Configure RADIUS IPSec Security for WLCs & Microsoft Windows 2003 IAS Server
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This guide documents how to configure the RADIUS IPSec feature supported by WCS and these WLAN Controllers:
-
4400 Series
-
WiSM
-
3750G
The Controller RADIUS IPSec feature is located on the Controller GUI under the Security > AAA > RADIUS Authentication Servers section. The feature provides a method for you to encrypt all RADIUS communications between Controllers and RADIUS servers (IAS) with IPSec.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
-
Knowledge on LWAPP
-
Knowledge on RADIUS Authentication and IPSec
-
Knowledge on how to configure services on the Windows 2003 Server Operating System
Components Used
These network and software components must be installed and configured in order to deploy the Controller RADIUS IPSec feature:
-
WLC 4400, WiSM, or 3750G Controllers. This example uses WLC 4400 that runs software version 5.2.178.0
-
Lightweight Access Points (LAPs). This example uses 1231 series LAP.
-
Switch with DHCP
-
Microsoft 2003 server configured as a Domain Controller installed with Microsoft Certificate Authority and with Microsoft Internet Authentication Service (IAS).
-
Microsoft Domain Security
-
Cisco 802.11 a/b/g Wireless Client Adapter with ADU version 3.6 configured with WPA2/ PEAP
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
IPSec RADIUS Configuration
This configuration guide does not address the installation or configuration of Microsoft WinServer, Certificate Authority, Active Directory or WLAN 802.1x client. These components must be installed and configured prior to the deployment of the Controller IPSec RADIUS feature. The remainder of this guide documents how to configure IPSec RADIUS on these components:
-
Cisco WLAN Controllers
-
Windows 2003 IAS
-
Microsoft Windows Domain Security Settings
Configure the WLC
This section explains how to configure IPSec on the WLC through the GUI.
From the Controller GUI, complete these steps.
-
Navigate to the Security > AAA > RADIUS Authentication tab in the Controller GUI, and add a new RADIUS server.
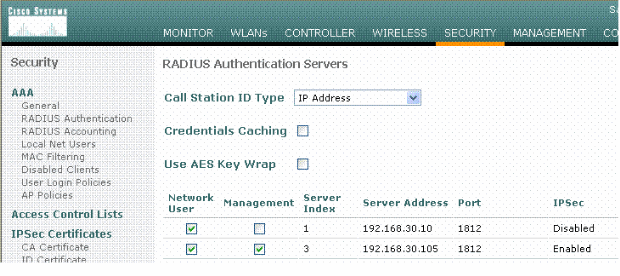
-
Configure the IP address, Port 1812, and a shared secret of the new RADIUS server. Check the IPSec Enable- check box, configure these IPSec parameters, and then click Apply.
Note: The shared secret is used both to authenticate the RADIUS server and as the Pre-shared key (PSK) for IPSec authentication.
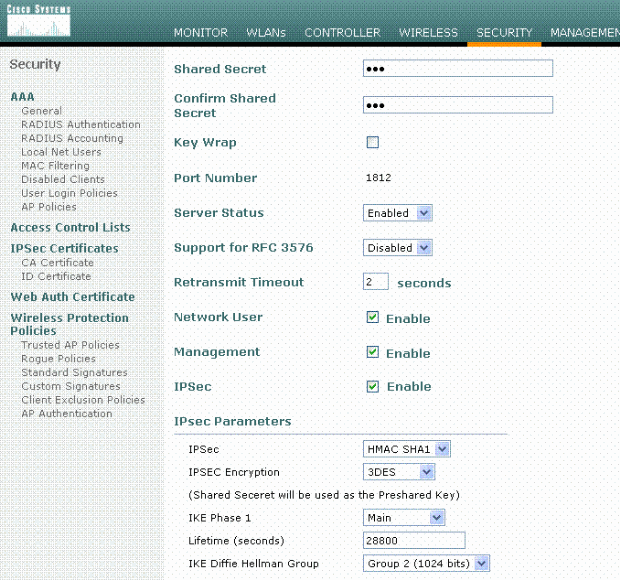
Configure the IAS
Complete these steps on the IAS:
-
Navigate to the IAS manager in Win2003 and add a new RADIUS Client.
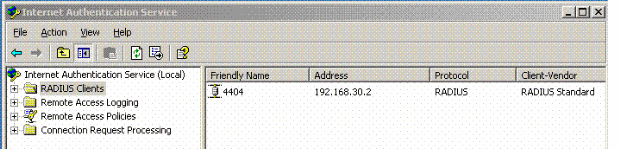
-
Configure the RADIUS client properties with the IP address and the shared secret configured on the Controller:
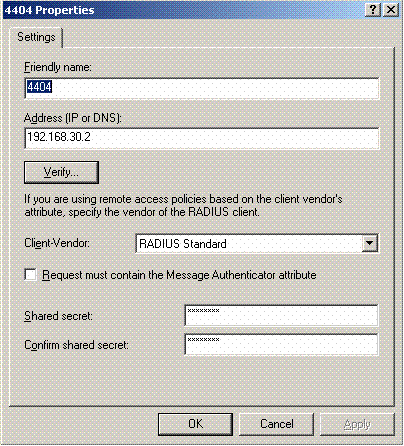
-
Configure a new Remote Access Policy for the Controller:

-
Edit the properties of the Controller Remote Access Policy. Make sure to add the NAS-Port Type - Wireless – IEEE 802.11:
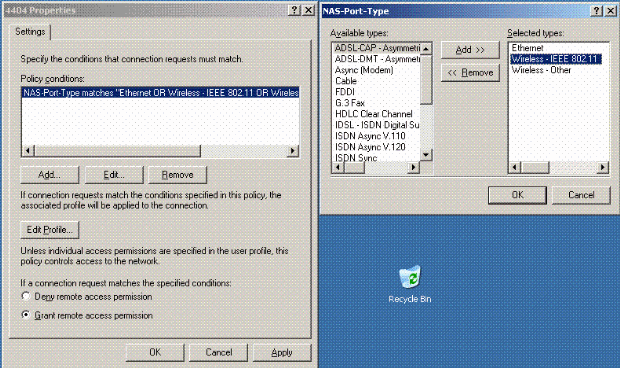
-
Click Edit Profile, click the Authentication tab, and check MS-CHAP v2 for Authentication:
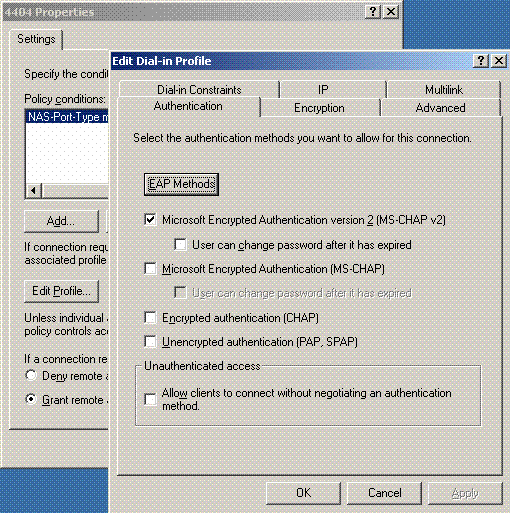
-
Click EAP Methods, select EAP Providers, and add PEAP as an EAP type:
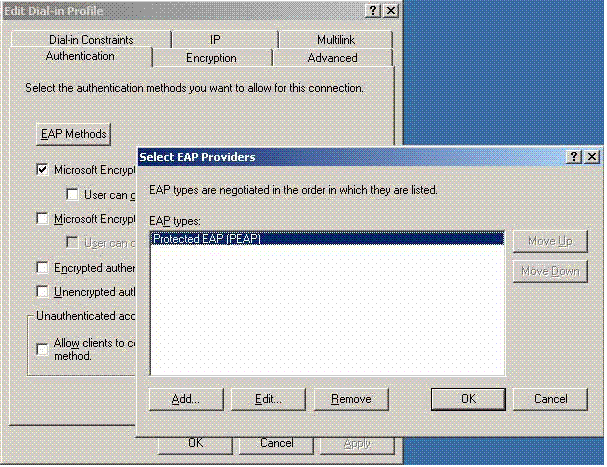
-
Click Edit on Select EAP Providers and choose from the pull down menu the server associated with your Active Directory user accounts and CA (e.g. tme.tme.com). Add the EAP type MSCHAP v2:
