Trunking 802.1Q tra gli switch Catalyst con software CatOS e Cisco IOS
Sommario
Introduzione
In questo documento vengono fornite configurazioni di esempio per il trunking IEEE 802.1Q tra gli switch Catalyst con software di sistema Catalyst OS (CatOS) e gli switch modulari di layer 3 (L3) con software di sistema Cisco IOS®. Gli switch con CatOS includono gli switch Catalyst serie 4500/4000, 5500/5000 e 6500/6000. Gli switch modulari L3 con software Cisco IOS includono gli switch Catalyst serie 4500/4000 e Catalyst serie 6500/6000. Le configurazioni di esempio usano Catalyst 4000 (CatOS) e Catalyst 6500 (software Cisco IOS), ma uno degli switch appena menzionati avrebbe potuto essere usato per ottenere gli stessi risultati.
Il trunking permette di trasmettere il traffico di VLAN diverse su un collegamento point-to-point tra due dispositivi. Il trunking Ethernet può essere implementato in due modi:
-
ISL (Inter-Switch Link Protocol) (protocollo proprietario Cisco)
-
802.1Q (standard IEEE)
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Per i requisiti di sistema, le linee guida e le restrizioni relative a 802.1Q e ISL sugli switch Catalyst, fare riferimento a: Requisiti di sistema per implementare il trunking.
Componenti usati
Per creare gli esempi riportati nel presente documento, sono stati usati questi switch:
-
Switch Catalyst 4000 con Supervisor Engine II (WS-X4013) e software CatOS versione 8.1.3
-
Catalyst 6509 con Supervisor Engine 2/Multilayer Switch Feature Card 2 (MSFC2) con software Cisco IOS versione 12.1(20)E2 sul Supervisor Engine e MSFC2
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Convenzioni
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle convenzioni usate, consultare il documento Cisco sulle convenzioni nei suggerimenti tecnici.
Nozioni di base
Questo documento include solo i file di configurazione degli switch e l'output dei relativi comandi show di esempio. Per i dettagli su come configurare un trunk 802.1Q tra gli switch Catalyst, consultare le pagine di supporto dei prodotti LAN.
Nel trunking 802.1Q, tutti i pacchetti VLAN sono contrassegnati sul collegamento trunk, ad eccezione della VLAN nativa. I pacchetti VLAN nativi vengono inviati senza tag sul collegamento trunk. Pertanto, la VLAN nativa deve essere la stessa su entrambi gli switch configurati per il trunking. In questo modo, è possibile dedurre a quale VLAN appartiene un frame quando si riceve un frame senza tag. Per impostazione predefinita, la VLAN 1 è la VLAN nativa su tutti gli switch.
-
Nel software CatOs, la VLAN nativa può essere modificata usando il comando set vlan vlan-id mod/porta, dove mod/porta è la porta trunk.
-
Nel software Cisco IOS, la VLAN nativa può essere modificata usando il comando switchport trunk native vlan id-vlan interface configurato sulla porta trunk.
Configurazione
In questa sezione vengono presentate le informazioni necessarie per configurare le funzionalità descritte più avanti nel documento.
Le configurazioni descritte in questo documento sono state implementate in un ambiente lab isolato. valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso di una configurazione o di un comando sulla rete. Le configurazioni su tutti i dispositivi sono state cancellate con i comandi clear config all e write erase per assicurarsi che disponessero di una configurazione predefinita.
Nota: per ulteriori informazioni sui comandi menzionati in questo documento, usare lo strumento di ricerca dei comandi ![]() (solo utenti registrati).
(solo utenti registrati).
