Configuration du service VRF EVPN VxLAN sur les commutateurs Catalyst 9000
Options de téléchargement
-
ePub (764.5 KB)
Consulter à l’aide de différentes applications sur iPhone, iPad, Android ou Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (531.5 KB)
Consulter sur un appareil Kindle ou à l’aide d’une application Kindle sur plusieurs appareils
Langage exempt de préjugés
Dans le cadre de la documentation associée à ce produit, nous nous efforçons d’utiliser un langage exempt de préjugés. Dans cet ensemble de documents, le langage exempt de discrimination renvoie à une langue qui exclut la discrimination en fonction de l’âge, des handicaps, du genre, de l’appartenance raciale de l’identité ethnique, de l’orientation sexuelle, de la situation socio-économique et de l’intersectionnalité. Des exceptions peuvent s’appliquer dans les documents si le langage est codé en dur dans les interfaces utilisateurs du produit logiciel, si le langage utilisé est basé sur la documentation RFP ou si le langage utilisé provient d’un produit tiers référencé. Découvrez comment Cisco utilise le langage inclusif.
À propos de cette traduction
Cisco a traduit ce document en traduction automatisée vérifiée par une personne dans le cadre d’un service mondial permettant à nos utilisateurs d’obtenir le contenu d’assistance dans leur propre langue. Il convient cependant de noter que même la meilleure traduction automatisée ne sera pas aussi précise que celle fournie par un traducteur professionnel.
Table des matières
Introduction
Ce document décrit la configuration de fuite de route pour EVPN (Ethernet VPN) VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) dans différents scénarios.
Conditions préalables
Il est recommandé que vous soyez familiarisé avec la fonctionnalité Unicast EVPN VxLAN, BGP.
Exigences
Ce guide suppose que les homologues BGP et NVE sont déjà corrects. En cas de problèmes avec l'activation de VxLAN EVPN de base (échec de la commande ping de monodiffusion, BGP, homologues NVE désactivés, etc.), veuillez vous reporter aux guides de dépannage BGP, EVPN, route/commutateur, si nécessaire.

Remarque : les exemples de configuration VRF de service sont pris en charge pour IPv4 uniquement.
Composants utilisés
Les informations contenues dans ce document sont basées sur les versions de matériel et de logiciel suivantes :
- C9300
- C9400
- C9500
- C9600
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. Si votre réseau est en ligne, assurez-vous de bien comprendre l’incidence possible des commandes.

Remarque : consultez le guide de configuration approprié pour connaître les commandes utilisées afin d'activer ces fonctionnalités sur d'autres plates-formes Cisco.
Configurer
La fonctionnalité de fuite de route est largement utilisée dans le cas de la création de services « VRF partagé » ou de la connexion de noeuds en limite au pare-feu. Généralement, les noeuds de périphérie sont les noeuds où la fuite de route est configurée.
- La fuite de route entre les VRF pour EVPN/VXLAN sur Cisco IOS® XE n'est pas effectuée au niveau BGP comme d'habitude. La fonction EVN (Easy Virtual Network) est utilisée à la place.
Diagramme du réseau
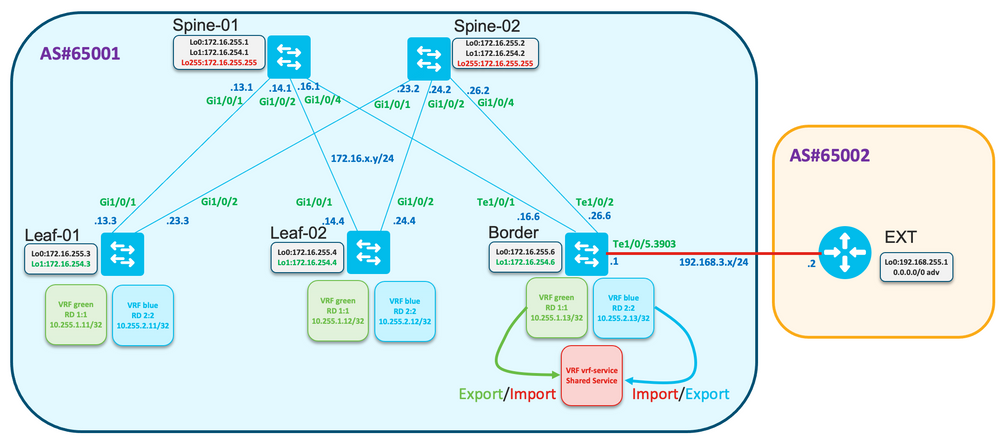
Fuite de route générique
Dans cet exemple, les fuites de route de VRF « vert » et « bleu » vers VRF « vrf-service » planifiées doivent être configurées sur le noeud Périphérie.
