Router de dos interfaces sin NAT con configuración de firewall de Cisco IOS
Contenido
Introducción
Este ejemplo de configuración corresponde a una oficina muy pequeña que se conecta directamente a Internet, con el supuesto de que Domain Name Service (DNS), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) y los servicios Web se proporcionaban a través de un sistema remoto ejecutado por el Proveedor de Servicios de Internet (ISP). No hay ningún servicio en la red interna y solamente dos interfaces. Tampoco existe registro ya que no hay ningún host disponible para brindar servicios de registro.
Puesto que esta configuración utiliza solamente listas de acceso de entrada, realiza tanto anti-simulación como filtrado de tráfico con la misma lista de acceso. Esta configuración sólo funciona para un router de dos puertos. Ethernet 0 es la red "interna". El Serial 0 es un link de Frame Relay al ISP.
Consulte Router de Dos Interfaces con Configuración de Firewall de Cisco IOS NAT para configurar un router de dos interfaces con NAT usando un Firewall de Cisco IOS®.
Consulte Router de Tres Interfaces sin NAT Cisco IOS Firewall Configuration para configurar un router de tres interfaces sin NAT usando un Cisco IOS Firewall.
Prerequisites
Requirements
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
La información de este documento se aplica a estas versiones de software y hardware:
-
Versión 12.2(15)T13 del software del IOS de Cisco, compatible con la versión 11.3.3.T del software del IOS de Cisco
-
Router 2611 de Cisco
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Convenciones
Consulte Convenciones de Consejos Técnicos de Cisco para obtener más información sobre las convenciones sobre documentos.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Utilice la herramienta Command Lookup (sólo para clientes registrados) para obtener más información sobre los comandos utilizados en esta sección.
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
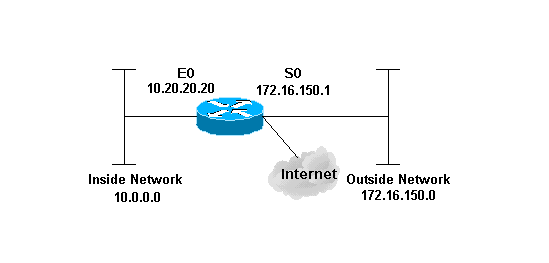
Configuración
Este documento usa esta configuración:
| Router 2514 |
|---|
version 12.2 ! service password-encryption no service udp-small-servers no service tcp-small-servers no cdp run ! hostname cbac-cisco ! no ip source-route ! enable secret 5 $1$FrMn$wBu0Xgv/Igy5Y.DarCmrm/ ! username cisco privilege 15 password 7 0822455D0A16 no ip source-route ip domain-name cisco.com ip name-server 172.16.150.5 ! !--- Set up inspection list "myfw". !--- Inspect for the protocols that actually get used. ! ip inspect name myfw cuseeme timeout 3600 ip inspect name myfw ftp timeout 3600 ip inspect name myfw http timeout 3600 ip inspect name myfw rcmd timeout 3600 ip inspect name myfw realaudio timeout 3600 ip inspect name myfw smtp timeout 3600 ip inspect name myfw tftp timeout 30 ip inspect name myfw udp timeout 15 ip inspect name myfw tcp timeout 3600 ! interface Ethernet0/0 description Cisco Ethernet RTP ip address 10.20.20.20 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! !--- Apply the access list in order to allow all legitimate traffic !--- from the inside network but prevent spoofing. ! ip access-group 101 in ! no ip proxy-arp ! !--- Apply inspection list "myfw" to Ethernet 0 inbound. !--- When conversations are initiated from the internal network !--- to the outside, this inspection list causes temporary additions !--- to the traffic allowed in by serial interface 0 acl 111 when !--- traffic returns in response to the initiation. ! ip inspect myfw in no ip route-cache ! no cdp enable ! interface Serial0/0 description Cisco FR ip address 172.16.150.1 255.255.255.0 encapsulation frame-relay IETF no ip route-cache no arp frame-relay bandwidth 56 service-module 56 clock source line service-module 56k network-type dds frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! !--- Access list 111 allows some ICMP traffic and administrative Telnet, !--- and does anti-spoofing. There is no inspection on Serial 0. !--- However, the inspection on the Ethernet interface adds temporary entries !--- to this list when hosts on the internal network make connections !--- out through the Frame Relay. ! ip access-group 111 in no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache bandwidth 56 no cdp enable frame-relay interface-dlci 16 ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0 ! !--- Access list 20 is used to control which network management stations !--- can access through SNMP. ! access-list 20 permit 172.16.150.8 ! !--- The access list allows all legitimate traffic from the inside network !--- but prevents spoofing. ! access-list 101 permit tcp 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 any access-list 101 permit udp 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 any access-list 101 permit icmp 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 any !--- This deny is the default. access-list 101 deny ip any any ! !--- Access list 111 controls what can come from the outside world !--- and it is anti-spoofing. ! access-list 111 deny ip 127.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 any access-list 111 deny ip 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 any ! !--- Perform an ICMP stuff first. There is some danger in these lists. !--- They are control packets, and allowing *any* packet opens !--- you up to some possible attacks. For example, teardrop-style !--- fragmentation attacks can come through this list. ! access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 administratively-prohibited access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 echo access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 echo-reply access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 packet-too-big access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 time-exceeded access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 traceroute access-list 111 permit icmp any 172.16.150.0 0.0.0.255 unreachable ! !--- Allow Telnet access from 10.11.11.0 corporate network administration people. ! access-list 111 permit tcp 10.11.11.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.16.150.1 eq telnet ! !--- This deny is the default. ! access-list 111 deny ip any any ! !--- Apply access list 20 for SNMP process. ! snmp-server community secret RO 20 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 password 7 14191D1815023F2036 login local line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 password 7 14191D1815023F2036 login local length 35 end |
Verificación
Actualmente, no hay un procedimiento de verificación disponible para esta configuración.
Troubleshoot
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para solucionar problemas de configuración.
Después de configurar el router de firewall del IOS, si las conexiones no funcionan, asegúrese de haber habilitado la inspección con el comando ip inspect (nombre definido) in o out en la interfaz. En esta configuración, ip inspect myfw in se aplica para la interfaz Ethernet0/0.
Para estos comandos, junto con otra información de resolución de problemas, consulte Resolución de problemas del Proxy de autenticación.
Nota: Consulte Información Importante sobre Comandos Debug antes de ejecutar los comandos debug.
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
20-Feb-2007 |
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios