500/5000 con software Catalyst OS (CatOS) e uno switch Catalyst 6500/6000 o Catalyst 4500/4000 con software Cisco IOS®. EtherChannel raggruppa i singoli collegamenti in un unico collegamento logico che fornisce maggiore larghezza di banda e ridondanza tra switch o altri dispositivi. È possibile fare riferimento a EtherChannel come FEC (Fast EtherChannel) o GEC (Gigabit EtherChannel); dipende dalla velocità delle interfacce o delle porte utilizzate per formare EtherChannel. Questa configurazione è valida anche per uno switch Catalyst serie 4500/4000 o 6500/6000 con CatOS collegato a uno switch Catalyst serie 4500/4000 o 6500/6000 con software Cisco IOS.
La configurazione illustrata in questo documento raggruppa due porte Fast Ethernet (FE) di ciascuno switch in una porta FEC. In questo documento, il termine "EtherChannel" viene usato per riferirsi a GEC, FEC, port channel, e port group.
In questo documento vengono visualizzati solo i file di configurazione degli switch e l'output dei relativi comandi show di esempio. Per i dettagli su come configurare EtherChannel, fare riferimento a questi documenti:
-
Configurazione di EtherChannel (per gli switch Catalyst 6500/6000 con software Cisco IOS)
-
Configurazione di EtherChannel (per gli switch Catalyst 4500/4000 con software Cisco IOS)
-
Configurazione di esempio: EtherChannel tra switch Catalyst con CatOS
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Prima di provare la configurazione, accertarsi di avere una conoscenza di base di:
-
Configurazione di EtherChannel
-
Configurazione degli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000 e Catalyst serie 5500/5000 con interfaccia della riga di comando (CLI)
Componenti usati
Le informazioni fornite in questo documento si basano sulle seguenti versioni software e hardware:
-
Switch Cisco Catalyst 5505 con software CatOS 6.4(8)
-
Switch Cisco Catalyst 6509 con software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(20)E
Nota: per i requisiti di sistema di EtherChannel sugli switch Catalyst, vedere Requisiti di sistema per implementare EtherChannel sugli switch Catalyst.
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Nozioni di base
È possibile configurare EtherChannel in modo incondizionato (con la modalità canale attivata) o tramite la negoziazione automatica. Quando si configura la negoziazione automatica, lo switch negozia il canale con l'estremità remota. A tal fine, usa il protocollo PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol) proprietario di Cisco (con il comando channel mode desiderabile) o il protocollo LACP (Link Aggregate Control Protocol) IEEE 802.3ad (con il comando channel mode attivo o channel mode passivo). In questo documento, la configurazione EtherChannel utilizza PAgP per la negoziazione automatica.
Tutti gli switch Catalyst con software di sistema CatOS supportano PAgP. Anche gli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000 o 4500/4000 con software di sistema Cisco IOS supportano PAgP. La modalità consigliata per stabilire un EtherChannel tra i dispositivi che supportano PAgP è una modalità desiderabile. La funzione PAgP protegge da eventuali configurazioni errate tra i due dispositivi. È possibile utilizzare la modalità canale su quando il dispositivo di connessione non supporta PAgP ed è necessario impostare il canale senza condizioni. È possibile utilizzare le parole chiave silent o non silent con le modalità di canale auto e desiderabili. sugli switch Catalyst 6500/6000 o 4500/4000, la parola chiave silent è abilitata per impostazione predefinita su tutte le porte. Sugli switch Catalyst serie 5500/5000, la parola chiave silent è abilitata per impostazione predefinita sulle porte in rame. Per tutte le porte in fibra ottica (FE e Gigabit Ethernet [GE]), sugli switch serie 5500/5000 la parola chiave non silent è abilitata per impostazione predefinita. Per la connessione tra switch Cisco, usare la parola chiave predefinita silent o non silent.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sulle modalità di channeling PAgP e sulle modalità silenziosa/non silenziosa, fare riferimento alla sezione Uso di PAgP per configurare EtherChannel (consigliato) e alla sezione Modalità silenziosa/non silenziosa del documento sulla configurazione di EtherChannel tra gli switch Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000 e 6500/6000 con software CatOS.