Vérifiez la table de routage pour les VRF « vert » et « bleu » sur la périphérie :
Border#show ip route vrf green
<…snip…>
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
B 10.1.1.0/24 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:19:43, Vlan901
B 10.1.2.0/24 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:19:43, Vlan901
B 10.255.1.11/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:19:43, Vlan901
B 10.255.1.12/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.4, 01:19:43, Vlan901
C 10.255.1.13/32 is directly connected, Loopback11
Border#show ip route vrf blue
<…snip…>
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
B 10.2.1.0/24 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:20:28, Vlan902
B 10.2.2.0/24 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:20:28, Vlan902
B 10.255.2.11/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:20:28, Vlan902
B 10.255.2.12/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.4, 01:20:28, Vlan902
C 10.255.2.13/32 is directly connected, Loopback12
Configuration pour importer toutes les routes du VRF « vert » vers le VRF « vrf-service »
vrf definition vrf-service rd 3:3 ! address-family ipv4 route-replicate from vrf green unicast all route-target export 3:3 route-target import 3:3 exit-address-family
Vérifiez que la table de routage du VRF « vrf-service » sur la périphérie contient des routes à partir du VRF « vert »
Border#show ip route vrf vrf-service
Routing Table: vrf-service
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, m - OMP
n - NAT, Ni - NAT inside, No - NAT outside, Nd - NAT DIA
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
H - NHRP, G - NHRP registered, g - NHRP registration summary
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
& - replicated local route overrides by connected
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
B + 10.1.1.0/24 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 00:00:42, Vlan901
B + 10.1.1.11/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 00:00:28, Vlan901
B + 10.255.1.11/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:32:49, Vlan901
B + 10.255.1.12/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.4, 01:32:49, Vlan901
C + 10.255.1.13/32 is directly connected, Loopback11
C 10.255.3.13/32 is directly connected, Loopback13
Notez que les routes « vertes » du VRF sont répliquées sur le VRF « vrf-service » et marquées du signe « + » dans la table de routage.
Fuite de route avec filtrage
La réplication de route peut être effectuée avec le filtrage. Les cartes de routage sont utilisées à cette fin.
Répliquez uniquement le préfixe 10.255.2.12 du VRF « bleu » au VRF « vrf-service ».
ip prefix-list PL-BLUE-2-VRF-SERVICE permit 10.255.2.12/32 ! route-map RM-BLUE-2-VRF-SERVICE permit 10 match ip adderess prefix-list PL-BLUE-2-VRF-SERVICE
Configurer la réplication avec le filtre
vrf definition vrf-service
rd 3:3
!
address-family ipv4
route-replicate from vrf green unicast all
route-replicate from vrf blue unicast all route-map RM-BLUE-2-VRF-SERVICE
route-target export 3:3
route-target import 3:3
exit-address-family
Observez que la table de routage du VRF « vrf-service » contient le préfixe 10.255.2.12/32 provenant du VRF « blue » :
Border#show ip route vrf VRF-SERVICE
<…snip…>
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masks
B + 10.1.1.0/24 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 00:09:38, Vlan901
B + 10.1.1.11/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 00:09:24, Vlan901
B + 10.255.1.11/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.3, 01:41:45, Vlan901
B + 10.255.1.12/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.4, 01:41:45, Vlan901
C + 10.255.1.13/32 is directly connected, Loopback11
B + 10.255.2.12/32 [200/0] via 172.16.254.4, 01:41:45, Vlan902 <--
C 10.255.3.13/32 is directly connected, Loopback13
Annonce de route par défaut uniquement et suivi de la route par défaut
La connectivité entre les hôtes connectés aux noeuds Leaf avec un réseau externe est établie au-delà de la frontière.
- En général, Border reçoit uniquement la route par défaut ou la route par défaut plus les routes récapitulatives.
- Pour optimiser la table de routage sur les noeuds Leaf, il est possible d'annoncer uniquement la route par défaut à partir de la frontière.
La route par défaut est reçue dans le VRF « vrf-service »/« Shared service ».
- Cette route peut être répliquée en VRF « vert », mais la route répliquée ne peut pas être annoncée à nouveau. Il est nécessaire de configurer l'annonce de route par défaut dans BGP pour VRF « vert ».