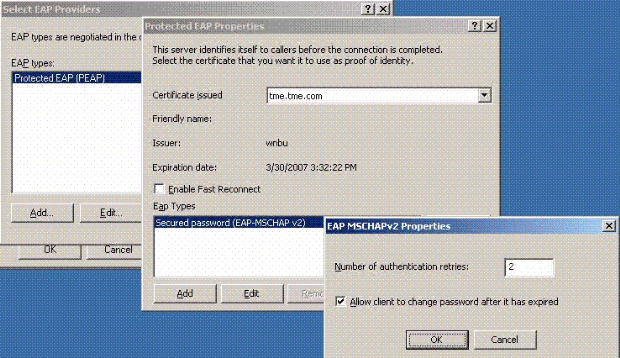
-
Click the Encryption tab, and check all encryption types for remote access:
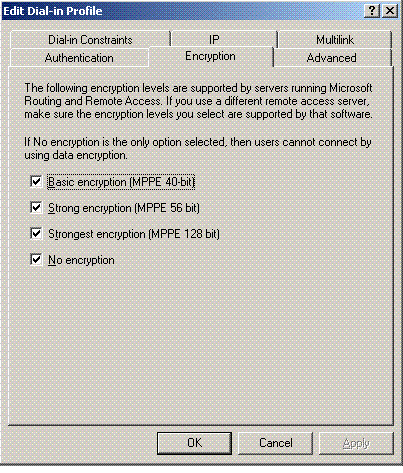
-
Click the Advanced tab, and add RADIUS Standard/Framed as the Service-Type:
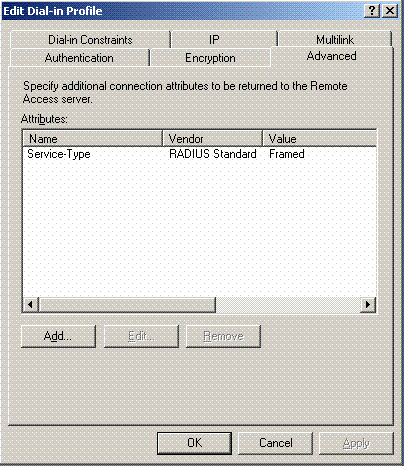
-
Click the IP tab, and check Client may request an IP address. This assumes you have DHCP enabled on a switch or WinServer.
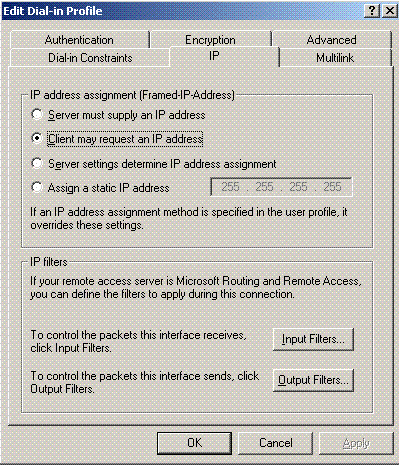
Microsoft Windows 2003 Domain Security Settings
Complete these steps in order to configure the Windows 2003 domain security settings:
-
Launch the Default Domain Security Settings manager, and create a new security policy for Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies.
