BGP Overview
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Configuring BGP |
Cisco IOS XR Release 7.11.1 |
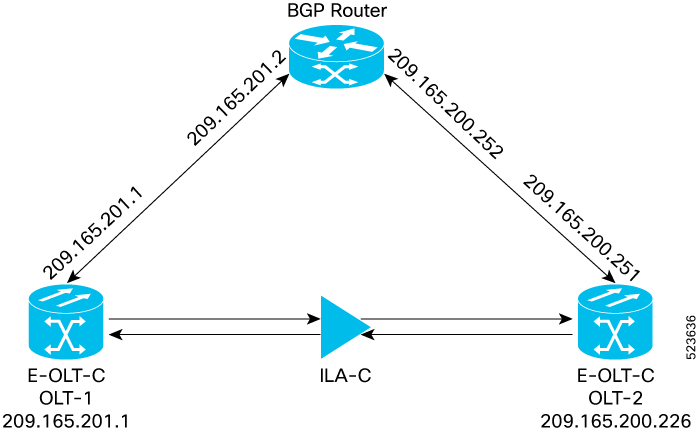
BGP routers from a TCP connection between peer routers to exchange network reachability information to open and confirm the connection parameters. BGP on NCS 1010 is enabled only on management port enabling the customer to manage the Dynamic Circuit Network(DCN) connectivity. |
BGP uses TCP as its transport protocol. Two BGP routers form a TCP connection between one another (peer routers) and exchange messages to open and confirm the connection parameters.
BGP routers exchange network reachability information. This information is mainly an indication of the full paths (BGP autonomous system numbers) that a route should take to reach the destination network. This information helps construct a graph that shows which autonomous systems are loop free and where routing policies can be applied to enforce restrictions on routing behavior.
Any two routers forming a TCP connection to exchange BGP routing information are called peers or neighbors. BGP peers initially exchange their full BGP routing tables. After this exchange, incremental updates are sent as the routing table changes. BGP keeps a version number of the BGP table, which is the same for all its BGP peers. The version number changes whenever BGP updates the table due to routing information changes. Keepalive packets are sent to ensure that the connection is alive between the BGP peers and notification packets are sent in response to error or special conditions.
 Note |
ASN change for the BGP process is not currently supported via commit replace . |
 Feedback
Feedback