- La route statique avec l'objet piste peut être configurée pour éviter une situation de trou noir lorsque la route par défaut dans VRF « vert » est annoncée, mais que la route par défaut dans VRF « vrf-service » n'est pas présente.
Examiner la topologie
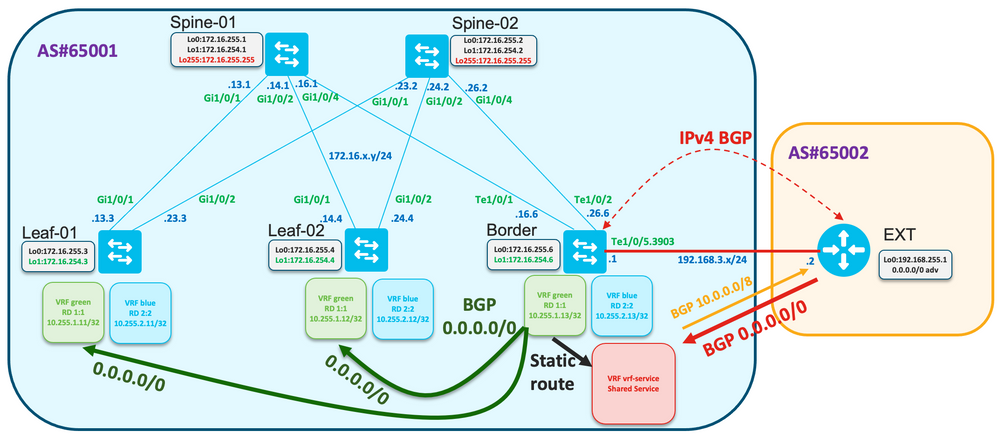
Vérifiez que la route par défaut est reçue sur le noeud périphérique :
Border#show ip route vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0
Routing Table: red
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 65001", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 65002, type external
Last update from 192.168.3.2 00:13:32 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.3.2, from 192.168.3.2, 00:13:32 ago
opaque_ptr 0x7FA2A139FE50
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65002
MPLS label: none Border#show ip cef vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0/0
0.0.0.0/0
nexthop 192.168.3.2 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3903
La piste 1 vérifie l'accessibilité de la route par défaut dans le VRF « vrf-service ».
track 1 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 reachability ip vrf vrf-service
Vérifiez que la route par défaut est présente dans le VRF « vrf-service » et que l'objet de piste est « Up ».
Border#show track 1
Track 1
IP route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 reachability
Reachability is Up (BGP)
2 changes, last change 00:23:12
VPN Routing/Forwarding table "vrf-service"
First-hop interface is TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3903
Tracked by:
Static IP Routing 0
Configurez la route par défaut dans le VRF « vert » avec l'option de piste
! ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3903 192.168.3.2 track 1 !
Border#show ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0
Routing Table: green
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0, candidate default path
Redistributing via bgp 65001
Advertised by bgp 65001
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.3.2, via TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3903
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
L'annonce de route par défaut est configurée sous le processus BGP pour le VRF « vert »
router bgp 65001 ! <...snip...> ! address-family ipv4 vrf green advertise l2vpn evpn redistribute static redistribute connected default-information originate exit-address-family ! <...snip...>
Vérifiez que la route par défaut est annoncée à L2VPN EVPN AF comme route-type 5 et propagée sur le fabric
Border#show bgp l2vpn evpn rd 1:1 route-type 5 0 0.0.0.0 0
BGP routing table entry for [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17, version 622
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
2
Refresh Epoch 1
Local, imported path from base
192.168.3.2 (via vrf red) from 0.0.0.0 (172.16.255.6)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, external, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, local vtep: 172.16.254.6, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 27
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD67.EF48
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Jul 8 2022 10:41:40 UTC
Vérifiez les informations EVPN, routage et cef sur Leaf-01
Leaf-01#show bgp l2vpn evpn rd 1:1 route-type 5 0 0.0.0.0 0
BGP routing table entry for [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17, version 595
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 7
Local
172.16.254.6 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.2 (172.16.255.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD67.EF48
Originator: 172.16.255.6, Cluster list: 172.16.255.2
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0
Updated on Jul 8 2022 10:41:40 UTC
Refresh Epoch 7
Local
172.16.254.6 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.1 (172.16.255.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD67.EF48
Originator: 172.16.255.6, Cluster list: 172.16.255.1
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Jul 8 2022 10:41:40 UTC
Leaf-01#show ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0
Routing Table: green