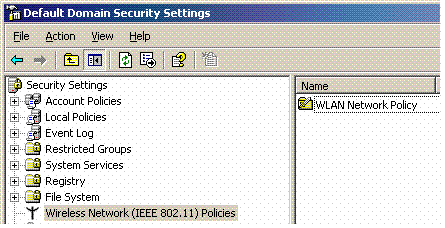
-
Open WLAN Network Policy Properties, and click Preferred Networks. Add a new preferred WLAN and type the name of your WLAN SSID, such as Wireless. Double click that new preferred network, and click the IEEE 802.1x tab. Choose PEAP as the EAP type:
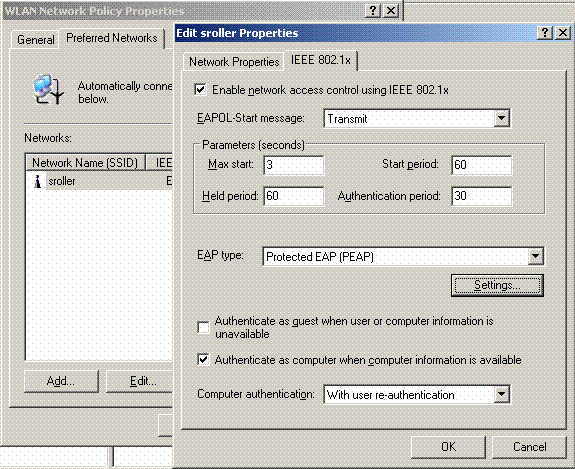
-
Click PEAP Settings, check Validate server certificate, and select the Trusted Root Cert installed on Certificate Authority. For testing purposes, uncheck the MS CHAP v2 box for Automatically use my Windows login and password.
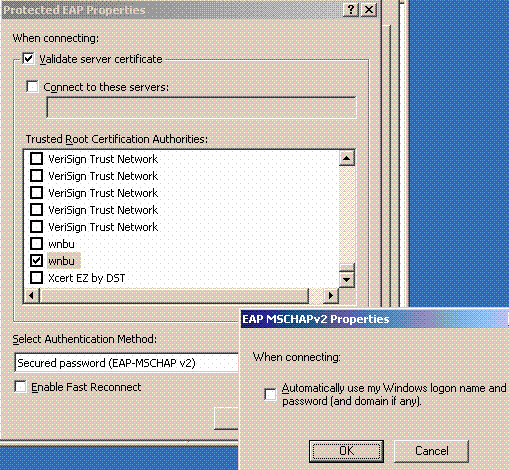
-
In the Windows 2003 Default Domain Security Settings manager window, create another new IP Security Policies on Active Directory policy, such as 4404.
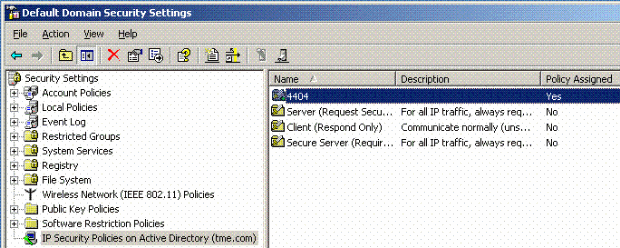
-
Edit the new 4404 policy properties, and click the Rules tab. Add a new filter rule - IP Filet List (Dynamic); Filter Action (Default Response); Authentication (PSK); Tunnel (None). Double click the newly created filter rule and select Security Methods:
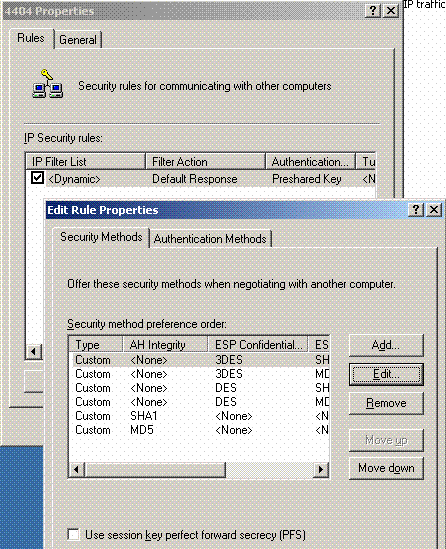
-
Click Edit Security Method, and click the Custom Settings radio button. Choose these settings.