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Esempio di rete
Nel documento viene usata questa impostazione di rete:
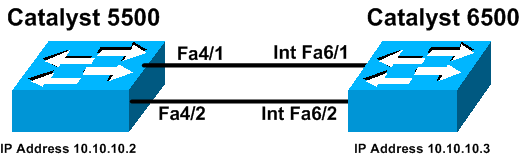
Linee guida
Quando i collegamenti attivi vengono aggregati in un EtherChannel, le porte abbandonano momentaneamente lo Spanning Tree e si uniscono nuovamente come un'unica porta logica. Finché lo Spanning Tree non riconverte, il traffico di rete viene interrotto.
Se non si utilizzano protocolli come PAgP o LACP per la configurazione di EtherChannel per altre considerazioni, verificare che i parametri richiesti siano gli stessi su entrambe le estremità. Se le estremità del canale sono diverse, la porta viene disabilitata a causa di un errore. Per ripristinare le porte dalla modalità err-disabled, fare riferimento alle seguenti indicazioni:
-
Ripristino di una porta disabilitata a causa di un errore sulle piattaforme Cisco IOS
-
Ripristino di una porta disabilitata a causa di un errore sulle piattaforme CatOS
Configurazioni
Nel documento vengono usate queste configurazioni:
Nota: per verificare le funzionalità di un modulo o di una porta dello switch configurata, usare il comando show port capabilities module per gli switch con CatOS. Per gli switch con software Cisco IOS, usare il comando show interfaces capabilities.
Nota: nelle configurazioni, i commenti tra le uscite appaiono in corsivo blu.
| Catalyst 5500 |
|---|
cat5500 (enable) show config This command shows non-default configurations only. Use 'show config all' to show both default and non-default configurations. ...... ................ ................ .. begin ! # ***** NON-DEFAULT CONFIGURATION ***** ! ! # time: Wed Jan 28 2004, 09:39:55 ! # version 6.4(2) ! # errordetection set errordetection portcounter enable ! # frame distribution method set port channel all distribution mac both ! # vtp set vtp domain cisco set vlan 1 name default type ethernet mtu 1500 said 100001 state active set vlan 1002 name fddi-default type fddi mtu 1500 said 101002 state active set vlan 1004 name fddinet-default type fddinet mtu 1500 said 101004 state active stp ieee set vlan 1005 name trnet-default type trbrf mtu 1500 said 101005 state active stp ibm set vlan 1003 name token-ring-default type trcrf mtu 1500 said 101003 state active mode srb aremaxhop 7 stemaxhop 7 backupcrf off ! # ip !--- This is the IP address for management. set interface sc0 1 10.10.10.2/255.255.255.0 10.10.10.255 ! # set boot command set boot config-register 0x2102 set boot system flash bootflash:cat5000-supg.6-4-8.bin ! # mls set mls nde disable ! # port channel !--- Ports are assigned to admin-group 200. Administrative groups !--- specify which ports can form an EtherChannel together. An administrative group !--- can contain a maximum of eight ports. This admin-group assignment happens !--- automatically with the configuration of the port channel. You can also !--- assign it manually, as done in this example. However, you do not need to assign !--- the admin-group manually. Let the switch create !--- the admin-group automatically. !--- Note: This configuration sets ports 4/1 through 4/4 !--- for port channel, but only configures ports 4/1-2. This is !--- normal behavior. You can use ports 4/3 and 4/4 for any other purpose. set port channel 4/1-4 200 ! # default port status is enable ! ! #module 1 : 0-port Supervisor III ! #module 2 : 2-port MM MIC FDDI ! #module 3 : 24-port 10/100BaseTX Ethernet ! #module 4 : 12-port 10/100BaseTX Ethernet !--- This enables port channeling with PAgP and configures desirable silent mode. set port channel 4/1-2 mode desirable silent ! #module 5 : 2-port MM OC-3 Dual-Phy ATM !--- Output suppressed. end |
Per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi in configurazione, consultare la guida di riferimento dei comandi della famiglia Catalyst 5000 (6.3 e 6.4).
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
Cat6509# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 3852 bytes ! version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Cat6509 ! ! redundancy main-cpu auto-sync standard ip subnet-zero ! ! interface port-channel1 no ip address !--- This example has configured a Layer 2 (L2) EtherChannel. !--- You can configure a Layer 3 (L3) EtherChannel on the Catalyst !--- 6500/6000 switches running Cisco IOS Software; however, this is not !--- the focus of this document. For details on the Layer 3 EtherChannel configuration, !--- refer to the document Configuring EtherChannels. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet6/1 no ip address !--- On the Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport command once, !--- without any keywords, to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default. !--- You do not need an additional command. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1 with autonegotiation !--- that uses PAgP and silent mode. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet6/2 no ip address !--- On the Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport command once, !--- without any keywords, to configure the interface as a L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default. !--- You do not need an additional command. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1 with autonegotiation !--- that uses PAgP and silent mode. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet6/3 no ip address ! interface FastEthernet6/4 no ip address ! !--- Output suppressed. interface FastEthernet6/45 no ip address shutdown ! interface FastEthernet6/46 no ip address shutdown ! interface FastEthernet6/47 no ip address shutdown ! interface FastEthernet6/48 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IP address for management. ip address 10.10.10.3 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! ! line con 0 line vty 0 4 ! end Cat6509# |
Per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi della configurazione, consultare la guida di riferimento dei comandi della famiglia Catalyst 5000 (6.3 e 6.4).
Nota: se si assegna un'interfaccia a una VLAN non esistente, l'interfaccia viene chiusa finché non si crea la VLAN nel database VLAN. Per ulteriori informazioni, consultare la sezione Creazione o modifica di una VLAN Ethernet in Configurazione delle VLAN.
Verifica
Le informazioni contenute in questa sezione permettono di verificare che la configurazione funzioni correttamente.
Alcuni comandi show sono supportati dallo strumento Output Interpreter (solo utenti registrati); lo strumento permette di visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show. ![]()
Per controllare il canale della porta negli switch CatOs, usare questi comandi:
Per controllare lo stato del protocollo Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) sugli switch CatOs, usare questi comandi:
Per controllare il canale delle porte sugli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000 o Catalyst 4500/4000 con software Cisco IOS, eseguire questi comandi:
Per controllare lo stato STP sugli switch Catalyst serie 6500/6000 o Catalyst serie 4500/4000 con software Cisco IOS, eseguire questi comandi:
Output di esempio del comando show
Catalyst 5500 Switch
Questo comando verifica se il modulo è in grado di eseguire il channeling. Indica inoltre il gruppo di porte che è possibile combinare per formare EtherChannel. Nell'esempio, è possibile raggruppare le due porte 4/1-2 o le quattro porte 4/1-4 per formare un canale:
cat5500 (enable) show port capabilities 4 Model WS-X5203 Port 4/1 Type 10/100BaseTX Speed auto,10,100 Duplex half,full Trunk encap type ISL Trunk mode on,off,desirable,auto,nonegotiate Channel 4/1-2,4/1-4 Broadcast suppression pps(0-150000),percentage(0-100) Flow control no Security yes Membership static,dynamic Fast start yes QOS scheduling rx-(none),tx-(none) CoS rewrite no ToS rewrite no Rewrite no UDLD yes AuxiliaryVlan no SPAN source,destination !--- Output suppressed.
Questo comando, insieme al comando show port, verifica lo stato del canale della porta.
cat5500 (enable) show port channel
Port Status Channel Admin Ch
Mode Group Id
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
4/1 connected desirable silent 200 865
4/2 connected desirable silent 200 865
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
Port Device-ID Port-ID Platform
----- ------------------------------- ------------------------- ----------------
4/1 Switch Fa6/1 cisco Catalyst 6000
4/2 Switch Fa6/2 cisco Catalyst 6000
----- ------------------------------- ------------------------- ----------------
cat5500 (enable)
cat5500 (enable) show port 4/1
Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------
4/1 connected 1 normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX
!--- Output suppressed.
Port Status Channel Admin Ch
Mode Group Id
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
4/1 connected desirable silent 200 865
4/2 connected desirable silent 200 865
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
!--- Output suppressed.
cat5500 (enable) show port 4/2
Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------
4/2 connected 1 normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX
!--- Output suppressed.
Port Status Channel Admin Ch
Mode Group Id
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
4/1 connected desirable silent 200 865
4/2 connected desirable silent 200 865
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
!--- Output suppressed.
cat5500 (enable) show port channel info
Switch Frame Distribution Method: Mac both
Port Status Channel Admin Channel Speed Duplex Vlan
mode group id
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- ------- ----- ------ ----
4/1 connected desirable silent 200 865 a-100 a-full 1
4/2 connected desirable silent 200 865 a-100 a-full 1
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- ------- ----- ------ ----
Port ifIndex Oper-group Neighbor Oper-Distribution PortSecurity/
Oper-group Method Dynamic port
----- ------- ---------- ---------- ----------------- -------------
4/1 334 1 65537 Mac both
4/2 334 1 65537 Mac both
----- ------- ---------- ---------- ----------------- -------------
Port Device-ID Port-ID Platform
----- ------------------------------- ------------------------- ----------------
4/1 Switch Fa6/1 cisco Catalyst 6000
4/2 Switch Fa6/2 cisco Catalyst 6000
----- ------------------------------- ------------------------- ----------------
!--- Output suppressed.
