Exemple de configuration de l'implémentation BGP à l'aide d'un numéro AS 32 bits
Contenu
Introduction
Ce document décrit comment configurer le protocole BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) à l'aide d'un numéro AS 32 bits. Dans BGP, chaque domaine de routage est un domaine administratif unique et un numéro de système autonome unique lui est attribué. Il est utilisé dans un ensemble uniforme de stratégies de routage. Il gère également le routage interdomaine.
Dans ce document, l'appairage BGP est configuré entre des routeurs BGP 16 bits et 32 bits parlant. Le nouveau mode AS 32 bits est compatible avec le mode AS 16 bits. Les homologues BGP qui peuvent fonctionner en mode 32 bits répondent positivement à la nouvelle fonctionnalité, et cette session fonctionne en nouveau mode. D'un autre côté, les homologues BGP 32 bits lors de la communication avec les haut-parleurs BGP 16 bits, les routeurs de conférence 16 bits ignorent cette nouvelle fonctionnalité et exploitent leur session BGP en mode 16 bits.
Conditions préalables
Conditions requises
Cisco vous recommande d'avoir une connaissance de base du protocole BGP.
Versions matérielles et logicielles
Les configurations de ce document sont basées sur le routeur de la gamme Cisco 7200 avec le logiciel Cisco IOS® version 15.0(1).
Conventions
Pour plus d'informations sur les conventions utilisées dans ce document, reportez-vous à Conventions relatives aux conseils techniques Cisco.
Configuration
Dans cet exemple, les routeurs R1 et R3 sont configurés pour être dans AS 100 formant une relation iBGP à l'aide du mode AS 16 bits. Les routeurs R2 et R4 sont configurés dans AS 10.1 et forment l'appairage iBGP en utilisant le mode AS 32 bits. Les routeurs R1 et R2 exécutent et protocole IGP, dans cet exemple, OSPF entre eux et forme également eBGP voisin entre eux.
Remarque : utilisez l'outil de recherche de commandes (clients enregistrés uniquement) afin de trouver plus d'informations sur les commandes utilisées dans ce document.
Diagramme du réseau
Ce document utilise la configuration réseau suivante :
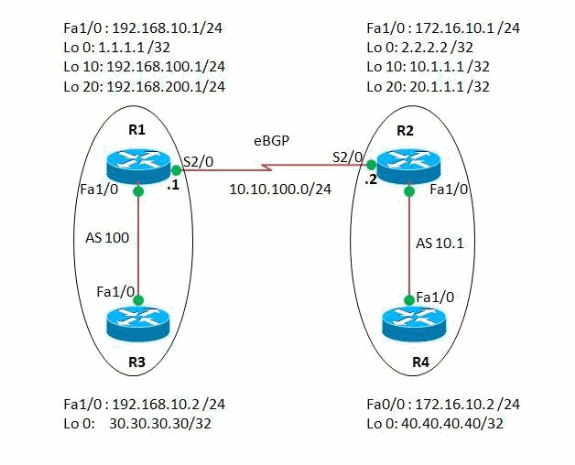
Configurations
Ce document utilise les configurations suivantes :
| Routeur R1 |
|---|
R1#show run Building configuration... ! version 15.0 ! hostname R1 ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback10 ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback20 ip address 192.168.200.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial2/0 ip address 10.10.100.1 255.255.255.0 serial restart-delay 0 ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.10.100.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! router bgp 100 !--- BGP is configured using 16-bit AS number no synchronization bgp router-id 10.10.10.10 bgp asnotation dot !--- This command change the default asplain notation to dot notation. !--- Note that without this command the AS number will treated as asplain notation i.e. 10.1 will be displayed as 655361 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.100.0 network 192.168.200.0 neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 10.1 !--- The AS number of the eBGP peer in 32-bit neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 192.168.10.2 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.10.2 next-hop-self no auto-summary ! end |
| Routeur R2 |
|---|
R2#show run ! version 15.0 ! hostname R2 ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Loopback10 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback20 ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial2/0 ip address 10.10.100.2 255.255.255.0 serial restart-delay 0 ! ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.10.100.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! router bgp 10.1 !--- BGP is configured using 32-bit AS number no synchronization bgp router-id 20.20.20.20 bgp asnotation dot bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 network 20.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 255 neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 172.16.10.2 remote-as 10.1 neighbor 172.16.10.2 next-hop-self no auto-summary ! end |
| Routeur R3 |
|---|
R3#show run Building configuration... ! version 15.0 ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 30.30.30.30 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 100 no synchronization bgp router-id 3.3.3.3 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 30.30.30.30 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 192.168.10.1 remote-as 100 neighbor 192.168.10.1 next-hop-self no auto-summary !--- iBGP peering is formed between routers R1 and R3 using 16-bit AS number. ! end |
| Routeur R4 |
|---|
R4#show run Building configuration... ! version 15.0 ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 40.40.40.40 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 172.16.10.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 10.1 no synchronization bgp router-id 4.4.4.4 bgp asnotation dot bgp log-neighbor-changes network 40.40.40.40 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 172.16.10.1 remote-as 10.1 no auto-summary ! end !--- iBGP peering is formed between routers R2 and R4 using 32-bit AS number. |
Vérification
Utilisez cette section pour confirmer que votre configuration fonctionne correctement.