Note: These settings must match the Controller RADIUS IPSec security settings.
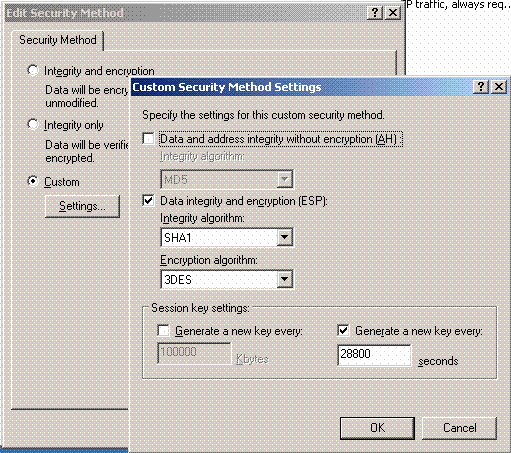
-
Click the Authentication Method tab under the Edit Rule Properties. Enter the same shared secret that you previously entered on the Controller RADIUS configuration.
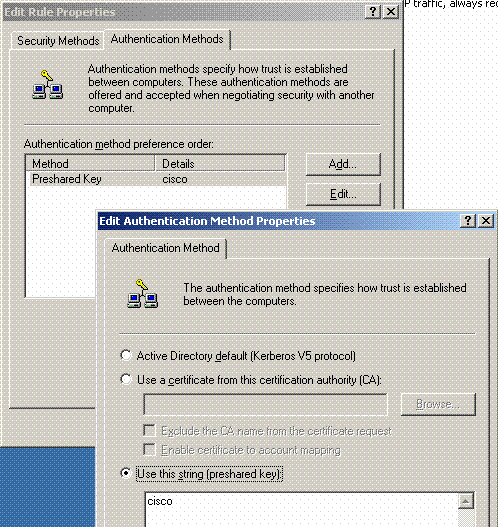
At this point, all configurations for the Controller, IAS and Domain Security Settings are completed. Save all configurations on both the Controller and WinServer and reboot all machines. On the WLAN client that is used for testing, install the root cert and configure for WPA2/PEAP. After the root cert is installed on the client, reboot the client machine. After all machines reboot, connect the client to the WLAN and capture these log events.
Note: A client connection is required in order to set up the IPSec connection between the Controller and WinServer RADIUS.
Windows 2003 System Log Events
A successful WLAN client connection configured for WPA2/PEAP with IPSec RADIUS enabled generates this System event on the WinServer:
192.168.30.105 = WinServer 192.168.30.2 = WLAN Controller
User TME0\Administrator was granted access. Fully-Qualified-User-Name = tme.com/Users/Administrator NAS-IP-Address = 192.168.30.2 NAS-Identifier = Cisco_40:5f:23 Client-Friendly-Name = 4404 Client-IP-Address = 192.168.30.2 Calling-Station-Identifier = 00-40-96-A6-D4-6D NAS-Port-Type = Wireless - IEEE 802.11 NAS-Port = 1 Proxy-Policy-Name = Use Windows authentication for all users Authentication-Provider = Windows Authentication-Server = <undetermined> Policy-Name = 4404 Authentication-Type = PEAP EAP-Type = Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2)
A successful Controller <> RADIUS IPSec connection generates this Security event on the WinServer logs:
IKE security association established. Mode: Data Protection Mode (Quick Mode) Peer Identity: Preshared key ID. Peer IP Address: 192.168.30.2 Filter: Source IP Address 192.168.30.105 Source IP Address Mask 255.255.255.255 Destination IP Address 192.168.30.2 Destination IP Address Mask 255.255.255.255 Protocol 17 Source Port 1812 Destination Port 0 IKE Local Addr 192.168.30.105 IKE Peer Addr 192.168.30.2 IKE Source Port 500 IKE Destination Port 500 Peer Private Addr Parameters: ESP Algorithm Triple DES CBC HMAC Algorithm SHA AH Algorithm None Encapsulation Transport Mode InboundSpi 3531784413 (0xd282c0dd) OutBoundSpi 4047139137 (0xf13a7141) Lifetime (sec) 28800 Lifetime (kb) 100000 QM delta time (sec) 0 Total delta time (sec) 0
Wireless LAN Controller RADIUS IPSec Success Debug Example
You can use the debug command debug pm ikemsg enable on the controller in order to verify this configuration. Here is an example.