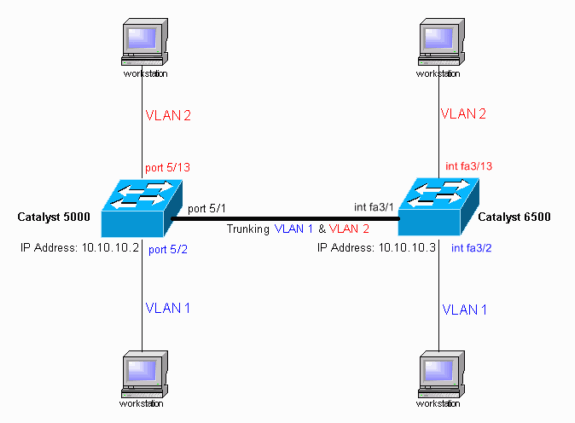
Esempio di rete
Nel documento viene usata questa impostazione di rete:
Configurazioni
Nel documento vengono usate queste configurazioni:
Nota: i commenti e le spiegazioni vengono visualizzati in corsivo blu.
| Catalyst 4000 Switch |
|---|
#version 8.1(3) ! ! #system web interface version(s) ! #system set system name cat4000 ! #frame distribution method set port channel all distribution mac both ! #vtp set vtp domain cisco !--- In this example, the VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) domain name is the same !--- on both sides. This is required for the autonegotiation of the trunk !--- by the Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP). set vtp mode client vlan !--- In this example, the VTP mode is set to client. !--- Set the VTP mode according to your network requirements. !--- For more details, refer to !--- Understanding and Configuring VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP). ! #ip set interface sc0 1 10.10.10.2/255.255.255.0 10.10.10.255 !--- This is the IP address used for management. !--- Output suppressed. ! #module 1 : 2-port 1000BaseX Supervisor ! #module 2 empty ! #module 3 empty ! #module 4 empty ! #module 5 : 48-port Inline Power Module set vlan 2 5/13-24 !--- Ports 5/13-24 have been assigned to VLAN 2. set trunk 5/1 desirable dot1q 1-1005,1025-4094 !--- The trunking mode is set to desirable mode, which means !--- the port automatically tries to form a trunk with a !--- neighboring port set to desirable, auto, or on mode. !--- For recommended trunk mode settings, refer to !--- the Dynamic Trunking Protocol section of !--- Best Practices for Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, and 6500/6000 Series Switches Running CatOS Configuration and Management. !--- Output suppressed. set spantree portfast 5/2-24 enable set port channel 5/2-24 mode off !--- The macro command set port host 5/2-24 was used to do three things: !--- disable trunking, disable port channeling, and enable spantree portfast. !--- For details on using the set port host command, refer to !--- Using Portfast and Other Commands to Fix Workstation Startup Connectivity Delays. ! #module 6 empty end |
| Catalyst 6500 Switch |
|---|
Current configuration : 4408 bytes ! version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname cat6500 ! boot system flash sup-bootflash:c6sup22-jsv-mz.121-20.E2 enable password mysecret !--- This is the privileged mode password used in the example. ! ip subnet-zero ! ! ! mls flow ip destination mls flow ipx destination ! redundancy mode rpr-plus main-cpu auto-sync running-config auto-sync standard ! ! ! interface GigabitEthernet2/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet2/2 no ip address shutdown ! interface fastethernet3/1 switchport !--- The switchport command must be entered once, !--- without any keywords, to configure the interface as a Layer 2 port. !--- The interface is now automatically configured with the default command !--- switchport mode dynamic desirable. !--- This means the interface is ready to autonegotiate trunking !--- encapsulation and form a trunk link (using DTP) with a neighbor port !--- in desirable, auto, or on mode. !--- For recommended trunk mode settings, refer to !--- the "Dynamic Trunking Protocol" section of !--- Best Practices for Catalyst 6500/6000 Series and Catalyst 4500/4000 Series Switches Running Cisco IOS Software. ! interface FastEthernet3/2 switchport switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- The interface range fastethernet mod/beginport - endport !--- command is used to configure interfaces 3/2 - 24 at once. !--- Next, the switchport command is issued (if this has not been done already). switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- Next, issue the macro command switchport host 3/2 - 24 to automatically !--- configure these ports as access ports and to enable spantree portfast. !--- For details on using the switchport host command, refer to !--- Using Portfast and Other Commands to Fix Workstation Startup Connectivity Delays. ! interface FastEthernet3/13 switchport switchport access vlan 2 !--- Interfaces 3/13 - 24 are placed in VLAN 2 !--- using the switchport access vlan 2 command. switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/24 shutdown switchport switchport access vlan 2 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address shutdown ! interface vlan 1 ip address 10.10.10.3 255.255.255.0 !--- This is the IP address used for management. ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! ! line con 0 line vty 0 4 password mysecret !--- This is the Telnet password used in the example. login transport input lat pad mop telnet rlogin udptn nasi ! ! end cat6500# |
Verifica
Le informazioni contenute in questa sezione permettono di verificare che la configurazione funzioni correttamente.
