Links Virtuales OSPF: Capacidad de tránsito
Opciones de descarga
-
ePub (218.3 KB)
Visualice en diferentes aplicaciones en iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader o Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (223.8 KB)
Visualice en dispositivo Kindle o aplicación Kindle en múltiples dispositivos
Lenguaje no discriminatorio
El conjunto de documentos para este producto aspira al uso de un lenguaje no discriminatorio. A los fines de esta documentación, "no discriminatorio" se refiere al lenguaje que no implica discriminación por motivos de edad, discapacidad, género, identidad de raza, identidad étnica, orientación sexual, nivel socioeconómico e interseccionalidad. Puede haber excepciones en la documentación debido al lenguaje que se encuentra ya en las interfaces de usuario del software del producto, el lenguaje utilizado en función de la documentación de la RFP o el lenguaje utilizado por un producto de terceros al que se hace referencia. Obtenga más información sobre cómo Cisco utiliza el lenguaje inclusivo.
Acerca de esta traducción
Cisco ha traducido este documento combinando la traducción automática y los recursos humanos a fin de ofrecer a nuestros usuarios en todo el mundo contenido en su propio idioma. Tenga en cuenta que incluso la mejor traducción automática podría no ser tan precisa como la proporcionada por un traductor profesional. Cisco Systems, Inc. no asume ninguna responsabilidad por la precisión de estas traducciones y recomienda remitirse siempre al documento original escrito en inglés (insertar vínculo URL).
Contenido
Introducción
El propósito de este documento es demostrar el comportamiento Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) cuando el bit V (bit de link virtual) está presente en un área que no es de estructura básica. El bit V se señala en el LSA Tipo 1 solamente si el router es el punto final de uno o más links virtuales completamente adyacentes. Cuando se configura el bit V, esto podría cambiar la preferencia de cálculo de trayectoria entre las rutas dentro del área y entre áreas.
Prerequisites
Consulte el diagrama de red de la Figura 1 mientras utiliza este documento:
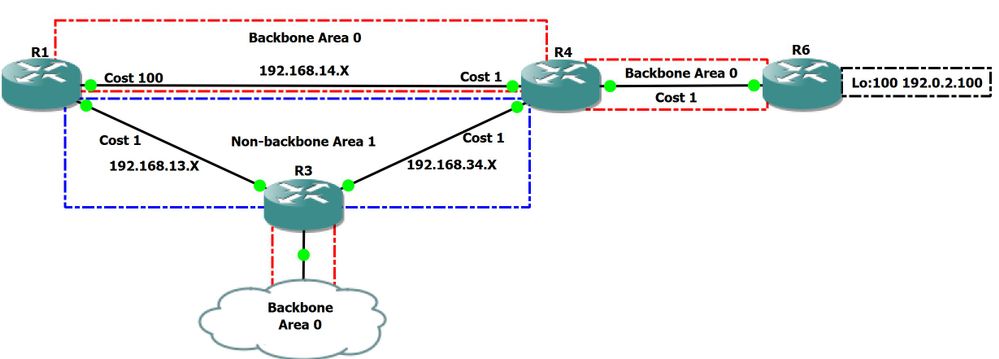
Figure 1
En el diagrama de red anterior, tenemos el área de estructura básica 0 y el área no de estructura básica 1. R1 es un router de borde de área (ABR) que conecta el área 0 y el área 1, R4 y R3 tienen un rol similar en esta red. En este área de topología 0 no es contigua ya que R3 y R4 no están conectados a través del área 0.
Antecedentes
Todas las áreas de un sistema autónomo OSPF deben estar conectadas al área de estructura básica (área 0). En algunos casos en los que tiene un área de estructura no básica entre su área de estructura básica, esto podría causar que algunas áreas del sistema autónomo se vuelvan inalcanzables y que la red no sea contigua. Cuando no es posible tener un área de estructura básica contigua, puede utilizar un link virtual para conectar su estructura básica a través de un área que no es de estructura básica. El área a través de la cual se configura el link virtual se conoce como área de tránsito.