(Cisco Controller) >debug pm ikemsg enable (Cisco Controller) >****** ERR: Connection timed out or error, calling callback TX MM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x0000000000000000 SA: doi=1 situation=0x1 Proposal 0, proto=ISAKMP, # transforms=1, SPI[0] Transform#=0 TransformId=1, # SA Attributes = 6 EncrAlgo = 3DES-CBC HashAlgo = SHA AuthMethod = Pre-shared Key GroupDescr =2 LifeType = secs LifeDuration =28800 VID: vendor id[16] = 0x8f9cc94e 01248ecd f147594c 284b213b VID: vendor id[16] = 0x27bab5dc 01ea0760 ea4e3190 ac27c0d0 VID: vendor id[16] = 0x6105c422 e76847e4 3f968480 1292aecd VID: vendor id[16] = 0x4485152d 18b6bbcd 0be8a846 9579ddcc VID: vendor id[16] = 0xcd604643 35df21f8 7cfdb2fc 68b6a448 VID: vendor id[16] = 0x90cb8091 3ebb696e 086381b5 ec427b1f VID: vendor id[16] = 0x7d9419a6 5310ca6f 2c179d92 15529d56 VID: vendor id[16] = 0x12f5f28c 457168a9 702d9fe2 74cc0100 RX MM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 SA: doi=1 situation=0x1 Proposal 1, proto=ISAKMP, # transforms=1 SPI[0] Transform payload: transf#=1 transfId=1, # SA Attributes = 6 EncrAlgo= 3DES-CBC HashAlgo= SHA GroupDescr=2 AuthMethod= Pre-shared Key LifeType= secs LifeDuration=28800 VENDOR ID: data[20] = 0x1e2b5169 05991c7d 7c96fcbf b587e461 00000004 VENDOR ID: data[16] = 0x4048b7d5 6ebce885 25e7de7f 00d6c2d3 VENDOR ID: data[16] = 0x90cb8091 3ebb696e 086381b5 ec427b1f TX MM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 KE: ke[128] = 0x9644af13 b4275866 478d294f d5408dc5 e243fc58... NONCE: nonce [16] = 0xede8dc12 c11be7a7 aa0640dd 4cd24657 PRV[payloadId=130]: data[20] = 0x1628f4af 61333b10 13390df8 85a0c0c2 93db6 c67 PRV[payloadId=130]: data[20] = 0xcf0bbd1c 55076966 94bccf4f e05e1533 191b1 378 RX MM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 KE: ke[128] = 0x9f0420e5 b13adb04 a481e91c 8d1c4267 91c8b486... NONCE: nonce[20] = 0x011a4520 04e31ba1 6089d2d6 347549c3 260ad104 PRV payloadId=130: data[20] = 0xcf0bbd1c 55076966 94bccf4f e05e1533 191b13 78 PRV payloadId=130: data[20] = 0x1628f4af 61333b10 13390df8 85a0c0c2 93db6c 67 TX MM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 ID: packet[8] = 0x01000000 c0a81e69 HASH: hash[20] = 0x04814190 5d87caa1 221928de 820d9f6e ac2ef809 NOTIFY: doi=1 proto=ISAKMP type=INITIAL_CONTACT, spi[0] NOTIFY: data[0] RX MM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 ID: packet[8] = 0x01000000 c0a81e69 HASH: hash[20] = 0x3b26e590 66651f13 2a86f62d 1b1d1e71 064b43f6 TX QM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 msgid=0x73915967 HASH: hash[20] = 0x00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 SA: doi=1 situation=0x1 Proposal 1, proto=ESP, # transforms=1, SPI[4] = 0xbb243261 Transform#=1 TransformId=3, # SA Attributes = 4 AuthAlgo = HMAC-SHA LifeType = secs LifeDuration =28800 EncapMode = Transport NONCE: nonce [16] = 0x48a874dd 02d91720 29463981 209959bd ID: packet[8] = 0x01110000 c0a81e02 ID: packet[8] = 0x01110714 c0a81e69 RX QM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 msgid=0x73915967 HASH: hash[20] = 0x2228d010 84c6014e dd04ee05 4d15239a 32a9e2ba SA: doi=1 situation=0x1 Proposal 