Introduction
This document describes how to reset Cisco Emergency Responder (CER) database replication.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions; however, the version used to create this document is CER version 10.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
CER Database Replication Reset Procedure
Summary Steps
Step 1. Detele entries on the cerremote database table using the Command Line Interface (CLI) of the CER primary node.
Step 2. Restart services on the primary and secondary nodes.
Step 3. Reset dbreplication from the CLI of the CER primary node.
Step 4. Reboot the secondary node.
Step 5. Check replication
Step 6. Repeat the process if necessary
Detailed Steps
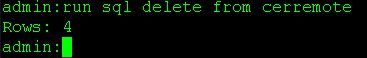
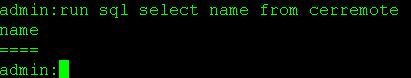
From the primary server's CLI delete the entries in the cerremote table
Use the command run sql delete from cerremote to delete the entries in the cerremote database table then confirm there are no entries in the cerremote table using the command run sql select name from cerremote.
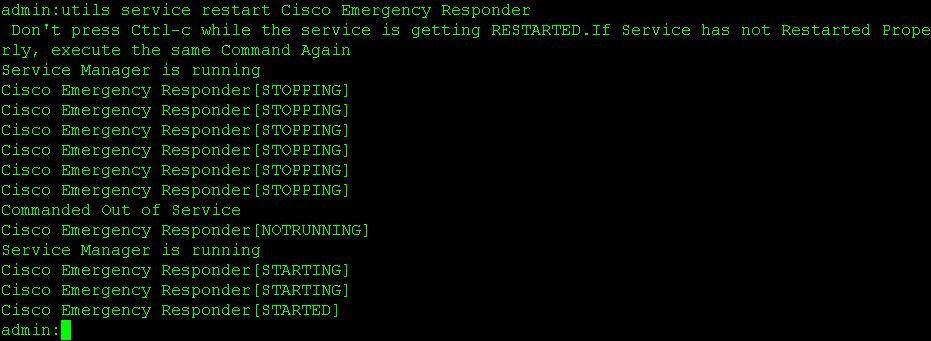
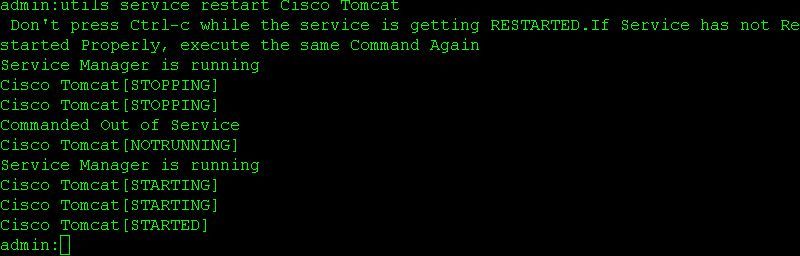
From both the Primary and Secondary servers' CLI restart services
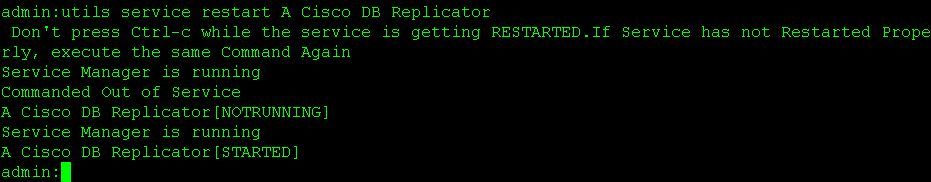
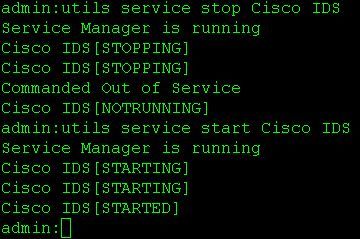
Use the commands below to restart services on both the primary and secondary nodes:
- utils service restart Cisco Emergency Responder
- utils service restart Cisco Tomcat
- utils service restart A Cisco DB Replicator
- utils service restart Cisco IDS or utils service stop Cisco IDS and utils service start Cisco IDS
From the primary server's CLI reset replication
From the CLI of the primary node use the command utils dbreplication reset all to reset replication in the cluster.
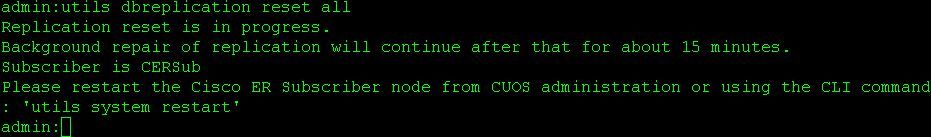
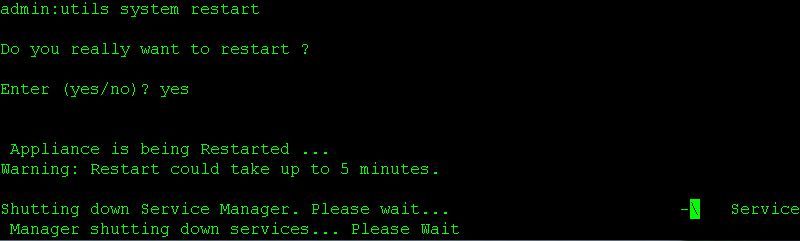
From the secondary server's CLI reboot the server
Once the reset finishes on the primary a prompt to reboot the secondary node is shown. At this point reboot the secondary from the CLI using the command utils system restart.
Check replication once the secondary is in full service
Once the secondary server is in full services check database replication from the CLI of the primary using the command utils dbreplication status.

There is a file view command in the output from the status command. Use the file view command to confirm there are no issues.
file view activelog er/trace/dbl/sdi/ReplicationStatus.YYYY_MM_DD_HH_MM_SS.out
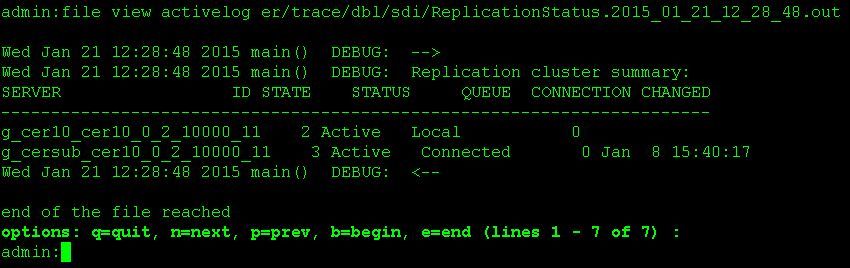
Replication can be noticed as not setting up properly if the following outputs are seen rather than Connected as seen above.
SERVER ID STATE STATUS QUEUE CONNECTION CHANGED
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
g_cer10_cer10_0_2_10000_11 2 Active Local 0
g_cersub_cer10_0_2_10000_11 3 Active Connecting 165527
SERVER ID STATE STATUS QUEUE CONNECTION CHANGED
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
g_cer10_cer10_0_2_10000_11 2 Active Local 0
g_cersub_cer10_0_2_10000_11 3 Active Disconnect 0
Repeat the process if necessary
If replication is still unsuccessful, you may need to repeat this procedure up to two more times. If replication is unsuccessful after performing this procedure 3 times, delete and reinstall the subscriber.