Escenario 1
Diagrama de la red:
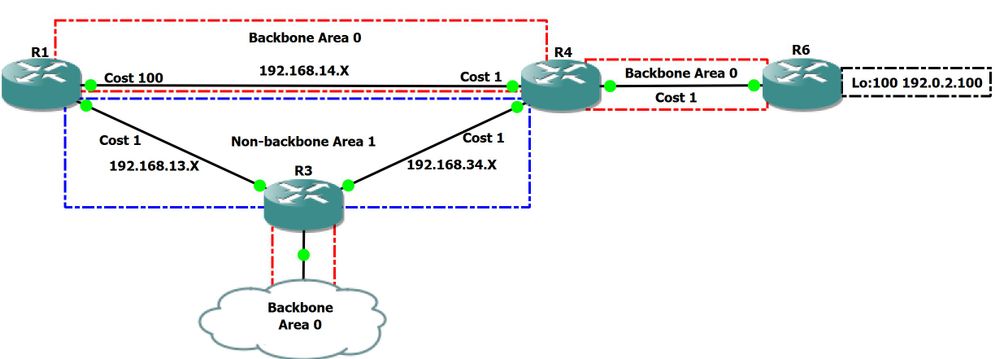
Figure 2
En este escenario, vamos a pasar por el cálculo del trayecto esperado en la topología de red anterior. Estaremos investigando qué trayectoria se prefiere cuando se rutea desde R1 hacia R6 loopback 100 que tiene una dirección ip de 192.0.2.100/32
Echemos un vistazo a la base de datos OSPF en R1 para comprender mejor la topología:
R1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 22 0x8000000C 0x00CD7A 2
4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 289 0x8000000F 0x00434E 4
6.6.6.6 6.6.6.6 374 0x80000009 0x00630A 3
Summary Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
192.168.13.0 1.1.1.1 18 0x80000001 0x00348D
192.168.13.0 4.4.4.4 207 0x80000001 0x00E3D0
192.168.34.0 1.1.1.1 8 0x80000001 0x005655
192.168.34.0 4.4.4.4 683 0x80000001 0x00F1AE
Router Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 17 0x80000009 0x00EC2B 2
3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 18 0x8000000E 0x005A64 4
4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 544 0x80000005 0x0007CF 2
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum
155.1.37.0 3.3.3.3 1558 0x80000004 0x00A7C3
192.0.2.100 1.1.1.1 23 0x80000001 0x009F0C <- R6 Loopback
192.0.2.100 4.4.4.4 370 0x80000001 0x0059AA <- R6 Loopback
192.168.14.0 1.1.1.1 23 0x80000001 0x000B52
192.168.14.0 4.4.4.4 331 0x80000001 0x00CEE5
192.168.34.0 1.1.1.1 3608 0x80000002 0x00406C
192.168.46.0 1.1.1.1 23 0x80000001 0x00B388
192.168.46.0 4.4.4.4 484 0x80000001 0x006D27
A partir de la salida anterior, podemos ver que R1 aprende R6 Lo100:192.0.2.100 a través de R4 como LSA de resumen tipo 3, R1 se está originando también como LSA de resumen tipo 3, ya que conoce R6 Lo100:192.0.2.100 a través del área interna estructura básica. En el siguiente resultado podemos ver que R6 tiene 192.0.2.100 conectado directamente.
R1#show ip ospf da router 6.6.6.6
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
LS age: 614
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 6.6.6.6
Advertising Router: 6.6.6.6
LS Seq Number: 8000000D
Checksum: 0x5B0E
Length: 60
Number of Links: 3
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.0.2.100 <-- Loopback 100 directly connected
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.255
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 4.4.4.4
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.46.6
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.168.46.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Resumen de RFC 2328, sección 16.2
16.2. Calculating the inter-area routes
(5) Next, look up the routing table entry for the destination N.