I comandi STP verificano se tutte le porte all'interno di un canale sono raggruppate e nello stato di inoltro.
cat5500 (enable) show spantree 1 VLAN 1 Spanning tree enabled Spanning tree type IEEE Designated Root 00-30-40-a7-a4-00 Designated Root Priority 32768 Designated Root Cost 0 Designated Root Port 1/0 Root Max Age 20 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID MAC ADDR 00-30-40-a7-a4-00 Bridge ID Priority 32768 Bridge Max Age 20 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Port Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Portfast Channel_id ------------------------ ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ---------- 2/1-2 1 not-connected 19 32 disabled 0 3/1 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/2 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/3 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/4 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/5 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/6 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/7 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/8 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/9 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/10 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/11 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/12 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/13 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/14 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/15 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/16 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/17 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/18 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/19 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/20 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/21 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/22 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/23 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 3/24 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/1-2 1 forwarding 12 32 disabled 865 4/3 1 forwarding 19 32 disabled 0 4/4 1 forwarding 19 32 disabled 0 4/5 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/6 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/7 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/8 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/9 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/10 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/11 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 4/12 1 not-connected 100 32 disabled 0 cat5500 (enable)
cat5500 (enable) show spantree 4/1 Port Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Portfast Channel_id ------------------------ ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ---------- 4/1-2 1 forwarding 12 32 disabled 865 cat5500 (enable) show spantree 4/2 Port Vlan Port-State Cost Priority Portfast Channel_id ------------------------ ---- ------------- ----- -------- ---------- ---------- 4/1-2 1 forwarding 12 32 disabled 865 cat5500 (enable)
Nota: l'output di show spantree module/port per le porte 4/1 e 4/2 visualizza risultati identici. Ciò è dovuto al fatto che sono raggruppati in un canale con l'ID di canale 865.
Catalyst 6500 Switch
Questo comando verifica se il modulo è in grado di eseguire il channeling.
Cat6509# show interfaces capabilities module 6 FastEthernet6/1 Model: WS-X6348-RJ-45 Type: 10/100BaseTX Speed: 10,100,auto Duplex: half,full Trunk encap. type: 802.1Q,ISL Trunk mode: on,off,desirable,nonegotiate Channel: yes Broadcast suppression: percentage(0-100) Flowcontrol: rx-(off,on),tx-(none) Membership: static Fast Start: yes QOS scheduling: rx-(1q4t), tx-(2q2t) CoS rewrite: yes ToS rewrite: yes Inline power: yes SPAN: source/destination UDLD yes Link Debounce: yes Link Debounce Time: no FastEthernet6/2 Model: WS-X6348-RJ-45 Type: 10/100BaseTX Speed: 10,100,auto Duplex: half,full Trunk encap. type: 802.1Q,ISL Trunk mode: on,off,desirable,nonegotiate Channel: yes Broadcast suppression: percentage(0-100) Flowcontrol: rx-(off,on),tx-(none) Membership: static Fast Start: yes QOS scheduling: rx-(1q4t), tx-(2q2t) CoS rewrite: yes ToS rewrite: yes Inline power: yes SPAN: source/destination UDLD yes Link Debounce: yes Link Debounce Time: no
-
show interfaces port-channel interface number
Questo comando controlla lo stato del canale della porta. Indica inoltre le porte che formano il canale.
Cat6509# show interfaces port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0009.1267.27d9 (bia 0009.1267.27d9)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is off
Members in this channel: Fa6/1 Fa6/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 0/2000/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue :0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
126880 packets input, 10173099 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 126758 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
6101 packets output, 1175124 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat6509#
Con questo comando viene visualizzato il riepilogo a riga singola per gruppo di canali. In questo output di esempio, è possibile visualizzare il flag P con le porte Fa6/1 e Fa6/2. Ciò significa che queste porte formano il canale della porta.
Cat6509# show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator u - unsuitable for bundling Number of channel-groups in use: 1 Number of aggregators: 1 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports --------- +-----------------------+ ----------------+ --------------- 1 Po1(SU) PAgP Fa6/1(P) Fa6/2(P)
Con questo comando vengono visualizzate le informazioni sul canale della porta.