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 65001", distance 200, metric 0, candidate default path, type internal
Last update from 172.16.254.6 on Vlan901, 02:07:17 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 172.16.254.6 (default), from 172.16.255.1, 02:07:17 ago, via Vlan901
opaque_ptr 0x7FC3606F4D80
Route metri c is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 0
MPLS label: none
Leaf-01#show ip cef vrf green 0.0.0.0/0
0.0.0.0/0
nexthop 172.16.254.6 Vlan901
La route inverse du fabric vers le réseau externe provient de BGP comme une route récapitulative
! ip route vrf vrf-service 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Null0 ! router bgp 65001 <…snip…> ! address-family ipv4 vrf vrf-service advertise l2vpn evpn aggregate-address 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 summary-only redistribute static redistribute connected neighbor 192.168.3.2 remote-as 65002 neighbor 192.168.3.2 activate exit-address-family ! <…snip…>
Vérifiez la table de routage sur le Leaf-01 dans le VRF « vert » et envoyez une requête ping à l'adresse IP distante 192.168.255.1
Leaf-01#show ip route vrf green 192.168.255.1
Routing Table: green
% Network not in table
Leaf-01#show ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0
Routing Table: green
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 65001", distance 200, metric 0, candidate default path, type internal
Last update from 172.16.254.6 on Vlan901, 05:15:19 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 172.16.254.6 (default), from 172.16.255.1, 05:15:19 ago, via Vlan901
opaque_ptr 0x7FC3606F4D80
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 0
MPLS label: none
Leaf-01#show ip cef vrf green 0.0.0.0/0
0.0.0.0/0
nexthop 172.16.254.6 Vlan901
Leaf-01#ping vrf green 192.168.3.2 source 10.255.1.11
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.3.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.255.1.11
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Si la route par défaut est perdue sur la frontière dans le VRF « vrf-service », l'objet de piste s'arrête, la route statique dans le VRF « vert » est supprimée du RIB et la route par défaut annoncée dans le BGP est supprimée
### Border ###
Border#show ip route vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0 Routing Table: vrf-service % Network not in table Border#show track 1 Track 1 IP route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 reachability Reachability is Down (no ip route) <-- Track object is down 3 changes, last change 00:03:15 VPN Routing/Forwarding table "vrf-service" First-hop interface is unknown Tracked by: Static IP Routing 0 Border#show ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0 Routing Table: green % Network not in table Border#show bgp l2vpn evpn rd 1:1 route-type 5 0 0.0.0.0 0 % Network not in table
### Leaf ### Leaf-01#show ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0 Routing Table: green % Network not in table
La route par défaut entre le VRF « vert » et le VRF « vrf-service » doit être filtrée
vrf definition vrf-service rd 3:3 ! address-family ipv4 route-replicate from vrf green unicast all route-map RM-GREEN-2-VRF-SERVICE route-target export 3:3 route-target import 3:3 exit-address-family ip prefix-list PL-DEFAULT seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 ! route-map RM-GREEN-2-VRF-SERVICE deny 10 match ip address prefix-list PL-DEFAULT ! route-map RM-GREEN-2-VRF-SERVICE permit 20

Attention : en raison du délai entre la perte de la route par défaut et la panne de l'objet de piste, la route statique par défaut est répliquée du VRF « vert » vers le VRF « vrf-service » et conserve l'objet de piste actif. Par conséquent, la route par défaut est annoncée au fabric et le trafic est bloqué.
Annonce de route par défaut uniquement avec des bordures redondantes
Cette section fournit un exemple de cas où des frontières redondantes sont utilisées.

Remarque : dans cet exemple, nous avons utilisé la fonctionnalité BGP additional-path. Une autre option est d'utiliser une RD différente sur la Border-01 et la Border-02 pour annoncer les DEUX routes par défaut des deux bordures aux leafs.