L'Outil Interpréteur de sortie (clients enregistrés uniquement) (OIT) prend en charge certaines commandes show. Employez l'OIT afin d'afficher une analyse de la sortie de la commande show.
Commandes show
Afin de vérifier que BGP peut prendre en charge ASN 32 bits, utilisez la commande show ip bgp neighbor.
| show ip bgp neighbor |
|---|
Dans le routeur R1
R1#show ip bgp neighbor 2.2.2.2
BGP neighbor is 2.2.2.2, remote AS 10.1, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 20.20.20.20
BGP state = Established, up for 03:28:22
Last read 00:00:41, last write 00:00:29, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Neighbor sessions:
1 active, is multisession capable
Neighbor capabilities:
Route refresh: advertised and received(new)
Four-octets ASN Capability: advertised and received
Address family IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Multisession Capability: advertised and received
Message statistics, state Established:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 1 1
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 3 3
Keepalives: 229 230
Route Refresh: 0 0
Total: 233 234
!--- Output omitted---!
|
Pour afficher les entrées de la table de routage BGP, utilisez la commande show ip bgp.
| show ip bgp |
|---|
Dans le routeur R1
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 13, local router ID is 10.10.10.10
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.1.1/32 2.2.2.2 0 0 10.1 I
*> 20.1.1.1/32 2.2.2.2 0 0 10.1 I
*>i30.30.30.30/32 192.168.10.2 0 100 0 I
*> 40.40.40.40/32 2.2.2.2 0 10.1 I
*> 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
*> 192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
!--- Note that the routes highlighted are received from the eBGP peer router R2 which is in 32-bit AS 10.1.
In router R3
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.1.1.1/32 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 655361 I
*>i20.1.1.1/32 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 655361 I
*> 30.30.30.30/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
*>i40.40.40.40/32 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 655361 I
*>i192.168.100.0 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 I
*>i192.168.200.0 192.168.10.1 0 100 0 I
!--- The router R3 does not have bgp asnotation dot configured in it. Therefore, the route received from the router in 32-bit AS AS 10.1 is displayed as 655361.
In router R4
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.1.1.1/32 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 I
*>i20.1.1.1/32 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 I
*>i30.30.30.30/32 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 100 I
*> 40.40.40.40/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 I
*>i192.168.100.0 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 100 I
*>i192.168.200.0 172.16.10.1 0 100 0 100 I
!--- The above output shows the entries in BGP routing table of router R4.
|
Afin de vérifier l'accessibilité entre les routeurs, utilisez la commande ping.
| ping |
|---|
À partir du routeur R3 R3#ping 40.40.40.40 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 40.40.40.40, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 68/101/148 msÀ partir du routeur R4 R4#ping 30.30.30.30 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 30.30.30.30, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/89/112 ms !--- The above output shows that End to End connectivity is established between R3 and R4, where R3 is AS 100(16-bit AS) and router R4 is in AS 10.1(32-bit AS). |
Informations connexes
Historique de révision
| Révision | Date de publication | Commentaires |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Jun-2012 |
Première publication |
 Commentaires
Commentaires