(If N is an AS boundary router, look up the "router" routing
table entry associated with Area A). If no entry exists for
N or if the entry's path type is "type 1 external" or "type
2 external", then install the inter-area path to N, with
associated area Area A, cost IAC, next hop equal to the list
of next hops to router BR, and Advertising router equal to
BR.
(6) Else, if the paths present in the table are intra-area
paths, do nothing with the LSA (intra-area paths are always
preferred).
(7) Else, the paths present in the routing table are also
inter-area paths. Install the new path through BR if it is
cheaper, overriding the paths in the routing table.
Otherwise, if the new path is the same cost, add it to the
list of paths that appear in the routing table entry.
En el resultado anterior podemos ver que se indica que las rutas dentro del área son preferidas a las rutas entre áreas. Por lo tanto, en nuestro escenario R1 debería preferir pasar por la estructura básica dentro del área según RFC 2328.
Verifiquemos si este comportamiento se observa en nuestra topología:
R1#show ip ospf rib 192.0.2.100 OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1) Base Topology (MTID 0) OSPF local RIB Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB LSA: type/LSID/originator *> 192.0.2.100/32, Intra, cost 102, area 0 SPF Instance 9, age 02:19:34 Flags: RIB, HiPrio via 192.168.14.4, GigabitEthernet3 label 1048578 Flags: RIB LSA: 1/6.6.6.6/6.6.6.6 R1#show ip route 192.0.2.100 Routing entry for 192.0.2.100/32 Known via "ospf 1", distance 110, metric 102, type intra area Last update from 192.168.14.4 on GigabitEthernet3, 02:26:29 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.14.4, from 6.6.6.6, 02:26:29 ago, via GigabitEthernet3 Route metric is 102, traffic share count is 1
Como puede ver en las salidas anteriores, preferimos pasar el área de estructura básica 0 hacia el loopback R6100. En nuestra base de datos de estado de link, también somos conscientes de una trayectoria entre áreas a través de R3 y luego R4. El resumen de LSA que se aprende a través de R4 con un costo de 2 puede verse a continuación:
R1#show ip ospf database summary 192.0.2.100
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 523
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC, Upward)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000005
Checksum: 0x9710
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32
MTID: 0 Metric: 102
LS age: 973
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC, Upward)
LS Type: Summary Links(Network)
Link State ID: 192.0.2.100 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 4.4.4.4 <- This is Type-3 LSA injected by ABR R4
LS Seq Number: 80000005
Checksum: 0x51AE
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32
MTID: 0 Metric: 2
Tenga en cuenta que este coste de 2 refleja el coste que ABR tiene para el prefijo de destino. Los LSA de tipo 3 se inundan del área 0 en áreas no troncales y viceversa, describe el alcance de ABR hacia los links en otras áreas. Incluye el costo desde la perspectiva de ABR que disfrutó del LSA de tipo 3, pero oculta el costo completo del router que recibió el LSA de tipo 3.
A partir de la salida anterior, ahora sabemos que tenemos dos trayectorias que podemos tomar para alcanzar el loopback R6 desde R1:
1. Área interna que tiene un costo de 102
2. Interárea que tiene un costo de 2 conocido a través del LSA tipo 3 + R1 costo hacia R4 que también es 2. Esto nos da un coste total de 4
En este escenario ya hemos observado que preferimos una trayectoria dentro del área de mayor costo, ya que se define en RFC 2328 que se prefiere dentro del área en lugar de entre áreas.