Examiner la topologie
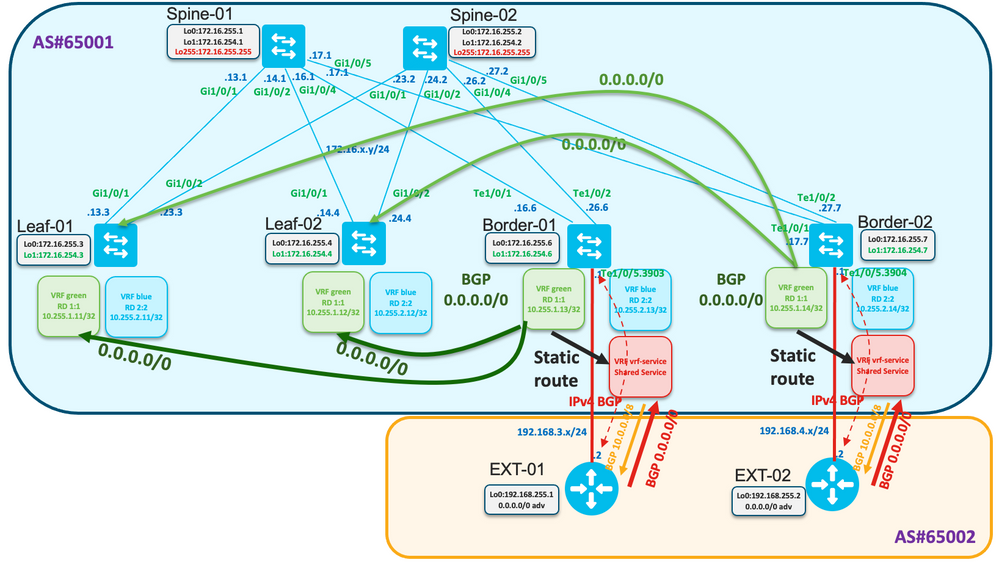
Border-01 et Border-02 reçoivent respectivement la route par défaut de EXT-01 et EXT-02.
De la frontière 01
Border-01#show ip route vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0
Routing Table: vrf-service
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 65001", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 65002, type external
Last update from 192.168.3.2 00:00:06 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.3.2, from 192.168.3.2, 00:00:06 ago
opaque_ptr 0x7F68E5AC02A0
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65002
MPLS label: none
Border-01#show ip cef vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0/0
0.0.0.0/0
nexthop 192.168.3.2 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3903
De la frontière 02
Border-02#show ip route vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0
Routing Table: vrf-service
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 65001", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 65002, type external
Last update from 192.168.4.2 01:22:08 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.4.2, from 192.168.4.2, 01:22:08 ago
opaque_ptr 0x7FE529FF3D48
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 65002
MPLS label: none
Border-02#show ip cef vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0/0
0.0.0.0/0
nexthop 192.168.4.2 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3904
La même approche est utilisée dans la configuration à double frontière comme dans l'exemple précédent : route statique par défaut avec suivi.
Configurez la piste Border-01/02, la route statique pour la route par défaut dans vrf "vert", la configuration bgp pour l'annonce.
track 1 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 reachability ip vrf vrf-service ! ip route vrf green 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5.3903 192.168.3.2 track 1 ! router bgp 65001 ! <...snip...> ! address-family ipv4 vrf green advertise l2vpn evpn redistribute static redistribute connected default-information originate exit-address-family ! <...snip...>
Vérifiez sur les spines que les routes par défaut des deux bordures sont reçues
Spine-01#show bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP table version is 25, local router ID is 172.16.255.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path, L long-lived-stale,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:1
* ia [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
*>i 172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ?
* i 172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ?
<...snip...>
Spine-02#show bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP table version is 75, local router ID is 172.16.255.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path, L long-lived-stale,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:1
* i [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ?
* ia 172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
*>i 172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ?
<...snip...>
Configurer sur les spines pour propager les DEUX routes par défaut BGP chemin-supplémentaire
router bgp 65001 ! <...snip...> ! address-family l2vpn evpn bgp additional-paths select all best 2 bgp additional-paths send receive <...snip...> neighbor 172.16.255.3 advertise additional-paths best 2 <...snip...> neighbor 172.16.255.4 advertise additional-paths best 2 ! <...snip...>
Observez que cette configuration modifie la propagation par défaut au mieux uniquement et annonce à la place les DEUX routes
Spine-01#show bgp l2vpn evpn neighbors 172.16.255.3 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 25, local router ID is 172.16.255.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path, L long-lived-stale,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:1
*>i [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ? <-- best path
* ia [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ? <-- addtional path (note the a flag indicating this)
<...snip...>
Observez sur le Leaf que nous voyons 4 routes par défaut BGP
Leaf-01#sh bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP table version is 63, local router ID is 172.16.255.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path, L long-lived-stale,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:1 (default for vrf green)
* i [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
* ia 172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
*>i 172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ?
* i 172.16.254.6 0 100 0 ?