1, proto=ESP, # transforms=1 SPI[4] = 0x7d117296 Transform payload: transf#=1 transfId=3, # SA Attributes = 4 LifeType= secs LifeDuration=28800 EncapMode= Transport AuthAlgo= HMAC-SHA NONCE: nonce[20] = 0x5c4600e4 5938cbb0 760d47f4 024a59dd 63d7ddce ID: packet[8] = 0x01110000 c0a81e02 ID: packet[8] = 0x01110714 c0a81e69 TX QM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 msgid=0x73915967 HASH: hash[20] = 0x0e81093e bc26ebf3 d367297c d9f7c000 28a3662d RX QM: 192.168.30.2 (Initiator) <-> 192.168.30.105 Icookie=0xaac8841687148dda Rc ookie=0x064bdcaf50d5f555 msgid=0x73915967 HASH: hash[20] = 0xcb862635 2b30202f 83fc5d7a 2264619d b09faed2 NOTIFY: doi=1 proto=ESP type=CONNECTED, spi[4] = 0xbb243261 data[8] = 0x434f4e4e 45435431
Ethreal Capture
Here is a sample Ethreal Capture.
192.168.30.105 = WinServer 192.168.30.2 = WLAN Controller 192.168.30.107 = Authenticated WLAN client No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info 1 0.000000 Cisco_42:d3:03 Spanning-tree-(for-bridges)_00 STP Conf. Root = 32769/00:14:a9:76:d7:c0 Cost = 4 Port = 0x8003 2 1.564706 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 3 1.591426 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 4 1.615600 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 5 1.617243 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 6 1.625168 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 7 1.627006 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 8 1.638414 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 9 1.639673 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 10 1.658440 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 11 1.662462 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 12 1.673782 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 13 1.674631 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 14 1.687892 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ESP ESP (SPI=0x7d117296) 15 1.708082 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ESP ESP (SPI=0xbb243261) 16 1.743648 192.168.30.107 Broadcast LLC U, func=XID; DSAP NULL LSAP Individual, SSAP NULL LSAP Command 17 2.000073 Cisco_42:d3:03 Spanning-tree-(for-bridges)_00 STP Conf. Root = 32769/00:14:a9:76:d7:c0 Cost = 4 Port = 0x8003 18 4.000266 Cisco_42:d3:03 Spanning-tree-(for-bridges)_00 STP Conf. Root = 32769/00:14:a9:76:d7:c0 Cost = 4 Port = 0x8003 19 5.062531 Cisco_42:d3:03 Cisco_42:d3:03 LOOP Reply 20 5.192104 192.168.30.101 192.168.30.255 NBNS Name query NB PRINT.CISCO.COM<00> 21 5.942171 192.168.30.101 192.168.30.255 NBNS Name query NB PRINT.CISCO.COM<00> 22 6.000242 Cisco_42:d3:03 Spanning-tree-(for-bridges)_00 STP Conf. Root = 32769/00:14:a9:76:d7:c0 Cost = 4 Port = 0x8003 23 6.562944 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.105 ARP Who has 192.168.30.105? Tell 192.168.30.2 24 6.562982 192.168.30.105 192.168.30.2 ARP 192.168.30.105 is at 00:40:63:e3:19:c9 25 6.596937 192.168.30.107 Broadcast ARP 192.168.30.107 is at 00:13:ce:67:ae:d2
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
05-Mar-2009 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)



















 Feedback
Feedback