Antes de continuar con el escenario 2, aquí hay un ejemplo de cómo OSPF interpreta los LSA de tipo 3:
· ABR R4 puede alcanzar el link A dentro del área con el coste de X
· R1 puede alcanzar ABR R4 con un coste Y
· Implica que R1 puede alcanzar el link A a través de SPT con un costo de X + Y
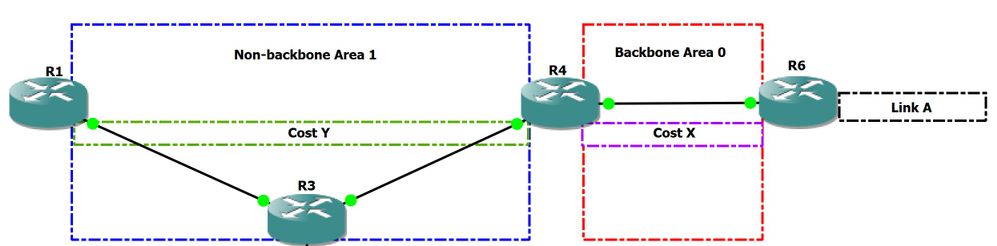
Figure 3
Esta es la razón por la que el ruteo entre áreas se compara generalmente con los protocolos de vector de distancia, ya que la información entre áreas se oculta.
Debido a que OSPF entre áreas es un vector de distancia, es vulnerable a los loops de ruteo. Evita los loops al exigir una topología interárea sin loops, en la que el tráfico de un área sólo puede alcanzar otro área a través del área 0.
Escenario 2
Diagrama de la red:
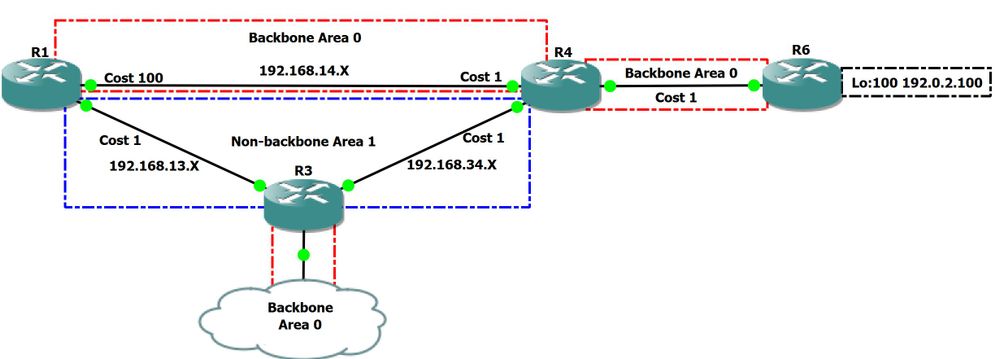
Figure 4
En este escenario, configuramos el bit V en R3 y R4 para que pudiéramos verificar la preferencia de trayectoria cuando este bit está presente en el LSA de tipo 1 del área de no estructura básica 1.
Resumen de RFC 2328, sección 6
6. The Area Data Structure
TransitCapability
This parameter indicates whether the area can carry data traffic
that neither originates nor terminates in the area itself. This
parameter is calculated when the area's shortest-path tree is
built (see Section 16.1, where TransitCapability is set to TRUE
if and only if there are one or more fully adjacent virtual
links using the area as Transit area), and is used as an input
to a subsequent step of the routing table build process (see
Section 16.3). When an area's TransitCapability is set to TRUE,
the area is said to be a "transit area".
Resumen de RFC 2328, sección 16.1
16.1 Calculating the shortest-path tree for an area
(2) Call the vertex just added to the tree vertex V. Examine
the LSA associated with vertex V. This is a lookup in the
Area A's link state database based on the Vertex ID. If
this is a router-LSA, and bit V of the router-LSA (see
Section A.4.2) is set, set Area A's TransitCapability to
TRUE. In any case, each link described by the LSA gives the
cost to an adjacent vertex. For each described link, (say
it joins vertex V to vertex W):
A partir de la instrucción anterior en RFC, podemos ver que cuando el bit V está configurado en el LSA del router, sabemos que el área en la que el bit está configurado para ser capaz de transitar o, en otras palabras, cuando se ejecuta el algoritmo Dijkstra, el TransitCapability es verdadero para ese área.