Cat6509# show etherchannel port-channel Channel-group listing: ----------------------- Group: 1 ---------- Port-channels in the group: ---------------------- Port-channel: Po1 ------------ Age of the Port-channel = 00d:00h:02m:25s Logical slot/port = 14/1 Number of ports = 2 GC = 0x00010001 HotStandBy port = null Port state = Port-channel Ag-Inuse Protocol = PAgP Ports in the Port-channel: Index Load Port EC state No of bits ------+------+------+------------------+----------- 1 55 Fa6/1 Desirable-Sl 4 0 AA Fa6/2 Desirable-Sl 4 Time since last port bundled: 00d:00h:01m:03s Fa6/1 Time since last port Un-bundled: 00d:00h:01m:05s Fa6/1
Questo comando verifica se il canale è in stato di inoltro per una VLAN specifica.
Cat6509# show spanning-tree detail
VLAN1 is executing the IEEE compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 00d0.029a.8001
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Current root has priority 32768, address 0030.40a7.a400
Root port is 833 (Port-channel1), cost of root path is 12
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:23:59 ago
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300
Port 833 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 131.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0030.40a7.a400
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0030.40a7.a400
Designated port id is 131.97, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 2, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 1, received 718
Con questo comando vengono visualizzate le informazioni dello Spanning Tree per la VLAN1.
Cat6509# show spanning-tree vlan 1 VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 32768 Address 0030.40a7.a400 Cost 12 Port 833 (Port-channel1) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32768 Address 00d0.029a.8001 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type ---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- -------------------------------- Po1 Root FWD 12 128.833 P2p
Considerazioni speciali sull'uso della modalità incondizionata
Cisco consiglia di utilizzare PAgP per la configurazione del canale della porta, come descritto in questo documento. Se si configura EtherChannel in modo incondizionato (con la modalità canale attivata), è necessario creare un canale porta. In questa sezione viene illustrata la procedura. Se si crea un canale di porta, si evitano possibili problemi con STP durante il processo di configurazione. Se si configura un lato come canale prima che l'altro diventi un canale, il rilevamento STP loop può disabilitare le porte.
-
Per impostare le porte per il channeling delle porte sulla modalità di disabilitazione sullo switch CatOs, eseguire il comando set port disable module/port.
-
Creare il canale della porta (gruppo di porte) sullo switch Cisco IOS e impostare la modalità del canale su on.
-
Creare il canale della porta sullo switch CatOs e impostare la modalità del canale su on.
-
Per riattivare le porte disabilitate in precedenza sul primo switch CatOS, usare il comando set port enable modulo/porta.
Risoluzione dei problemi
Problemi di prestazioni con EtherChannel
I problemi di prestazioni con EtherChannels sono causati da diverse condizioni. Le cause più comuni includono un algoritmo di bilanciamento del carico non corretto e problemi di livello fisico specifici della porta.
Per una migliore comprensione e configurazione dell'algoritmo di bilanciamento del carico, fare riferimento ai seguenti documenti:
-
Sezione Informazioni sul funzionamento della distribuzione dei frame di EtherChannel della Guida alla configurazione del software Catalyst serie 6500, 8.6.
-
Sezione Understanding Load Balancing della guida alla configurazione del software Cisco IOS Catalyst serie 6500, 12.2SX.
Per informazioni su come risolvere i problemi relativi ai livelli fisici, consultare il documento sulla risoluzione dei problemi relativi alle porte e alle interfacce dello switch.
Informazioni correlate
- Configurazione di EtherChannel tra gli switch Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000 e 6500/6000 con software CatOS
- Configurazione di LACP (802.3ad) tra un Catalyst 6500/6000 e un Catalyst 4500/4000
- Requisiti di sistema per implementare EtherChannel sugli switch Catalyst
- Guide alla configurazione degli switch Catalyst serie 6500
- Guida alla configurazione del software della famiglia Catalyst 5000 (6.3 e 6.4)
- Guide alla configurazione degli switch Catalyst serie 4000
- Switch Catalyst serie 5500 - Supporto tecnico
- Switch Catalyst serie 6500 - Supporto tecnico
- Pagina di supporto tecnico di EtherChannel
- Supporto dei prodotti LAN
- Supporto della tecnologia di switching LAN
- Supporto tecnico – Cisco Systems
 Feedback
Feedback