<...snip...>
Leaf-01#sh bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 5 0 0.0.0.0 0
BGP routing table entry for [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17, version 64
Paths: (4 available, best #3, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 4
Local
172.16.254.7 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.2 (172.16.255.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD68.E548
Originator: 172.16.255.7, Cluster list: 172.16.255.2
rx pathid: 0x1, tx pathid: 0
Updated on Aug 24 2022 16:52:56 UTC
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
172.16.254.7 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.1 (172.16.255.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD68.E548
Originator: 172.16.255.7, Cluster list: 172.16.255.1
rx pathid: 0x1, tx pathid: 0
Updated on Aug 24 2022 16:49:48 UTC
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
172.16.254.6 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.1 (172.16.255.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD67.EF48
Originator: 172.16.255.6, Cluster list: 172.16.255.1
rx pathid: 0x0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Aug 24 2022 16:49:48 UTC
Refresh Epoch 4
Local
172.16.254.6 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.2 (172.16.255.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD67.EF48
Originator: 172.16.255.6, Cluster list: 172.16.255.2
rx pathid: 0x0, tx pathid: 0
Updated on Aug 24 2022 16:52:56 UTC
La configuration du leaf est illustrée ici
router bgp 65001 ! <...snip...> ! address-family l2vpn evpn bgp additional-paths receive <...snip...> ! address-family ipv4 vrf green import path selection all maximum-paths ibgp 2 <...snip...>
Vérifiez que la table de routage Leaf contient deux routes vers les deux bordures
Leaf-01#show ip route vrf green
Routing Table: green
<...snip...>
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.254.7 to network 0.0.0.0
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 172.16.254.7, 00:02:15, Vlan901
[200/0] via 172.16.254.6, 00:02:15, Vlan901
<...snip...>
Leaf-01#show ip cef vrf green 0.0.0.0/0
0.0.0.0/0
nexthop 172.16.254.6 Vlan901
nexthop 172.16.254.7 Vlan901
Observez ce qui se passe en cas de perte de la route par défaut de Border-01.
Border-01#show ip route vrf vrf-service 0.0.0.0 Routing Table: vrf-service % Network not in table
La piste s'arrête
Border-01#show track 1
Track 1
IP route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 reachability
Reachability is Down (no ip route)
5 changes, last change 00:00:56
VPN Routing/Forwarding table "vrf-service"
First-hop interface is unknown
Tracked by:
Static IP Routing 0
Sur les épines, nous voyons la route seulement de Border-02
Spine-01#show bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP table version is 27, local router ID is 172.16.255.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path, L long-lived-stale,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:1
* i [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
*>i 172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
<...snip...>
Sur la feuille, nous voyons la route seulement de la frontière-02
Leaf-01#show bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP table version is 68, local router ID is 172.16.255.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path, L long-lived-stale,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 1:1 (default for vrf green)
*>i [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17
172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
* i 172.16.254.7 0 100 0 ?
<...snip...>
Leaf-01#sh bgp l2vpn evpn route-type 5 0 0.0.0.0 0
BGP routing table entry for [5][1:1][0][0][0.0.0.0]/17, version 68
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table EVPN-BGP-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 1
Local
172.16.254.7 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.1 (172.16.255.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD68.E548
Originator: 172.16.255.7, Cluster list: 172.16.255.1
rx pathid: 0x0, tx pathid: 0x0
Updated on Aug 24 2022 17:17:31 UTC
Refresh Epoch 4
Local
172.16.254.7 (metric 3) (via default) from 172.16.255.2 (172.16.255.2)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
EVPN ESI: 00000000000000000000, Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0, VNI Label 50901, MPLS VPN Label 0
Extended Community: RT:1:1 ENCAP:8 Router MAC:0C75.BD68.E548
Originator: 172.16.255.7, Cluster list: 172.16.255.2
rx pathid: 0x0, tx pathid: 0
Updated on Aug 24 2022 17:17:31 UTC
Une seule route est présente dans la table de routage et dans CEF sur le Leaf-01
Leaf-01#show ip route vrf green Routing Table: green <...snip...> Gateway of last resort is 172.16.254.7 to network 0.0.0.0 B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 172.16.254.7, 00:04:02, Vlan901 <...snip...> Leaf-01#show ip cef vrf green 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 nexthop 172.16.254.7 Vlan901
Informations connexes
Historique de révision
| Révision | Date de publication | Commentaires |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
08-Feb-2023 |
Première publication |
Contribution de
- Dmytro Vishchuk
Contacter Cisco
- Ouvrir un dossier d’assistance

- (Un contrat de service de Cisco est requis)
 Commentaires
Commentaires