Una vez que sabemos que un área podría considerarse para el tránsito de capacidades si hay un conjunto de bits V, debemos verificar si esta funcionalidad está configurada: La función OSPF Area Transit Capability se habilita de forma predeterminada.
R1#show run all | sec ospf router ospf 1 capability opaque capability lls capability transit
Para configurar el bit V en el área 1, crearemos un link virtual de R3 a R4. Cuando se activa el link virtual, debemos ver el bit V configurado en el LSA de tipo 1.
R3(config)#router ospf 1 R3(config-router)#area 1 virtual-link 4.4.4.4 R3#show ip ospf interface brief Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C VL0 1 0 192.168.34.3/24 1 P2P 1/1 <-- Here we have Virtual-link present and 1 neighborship over VLO Gi3 1 0 192.168.80.3/24 1 DR 0/0 Gi2 1 1 192.168.13.3/24 1 P2P 1/1 Gi1 1 1 192.168.34.3/24 1 P2P 1/1 R3#
Ahora verifiquemos el LSA tipo 1 para el área R3 1.
R3#show ip ospf 1 1 database router 3.3.3.3
OSPF Router with ID (3.3.3.3) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 1)
LS age: 189
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: Router Links
Link State ID: 3.3.3.3
Advertising Router: 3.3.3.3
LS Seq Number: 80000018
Checksum: 0x525E
Length: 72
Area Border Router
Virtual Link Endpoint <- V-bit set
Number of Links: 4
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 1.1.1.1
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.13.3
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.168.13.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: another Router (point-to-point)
(Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: 4.4.4.4
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 192.168.34.3
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Link connected to: a Stub Network
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 192.168.34.0
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.0
Number of MTID metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metrics: 1
Como podemos ver en el resultado anterior, R3 ahora tiene el bit V configurado en su LSA Tipo 1 para el área 1 y tiene habilitado el tránsito de capacidad en el nivel del proceso de ruteo.
También podemos ver que R1 tiene habilitado el tránsito de cableado para el área 1 en el siguiente resultado:
R1#show ip ospf
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 1.1.1.1
Start time: 00:02:48.412, Time elapsed: 01:27:00.690
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Supports area transit capability
Supports NSSA (compatible with RFC 3101)
Supports Database Exchange Summary List Optimization (RFC 5243)
Event-log enabled, Maximum number of events: 1000, Mode: cyclic
It is an area border router
Router is not originating router-LSAs with maximum metric
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Incremental-SPF disabled
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
EXCHANGE/LOADING adjacency limit: initial 300, process maximum 300
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 2. 2 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Number of areas transit capable is 1
External flood list length 0
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 1
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:00:33.554 ago
SPF algorithm executed 11 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 10. Checksum Sum 0x05EB7B
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 3
Flood list length 0
Area 1
Number of interfaces in this area is 1
This area has transit capability <-- This area is transit capabile
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:00:04.259 ago
SPF algorithm executed 8 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 10. Checksum Sum 0x0517AA
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
Dado que el área 1 ahora pasa todos los criterios para convertirse en un área de tránsito, ahora debemos observar un cálculo/preferencia de trayectoria diferente que antes se veía en nuestro primer escenario.
Se establece RFC 2328 si un área se considera como área de tránsito, debe ser examinada de manera diferente que las áreas que no son de tránsito
Resumen de RFC 2328, sección 16.1
16.3. Examining transit areas' summary-LSAs This step is only performed by area border routers attached to one or more non-backbone areas that are capable of carrying transit traffic (i.e., "transit areas", or those areas whose TransitCapability parameter has been set to TRUE in Step 2 of the Dijkstra algorithm (see Section 16.1). The purpose of the calculation below is to examine the transit areas to see whether they provide any better (shorter) paths than the paths previously calculated in Sections 16.1 and 16.2. Any paths found that are better than or equal to previously discovered paths are installed in the routing table.