Comandi show
Alcuni comandi show sono supportati dallo strumento Output Interpreter ![]() (solo utenti registrati); lo strumento permette di visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
(solo utenti registrati); lo strumento permette di visualizzare un'analisi dell'output del comando show.
Sugli switch Catalyst con CatOS, utilizzare questi comandi:
-
show port capabilities modulo/porta
-
show port module/port
-
show trunk module/port
-
show vtp domain
Sugli switch Catalyst 6000 con software Cisco IOS, utilizzare i seguenti comandi:
-
show interfaces interface-type module/port trunk
-
show vlan
Output di esempio del comando show
Catalyst 4000 Switch
Il comando show port capabilities modulo/porta viene usato per verificare se la porta è in grado di trunking.
cat4000> (enable) show port capabilities 5/1 Model WS-X4148-RJ45V Port 5/1 Type 10/100BaseTX Speed auto,10,100 Duplex half,full Trunk encap type 802.1Q Trunk mode on,off,desirable,auto,nonegotiate Channel 5/1-48 Flow control no Security yes Dot1x yes Membership static,dynamic Fast start yes QOS scheduling rx-(none),tx-(2q1t) CoS rewrite no ToS rewrite no Rewrite no UDLD yes Inline power auto,off,static AuxiliaryVlan 1..1000,1025..4094,untagged,none SPAN source,destination,reflector Link debounce timer yes IGMPFilter yes Dot1q-all-tagged no cat4000> (enable)
Il comando show port module/port restituisce lo stato di una porta specifica e se è trunking.
cat4000> (enable) show port status 5/1 Port Name Status Vlan Level Duplex Speed Type ----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ----- ------------ 5/1 connected trunk normal a-full a-100 10/100BaseTX cat4000> (enable)
Il comando show trunk viene usato per verificare lo stato e la configurazione del trunking.
cat4000> (enable) show trunk * - indicates vtp domain mismatch # - indicates dot1q-all-tagged enabled on the port Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan -------- ----------- ------------- ------------ ----------- 5/1 desirable dot1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5/1 1-1005,1025-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5/1 1-2 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned -------- --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5/1 1-2 cat4000> (enable)
Per controllare le informazioni VTP, usare il comando show vtp domain.
cat4000> (enable) show vtp domain Version : running VTP1 (VTP3 capable) Domain Name : cisco Password : not configured Notifications: disabled Updater ID: 10.10.10.3 Feature Mode Revision -------------- -------------- ----------- VLAN Client 21 Pruning : disabled VLANs prune eligible: 2-1000
Catalyst 6500 Switch
Il comando show interfaces interface-type module/port trunk indica se la porta è trunking.
cat6500# show interfaces fastethernet 3/1 trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa3/1 desirable n-802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa3/1 1-4094 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa3/1 1-2 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa3/1 1-2 cat6500#
Il comando show vlan fornisce informazioni sulle VLAN e sulle porte che appartengono a una VLAN specifica.
cat6500# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa3/2, Fa3/3, Fa3/4, Fa3/5
Fa3/6, Fa3/7, Fa3/8, Fa3/9
Fa3/10, Fa3/11, Fa3/12
2 VLAN0002 active Fa3/13, Fa3/14, Fa3/15, Fa3/16
Fa3/17, Fa3/18, Fa3/19, Fa3/20
Fa3/21, Fa3/22, Fa3/23, Fa3/24
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
!--- Output suppressed.
cat6500#
Nota: vengono visualizzate solo le porte configurate come porte non trunk di livello 2.
Risoluzione dei problemi
Al momento non sono disponibili informazioni specifiche per la risoluzione dei problemi di questa configurazione.
 Feedback
Feedback