Según el RFC, si el área tiene capacidad de tránsito, está sujeta al cálculo de trayectoria descrito en la sección 16.3 del RFC 2328
Nota: que en este ejemplo el link virtual permite que el tráfico de datos de tránsito se reenvíe a través del Área 1, pero la trayectoria real que toma el tráfico de datos de tránsito no necesita seguir el link virtual. En otras palabras, los links virtuales permiten que el tráfico de tránsito se reenvíe a través de un área, pero no dictan la ruta precisa que tomará el tráfico.
Supongamos que el tránsito de capacidad se inhabilitó en R1. Verifiquemos el trayecto hacia el loopback R6 de destino:100 192.0.2.100 con un traceroute.
R1#traceroute 192.0.2.100 Tracing the route to 192.0.2.100 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 192.168.14.4 2 msec 2 msec 2 msec <--R4 2 192.168.46.6 3 msec 3 msec * <--R6
Una vez que activamos esta funcionalidad con el bit V configurado en el área 1, observamos los siguientes registros:
R1#debug ip ospf spf intra OSPF SPF intra debugging is on
R1#debug ip ospf spf inter OSPF SPF inter debugging is on R1#conf Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#capability transit R1(config-router)# *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 INTER: Running spf for summaries in transit area 1 *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 INTER: Summary transit processing lsid 192.0.2.100 adv_rtr 4.4.4.4 type 3 seq 0x8000000B *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 INTER: Summary metric 2 *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 INTER: found best path to adv_rtr: i,ABR [2] via 192.168.13.3, GigabitEthernet1, Area 1 orp_txit_adv_rtr 0.0.0.0 pathflag 0x0 *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 INTER: Add transit path via area 1 *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 SPF : Exist path: next-hop 192.168.13.3, interface GigabitEthernet1 *Aug 14 15:28:07.934: OSPF-1 INTRA: Route update succeeded for 192.0.2.100/255.255.255.255, metric 4, Next Hop: GigabitEthernet1/192.168.13.3 area 0
Ahora verifiquemos cómo la R1 se dirige hacia el loopback R6100
R1#show ip ospf rib 192.0.2.100
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
OSPF local RIB
Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB
LSA: type/LSID/originator
*> 192.0.2.100/32, Intra, cost 4, area 0
SPF Instance 14, age 00:12:28
Flags: RIB, HiPrio, Transit
via 192.168.13.3, GigabitEthernet1 label 1048578
Flags: RIB
LSA: 1/6.6.6.6/6.6.6.6
R1#show ip route 192.0.2.100
Routing entry for 192.0.2.100/32
Known via "ospf 1", distance 110, metric 4, type intra area
Last update from 192.168.13.3 on GigabitEthernet1, 00:01:26 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.13.3, from 6.6.6.6, 00:01:26 ago, via GigabitEthernet1
Route metric is 4, traffic share count is 1
¿Por qué vemos Intra-area en lugar de Inter-area? En la sección 16.3 de RFC 2328 se menciona que al realizar el cálculo de la trayectoria si tenemos una ruta de menor costo sobre el área de tránsito (Tipo 3), deberíamos actualizar el siguiente salto del prefijo. Este es el comportamiento que estamos viendo en el resultado anterior. El siguiente salto mencionado es correcto, pero el tipo es engañoso.
Resumen de RFC 2328, sección 16.3
16.3. Examining transit areas' summary-LSAs
(4) Look up the routing table entry for the advertising router
BR associated with the Area A. If it is unreachable, examine
the next LSA. Otherwise, the cost to destination N is the
sum of the cost in BR's Area A routing table entry and the
cost advertised in the LSA. Call this cost IAC.
(5) If this cost is less than the cost occurring in N's routing table entry, overwrite N's list of next hops with those used for BR, and set N's routing table cost to IAC. Else, if IAC is the same as N's current cost, add BR's list of next hops to N's list of next hops. In any case, the area associated with N's routing table entry must remain the backbone area, and the path type (either intra-area or inter-area) must also remain the same.
R1 prefiere la ruta dentro del área entre áreas Tipo 3 a la ruta dentro del área Tipo 1, aunque se indica como intra-área en la salida. Vemos claramente que el salto siguiente no está asociado al área 0
R1#show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 4.4.4.4 0 FULL/ - 00:00:39 192.168.14.4 GigabitEthernet3 3.3.3.3 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 192.168.13.3 GigabitEthernet1
R1#show ip ospf neighbor detail Neighbor 4.4.4.4, interface address 192.168.14.4 In the area 0 via interface GigabitEthernet3 Neighbor priority is 0, State is FULL, 6 state changes DR is 0.0.0.0 BDR is 0.0.0.0 Options is 0x12 in Hello (E-bit, L-bit) Options is 0x52 in DBD (E-bit, L-bit, O-bit) LLS Options is 0x1 (LR) Dead timer due in 00:00:36 Neighbor is up for 00:30:20 Index 1/1/1, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 3 First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last retransmission scan length is 1, maximum is 2 Last retransmission scan time is 135 msec, maximum is 135 msec Neighbor 3.3.3.3, interface address 192.168.13.3 In the area 1 via interface GigabitEthernet1 Neighbor priority is 0, State is FULL, 6 state changes DR is 0.0.0.0 BDR is 0.0.0.0 Options is 0x12 in Hello (E-bit, L-bit) Options is 0x52 in DBD (E-bit, L-bit, O-bit) LLS Options is 0x1 (LR) Dead timer due in 00:00:39 Neighbor is up for 00:30:20 Index 1/1/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 3 First 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last retransmission scan length is 4, maximum is 4 Last retransmission scan time is 126 msec, maximum is 126 msec
También seguiremos hacia el destino del loopback100 R6:
R1#traceroute 192.0.2.100 Tracing the route to 192.0.2.100 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 192.168.13.3 2 msec 4 msec 3 msec <-- R3 2 192.168.34.4 5 msec 3 msec 3 msec <-- R4 3 192.168.46.6 5 msec 6 msec * <-- R6 R1#
Por lo tanto, en el resultado anterior se observa que el área no troncal 1 es preferible sobre el área de estructura básica 0 para alcanzar el loopback R6 100.
También es posible tener ECMP (trayecto múltiple de igual costo) usando rutas dentro del área y entre áreas si el costo entre ellas es igual. Esto podría hacerse en nuestra topología disminuyendo el link R1s hacia R4 de 100 a 2.
Cuando esto se hace, tenemos el siguiente resultado en RIB y OSPF RIB:
R1#show ip ospf rib 192.0.2.100
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Base Topology (MTID 0)
OSPF local RIB
Codes: * - Best, > - Installed in global RIB
LSA: type/LSID/originator
*> 192.0.2.100/32, Intra, cost 4, area 0
SPF Instance 14, age 00:13:08
Flags: RIB, HiPrio, Transit, OldTrans
via 192.168.13.3, GigabitEthernet1 label 1048578
Flags: RIB
LSA: 1/6.6.6.6/6.6.6.6
via 192.168.14.4, GigabitEthernet3 label 1048578
Flags: RIB
LSA: 1/6.6.6.6/6.6.6.6
R1#show ip route 192.0.2.100
Routing entry for 192.0.2.100/32
Known via "ospf 1", distance 110, metric 4, type intra area
Last update from 192.168.14.4 on GigabitEthernet3, 00:12:44 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
192.168.14.4, from 6.6.6.6, 00:12:44 ago, via GigabitEthernet3
Route metric is 4, traffic share count is 1
* 192.168.13.3, from 6.6.6.6, 00:12:44 ago, via GigabitEthernet1
Route metric is 4, traffic share count is 1
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Jan-2018 |
Versión inicial |
Con la colaboración de ingenieros de Cisco
- Aleksandar Sofranic
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios