Troubleshoot LISP VXLAN Fabric on Catalyst 9000 Series Switches
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the basic components of a LISP VXLAN based fabric and how to verify its operation.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Catalyst 9300
-
Catalyst 9400
-
Catalyst 9500
- Cisco IOS XE 17.9.3 or later
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
LISP VXLAN based fabric
The purpose to deploy a LISP VXLAN network is to be able to create an architecture where multiple Overlay networks, also known an Virtual Networks, are defined on top of an underlay network.
- The Underlay network in such topology would act primarily as a transport layer and would be unaware of the overlay topologies thare are run over it.
- Overlay networks can be added and removed withouth impact to the underlay network.
- The use of overlay networks effectively seperates the users from the underlay network.
Technologes Used to Build a LISP VXLAN Fabric
Locator Identity Separation Protocol (LISP)
- The LISP protocol is the control plane protocol used inside the fabric. It runs on all fabric devices to build the fabric and control how traffic is send through the fabric.
- LISP creates 2 address spaces. One is for the Routing Locator (RLOCs) which are used to advertise reachability. The other address space is for the Endpoint Identifiers (EID) , those are where endpoints reside and is used for the overlay.
- Within LISP the EIDs are advertised with a advertised RLOC. If an EID moves all that needs to be done is update the Routing Locator Associated with it.
- To reach an endpoint with LISP traffic towards an EID is to be encapsulated and tunneled towards the RLOC which de-encapsulates it and forwards it to the Endpoint.
Group-Based policies
- To be able to allow for segmentation inside a fabric group based policies is used.
- When group based policies are deployed traffic is classified with Secure Group rather then based upon the source/destination IP.
- This reduces the complexity of complex access-control lists. In stead of lists of IP addresses that need to be maintained IP addresses/subnets are assigned to a Secure Group Tag.
- On ingress into the fabric gets tagged with an SGT when traffic exits the fabric the destination of the frame is looked up for its SGT .
- With the use of a matrix the source and destination SGT is matched and a Secure Group ACL is applied to enforce the traffic as it leaves the fabric.
VXLAN Encapsulation
- Inside the fabric VXLAN is used to encapsulate all traffic
- The benefit to use VXLAN over the legacy LISP encapsulation is that it allows to encapsulate the entire Layer 2 frame, not just the Layer 3 frame. As the entire frame gets encapsulated it allows overlays to be both Layer 2 and Layer 3.
- VXLAN uses UDP with destination port 4789. This allows LISP VXLAN frames to be transported as well through device that would be unaware of the overlay topology.
- As VXLAN encapsulates the entire frame, it important to increase the MTU so no fragmentation would be needed as traffic is send between RLOCs. Any intermediate devices would need to support a larger MTU to transport the encapsulated frames.
Authentication
- To be able to assign endpoints to their respective resources authentication can be used.
- With protocols as 802.1x, MAB and Webauth endpoints can be authenticated and/or profiled against a Radius server and be granted access to the network based upon their authorization profiles.
- With their respective Radius attributes Endpoints can be assigned to their respective VLAN ,SGT and any other attributes to provide an endpoint/user network access.
Key Components in LISP VXLAN Fabric
Control Plane node
- holds the LISP Map Server and Map Resolver functionality.
- All other fabric devices query the Control Plane node for the location of EID and send registrations for their EID to the Control Plane nodes.
- This gives the Control Plane nodes a complete view of the fabric with regards to behind what RLOC the various EID are.
Border Nodes
- Provides connectivity outside the fabric either to other fabrics or to the outside world.
- Internal borders import routes into the fabric and register them with the Control Plane nodes.
- External borders connect to the outside world and provide a default path outside the fabric for unknown IP destinations.
Edge nodes
- These nodes provide connectivity to endpoints inside the fabric.
- In the definition of LISP these would be XTRs as they would perform both the function of an Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR) and Egress Tunnel Router(ETR).
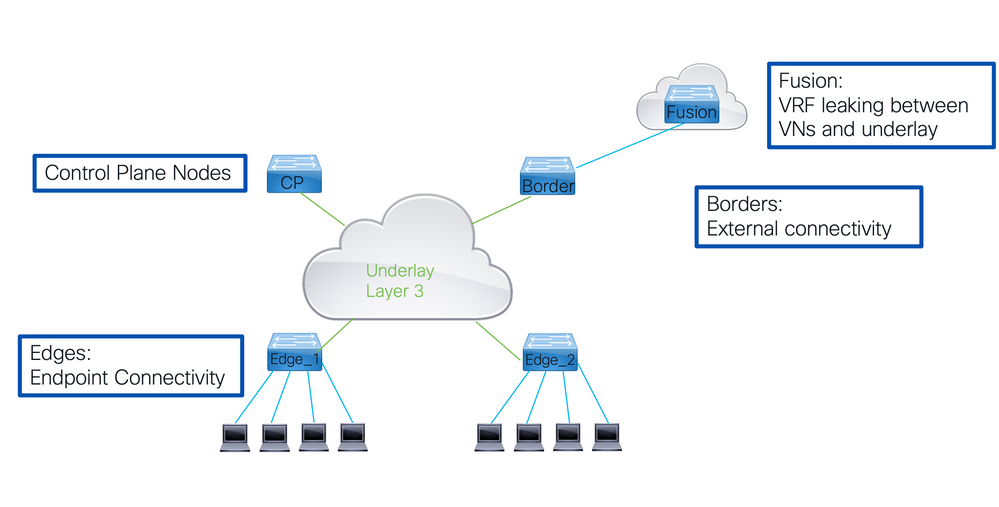
Nodes are not limited to just perform one tasks.
- They can perform a combination or even all functions inside the fabric.
- When a Border Node and Control Plane node reside on one device they referred to as colocated.
- If that node also provides the Edge functionality it to be referred to as a Fabric In A Box (FIAB).
Borders provide handoffs to the rest of the network use VRF lite.
- Each overlay or a virtual network is associated with a VRF instance on the border node.
- To connect those various VRFs together a Fusion router is used. That fusion router is not part of the Fabric itself, but is crucial to the operation to be able to connect the Overlay networks to the fabric.
Another important concept within a LISP VXLAN fabric is the concept to use an IP Anycast.
- This means that on all Edge devices the IP address and its MAC addresses for the Switched Virtual Interfaces (SVI) are replicated.
- Every Edge has the same configuration on the SVI with regards to IPv4,IPv6 and MAC addresses.
- To troubleshoot this imposes some challenges.
- To test reachability with ping works with local connected devices.
- To reach remote destinations through the LISP VXLAN fabric does not return a response as the device that sends a response sends this as well to the anycast IP address which gets punted to the local fabric device which is not aware of which other fabric node has send the original ping.
Endpoint Registration
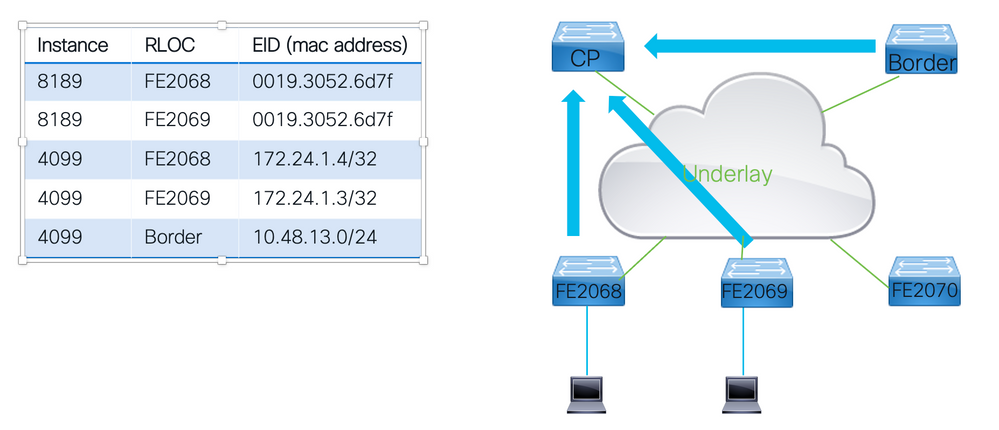
For a LISP VXLAN fabric to work it is crucial that the Control Plane node has awareness of how all endpoints are reachable through the fabric.
- For the control plane to learn about all EIDs in the network it depends on all other fabric devices to register all EID it knows about with the control plane.
- A fabric node sends LISP map-register messages to the control plane node. Amongst the information that is advertised with the map-register message.
Important Information
LISP Instance Identifier:
- This identifier is carried through the fabric and indicates what Virtual Network is to be used.
- Within a LISP VXLAN fabric per Layer 3 Overlay one instance is used per used VLAN in the fabric there also a Layer 2 Instance.
Endpoint Identified (EID):
- If this is a layer 2 or layer 3 Instance this is the MAC address, IP host route (/32 or /128) or an IP subnet registered
Routing Locator (RLOC):
- This the fabric node own IP address with which it advertises reachability where other fabric devices send encapsulated traffic that would need to reach the EID.
Proxy flag:
- When this flag is set it allows the Control Plane node to respond to map-requests from other fabric nodes directly , without the proxy flag set all requests to be forwarded to the fabric node that regitered the EID.
Registration Steps
Step 1: Fabric Devices learn about End Point Identifiers. This can be through either configuration, routing protocols or when it learned on the fabric devices.
Step 2: Fabric Devices register the learned Endpoints with each known and reachable Control Plane nodes inside the fabric.
Step 3: Control Plane nodes maintain a table of registered EIDs with the related Instance ID,the RLOC and the EID learned
Verify
1.1 MAC Address Learning
For Layer 2 Instances the EID that are used are the MAC addresses that are learned inside the associated VLAN. Fabric Edges learn the Layer 2 Addresses through standard methods on the switches.
Locate the VLAN Associated with a specific Layer 2 Instance id the configuration can be reviewed or the command
Use "show lisp instance-id <instance> ethernet"
FE2068#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet
Instance ID: 8191
Router-lisp ID: 0
Locator table: default
EID table: Vlan 150
Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR): enabled
Egress Tunnel Router (ETR): enabled
..
Site Registration Limit: 0
Map-Request source: derived from EID destination
ITR Map-Resolver(s): 172.30.250.19
ETR Map-Server(s): 172.30.250.19
As seen in the output, the instance-id 8191 is associated with VLAN 150. That results in all MAC-addresses inside the vlan to be registered with LISP and become part of the LISP VXLAN fabric.
FE2068#show mac address-table vlan 150
Mac Address Table
-------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports
---- ----------- -------- -----
150 0000.0c9f.f18e STATIC Vl150
150 0050.5693.8930 DYNAMIC Gi1/0/1
150 2416.9db4.33fd STATIC Vl150
150 0019.3052.6d7f CP_LEARN L2LI0
Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 3
Total Mac Addresses installed by LISP: REMOTE: 1
Static entries with interface Vl150 are the MAC addresses of the Switch Virtual Interface (interface vlan 150).
- Those MAC addresses are not registered with the control plane node as they would be the same on all edge devices.
- The CP_LEARN entry displayed are entries that are learned through the fabric. For all other entries if they are dynamic or static they are to be registered with the control plane node.
Once they are learned through their respective means they appear in the lisp database outputs, this output contains all local entries on this fabric device.
FE2068#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet database
LISP ETR MAC Mapping Database for LISP 0 EID-table Vlan 150 (IID 8191), LSBs: 0x1
Entries total 3, no-route 0, inactive 0, do-not-register 2
0000.0c9f.f18e/48, dynamic-eid Auto-L2-group-8191, do not register, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 14:56:40, Last-change: 14:56:40
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
0050.5693.8930/48, dynamic-eid Auto-L2-group-8191, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 14:03:06, Last-change: 14:03:06
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
2416.9db4.33fd/48, dynamic-eid Auto-L2-group-8191, do not register, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 14:56:50, Last-change: 14:56:50
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
For all known local MAC addresses that are shown in the database the Locator is shown.
- This is the Locator that is to be used to register this entry with the control plane node.
- It also indicated the state of the Locator.The 2 MAC addresses that belonged to the Switches SVI are also shown but are displayed with the "do not register" flag that prevents them to be registered.
- The remote entry that was seen in the show mac address table command is not a local MAC address and as such do not show up under the lisp database.
For a Layer 2 Instance not only the Layer 2 MAC addresses are learned as EID, there also a need to learn address resolution information from ARP and ND frames.
- This for the LISP VXLAN fabric to be able to forward those frames as they are normally flooded inside the VLAN.
- As a Layer 2 Instance-ID does not always have the ability to flood there another mechanism that would allow Endpoints to resolve Address Resolution information for other endpoints in the same instance. For this the fabric devices learn and register this information that gets learned locally by Device-Tracking .
- This is then registered with the Control Plane Nodes as well. Due to ND or ARP snooping those packets are punted to the CPU to trigger a request to the Control Plane nodes to see if there any known MAC address associated.
- If a positive response comes back the ARP/ND packets are rewritten so that the destination mac-address is changed from broadcast or multicast to the unicast mac address.
- This rewritten packet can then be forwarded through the LISP VXLAN fabric as a unicast frame.
To see the Address Resolution information that is known on the switch the command show device-tracking database can be used.
- This does show all mappings known by device-tracking.
- The switches own IP addresses are labelled as L(Local) and needs to be present in the device-tracking database.
Remote entries also are displayed in this output.
- As they are resolved after it has been snooped the ND or ARP request they are put into the device-tracking database with a Link Layer Address of 0000.0000.00fd.
- The moment they are resolved the information is changed towards the resolved mac address and the port is changed to Tu0.
Display the device tracking database
FE2068#show device-tracking database vlanid 150
vlanDB has 6 entries for vlan 150, 3 dynamic
Codes: L - Local, S - Static, ND - Neighbor Discovery, ARP - Address Resolution Protocol, DH4 - IPv4 DHCP, DH6 - IPv6 DHCP, PKT - Other Packet, API - API created
Preflevel flags (prlvl):
0001:MAC and LLA match 0002:Orig trunk 0004:Orig access
0008:Orig trusted trunk 0010:Orig trusted access 0020:DHCP assigned
0040:Cga authenticated 0080:Cert authenticated 0100:Statically assigned
Network Layer Address Link Layer Address Interface vlan prlvl age state Time left
ARP 172.24.1.3 0050.5693.8930 Gi1/0/1 150 0005 31s REACHABLE 213 s try 0
RMT 172.24.1.4 0050.5693.3120 Tu0 150 0005 51s REACHABLE
API 172.24.1.99 0000.0000.00fd Gi1/0/1 150 0000 5s UNKNOWN try 0 (25 s)
ND FE80::1AE4:8804:5B8F:50F6 0050.5693.8930 Gi1/0/1 150 0005 127s REACHABLE 115 s try 0
ND 2001:DB8::E70B:E8E1:E368:BDB7 0050.5693.8930 Gi1/0/1 150 0005 137s REACHABLE 110 s try 0
L 172.24.1.254 0000.0c9f.f18e Vl150 150 0100 1078mn REACHABLE
L 2001:DB8::1 0000.0c9f.f18e Vl150 150 0100 1077mn REACHABLE
L FE80::200:CFF:FE9F:F18E 0000.0c9f.f18e Vl150 150 0100 1077mn REACHABLE
Display the locally registered mappings with the command 'show lisp instance-id <instance> ethernet database address-resolution'
FE2068#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet database address-resolution
LISP ETR Address Resolution for LISP 0 EID-table Vlan 150 (IID 8191)
(*) -> entry being deleted
Hardware Address L3 InstID Host Address
0000.0c9f.f18e 4099 FE80::200:CFF:FE9F:F18E/128
4099 2001:DB8::1/128
0050.5693.8930 4099 172.24.1.3/32
4099 2001:DB8::E70B:E8E1:E368:BDB7/128
4099 FE80::1AE4:8804:5B8F:50F6/128
1.2 Dynamic IP Addresses Learning
On the fabric devices on an IP layer a Virtual network is formed by associating a LISP Instance-id with a VRF.
- This VRF is then configured under the various Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) and they become part of the Layer 3 Overlay network
- In most cases these SVI also belong to VLANs that are registered with their respective Layer 2 Instances.
Find the mapping between VRF and LISP Instance id with command 'show lisp instance-id <instance> ipv4'
FE2068#sh lisp instance-id 4099 ipv4
Instance ID: 4099
Router-lisp ID: 0
Locator table: default
EID table: vrf Fabric_VN_1
Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR): enabled
Egress Tunnel Router (ETR): enabled
..
ITR Map-Resolver(s): 172.30.250.19
ETR Map-Server(s): 172.30.250.19

Note: This command also can be used to verify the various functions that could be enabled for this Instance as well it shows the used Control Plane nodes inside the LISP VXLAN fabric
Once an Layer 3 Instance is created and linked to a VRF an LISP 0 <instance-id> interface is created and is visible in the running configuration and under show vrf.
- This interface does NOT need to be created manually and would typically needs no configuration (apart from Multicast Configuration when Underlay Multicast is used).
FE2068#show vrf Fabric_VN_1
Name Default RD Protocols Interfaces
Fabric_VN_1 <not set> ipv4,ipv6 LI0.4099
Vl150
Vl151
Unlike with Ethernet frames where all MAC addresses in a VLAN is used for IP there is a need for IP addresses to be inside a Dynamic EID range to be learned.
Display a LISP instance
FE2068#sh lisp instance-id 4099 dynamic-eid
LISP Dynamic EID Information for router 0, IID 4099, EID-table VRF "Fabric_VN_1"
Dynamic-EID name: Fabric_VN_Subnet_1_IPv4
Database-mapping EID-prefix: 172.24.1.0/24, locator-set rloc_hosts
Registering more-specific dynamic-EIDs
Map-Server(s): none configured, use global Map-Server
Site-based multicast Map-Notify group: none configured
Number of roaming dynamic-EIDs discovered: 2
Last dynamic-EID discovered: 172.24.1.3, 21:17:45 ago
Dynamic-EID name: Fabric_VN_Subnet_1_IPv6
Database-mapping EID-prefix: 2001:DB8::/64, locator-set rloc_hosts
Registering more-specific dynamic-EIDs
Map-Server(s): none configured, use global Map-Server
Site-based multicast Map-Notify group: none configured
Number of roaming dynamic-EIDs discovered: 2
Last dynamic-EID discovered: 2001:DB8::E70B:E8E1:E368:BDB7, 21:17:44 ago
Dynamic-EID name: Fabric_VN_Subnet_2_IPv4
Database-mapping EID-prefix: 172.24.2.0/24, locator-set rloc_hosts
Registering more-specific dynamic-EIDs
Map-Server(s): none configured, use global Map-Server
Site-based multicast Map-Notify group: none configured
Number of roaming dynamic-EIDs discovered: 2
Last dynamic-EID discovered: 172.24.2.2, 21:55:56 ago
IP address that is outside these defined ranges are deemed ineligible for the fabric and are not put into the LISP databases and not registered with the control plane nodes.
FE2068#show lisp instance-id 4099 ipv4 database
LISP ETR IPv4 Mapping Database for LISP 0 EID-table vrf Fabric_VN_1 (IID 4099), LSBs: 0x1
Entries total 4, no-route 0, inactive 0, do-not-register 2
172.24.1.3/32, dynamic-eid Fabric_VN_Subnet_1_IPv4, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 21:28:51, Last-change: 21:28:51
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
172.24.1.254/32, dynamic-eid Fabric_VN_Subnet_1_IPv4, do not register, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 22:22:35, Last-change: 22:22:35
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
172.24.2.2/32, dynamic-eid Fabric_VN_Subnet_2_IPv4, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 22:07:03, Last-change: 22:07:03
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
172.24.2.254/32, dynamic-eid Fabric_VN_Subnet_2_IPv4, do not register, inherited from default locator-set rloc_hosts
Uptime: 22:22:35, Last-change: 22:22:35
Domain-ID: local
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.44 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
The output shows all locally known IP address information.
- For hosts these are typically host routes (/32 or /128), but they could also be subnets if those would have been imported into the LISP databased on the border node.
- The IP addresses from the SVI itself are flagged as "do not register" . This to avoid all fabric devices to register the Anycast IP address with the control plane node.
CP_BN_2071#sh lisp instance-id 4099 ipv4 database
LISP ETR IPv4 Mapping Database for LISP 0 EID-table vrf Fabric_VN_1 (IID 4099), LSBs: 0x1
Entries total 2, no-route 0, inactive 0, do-not-register 0
0.0.0.0/0, locator-set rloc_border, auto-discover-rlocs, default-ETR
Uptime: 2d17h, Last-change: 2d17h
Domain-ID: local
Metric: 0
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.19 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
10.48.13.0/24, route-import, inherited from default locator-set rloc_border, auto-discover-rlocs
Uptime: 2d17h, Last-change: 2d16h
Domain-ID: local, tag: 65101
Service-Insertion: N/A
Locator Pri/Wgt Source State
172.30.250.19 10/10 cfg-intf site-self, reachable
1.3 Registration of EID with the Control Plane
Endpoint Registration in a LISP VXLAN based fabric is through LISP reliable registration. This means that all registrations are done through an established TCP session , the LISP session. From every fabric device a LISP session is established with each of the control plane nodes in the fabric.Through this LISP session then all registrations does occur. If multiple Control Plane nodes are present inside a fabric they all are to be used to register EIDs with.
The state is Down when there is not anything to register on the fabric device, which typically would only occur on External borders
that do not register any IP ranges with the Control Plane node or on Edge devices without any endpoint
The registration of EID happens through LISP Registration messages
that get send to all configured control plane nodes.
To see the LISP session on a fabric device the command show lisp session can be used.
It does show the State of the session and the time it been Up.
FE2068#show lisp session
Sessions for VRF default, total: 1, established: 1
Peer State Up/Down In/Out Users
172.30.250.19:4342 Up 22:06:07 9791/6531 10
The LISP session shown as Down can occur on devices that do not have any EID to register with the Control Plane node.
Typically that would be border nodes that do not import routes into the fabric or Edge devices without any endpoints connected.
Display more detailed information about a LISP session with the command 'show lisp session vrf default <ip address>'
FE2068#show lisp vrf default session 172.30.250.19
Peer address: 172.30.250.19:4342
Local address: 172.30.250.44:13255
Session Type: Active
Session State: Up (22:07:24)
Messages in/out: 9800/6537
Bytes in/out: 616771/757326
Fatal errors: 0
Rcvd unsupported: 0
Rcvd invalid VRF: 0
Rcvd override: 0
Rcvd malformed: 0
Sent deferred: 1
SSO redundancy: N/A
Auth Type: None
Accepting Users: 0
Users: 10
Type ID In/Out State
Policy subscription lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv4 2/1 Established
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv6 1/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 8191 AFI MAC 2/0 Idle
Pubsub subscriber lisp 0 IID 8192 AFI MAC 0/0 Idle
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv4 6/5 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 4099 AFI IPv6 1/3 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 8191 AFI MAC 9769/6517 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 8192 AFI MAC 2/6 TCP
ETR Reliable Registration lisp 0 IID 16777214 AFI IPv4 4/4 TCP
Capability Exchange N/A 1/1 waiting
This detailed output of the session shows which Instances are active with EID that are registered with the control plane nodes.
CP_BN_2071#show lisp session
Sessions for VRF default, total: 7, established: 4
Peer State Up/Down In/Out Users
172.30.250.19:4342 Up 22:10:52 1198618/1198592 4
172.30.250.19:49270 Up 22:10:52 1198592/1198618 3
172.30.250.30:25780 Up 22:10:38 6534/9805 6
172.30.250.44:13255 Up 22:10:44 6550/9820 7
Whe one looks at the number of sessions on a Control Plane node shows typically more sessions that are Up.
- If this is a colocated Border/CP node there also an LISP session established towards itself.
- In this case there is an session from 172.30.250.19:4342 to 172.30.250.19:49270.
- Through this session the Border component registers its EID with the Control Plane Node.
1.4 Control Plane Information
With the information that is provided by the Fabric Devices through registration the control plane node is able to build a complete view of the fabric. Per Instance-id it maintains a table with the learned EIDs and its associated Routing Locators.
Display this for the Layer 3 instances the command show lisp site
CP_BN_2071#show lisp site
LISP Site Registration Information
* = Some locators are down or unreachable
# = Some registrations are sourced by reliable transport
Site Name Last Up Who Last Inst EID Prefix
Register Registered ID
site_uci never no -- 4097 0.0.0.0/0
never no -- 4097 172.23.255.0/24
never no -- 4097 172.24.255.0/24
never no -- 4099 0.0.0.0/0
00:00:00 yes# 172.30.250.19:49270 4099 10.48.13.0/24
never no -- 4099 172.23.1.0/24
never no -- 4099 172.24.1.0/24
21:35:06 yes# 172.30.250.44:13255 4099 172.24.1.3/32
22:11:46 yes# 172.30.250.30:25780 4099 172.24.1.4/32
never no -- 4099 172.24.2.0/24
22:11:52 yes# 172.30.250.44:13255 4099 172.24.2.2/32
This command shows all registered EID and the last who registered the EID. It important to note this typically would also be the RLOC that be in use, but this is can differ. Also EID 's can be registered with multiple RLOCs .
To display the complete detail the command include the EID and the instance
CP_BN_2071#show lisp site 172.24.1.3/32 instance-id 4099
LISP Site Registration Information
Site name: site_uci
Description: map-server
Allowed configured locators: any
Requested EID-prefix:
EID-prefix: 172.24.1.3/32 instance-id 4099
First registered: 21:35:53
Last registered: 21:35:53
Routing table tag: 0
Origin: Dynamic, more specific of 172.24.1.0/24
Merge active: No
Proxy reply: Yes
Skip Publication: No
Force Withdraw: No
TTL: 1d00h
State: complete
Extranet IID: Unspecified
Registration errors:
Authentication failures: 0
Allowed locators mismatch: 0
ETR 172.30.250.44:13255, last registered 21:35:53, proxy-reply, map-notify
TTL 1d00h, no merge, hash-function sha1
state complete, no security-capability
nonce 0x6ED7000E-0xD4C608C5
xTR-ID 0x88F15053-0x40C0253D-0xAE5EA874-0x2551DB71
site-ID unspecified
Domain-ID local
Multihoming-ID unspecified
sourced by reliable transport
Locator Local State Pri/Wgt Scope
172.30.250.44 yes up 10/10 IPv4 none

Note: In detailed output a few things are important to be aware of:
- Proxy, with this set the Control Plane node does respond directly to a Map-request. In traditional LISP a map-request is forwarded to the XTR that registered the EID but with Proxy set the control plane node does directly respond
- TTL, this is the Time To Live of the EID registration. By default this is 24 hours
- ETR information, this relates to the fabric device that has send the EID registration
- RLOC information, this is the RLOC to be used to reach the EID. This also contains state information as in up/down. if the RLOC is down it is not be used. It contains as well a weight and priority which can be used when multiple RLOCs exist for an EID to give preference to one of them.
To see the registration history on the Control Plane node the command show lisp server registration history can be used.
- It gives an overview of EID that have been registered and de-registered.
Display registration history
CP_BN_2071#show lisp server registration-history last 10
Map-Server registration history
Roam = Did host move to a new location?
WLC = Did registration come from a Wireless Controller?
Prefix qualifier: + = Register Event, - = Deregister Event, * = AR register event
Timestamp (UTC) Instance Proto Roam WLC Source
EID prefix / Locator
*Mar 24 20:49:51.490 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
+ 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.491 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
- 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.621 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
+ 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.622 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
- 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.752 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
+ 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.754 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
- 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.884 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
+ 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:51.886 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
- 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:52.017 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
+ 10.48.13.0/24
*Mar 24 20:49:52.019 4099 TCP No No 172.30.250.19
- 10.48.13.0/24
Display the registered EID for Ethernet the command is show lisp instance-id <instance> ethernet server (This gives a similar output like for Layer 3)
CP_BN_2071#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet server
LISP Site Registration Information
* = Some locators are down or unreachable
# = Some registrations are sourced by reliable transport
Site Name Last Up Who Last Inst EID Prefix
Register Registered ID
site_uci never no -- 8191 any-mac
00:00:04 yes# 172.30.250.44:13255 8191 0019.3052.6d7f/48
21:36:41 yes# 172.30.250.44:13255 8191 0050.5693.8930/48
22:13:20 yes# 172.30.250.30:25780 8191 0050.5693.f1b2/48
Append the MAC address to get more detailed information about a registration
CP_BN_2071#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet server 0019.3052.6d7f
LISP Site Registration Information
Site name: site_uci
Description: map-server
Allowed configured locators: any
Requested EID-prefix:
EID-prefix: 0019.3052.6d7f/48 instance-id 8191
First registered: 22:14:38
Last registered: 00:00:03
Routing table tag: 0
Origin: Dynamic, more specific of any-mac
Merge active: No
Proxy reply: Yes
Skip Publication: No
Force Withdraw: No
TTL: 1d00h
State: complete
Extranet IID: Unspecified
Registration errors:
Authentication failures: 0
Allowed locators mismatch: 0
ETR 172.30.250.30:25780, last registered 00:00:03, proxy-reply, map-notify
TTL 1d00h, no merge, hash-function sha1
state complete, no security-capability
nonce 0x0465A327-0xA3A2974C
xTR-ID 0x280403CF-0x598BAAF1-0x3E70CE52-0xE8F09E6E
site-ID unspecified
Domain-ID local
Multihoming-ID unspecified
sourced by reliable transport
Locator Local State Pri/Wgt Scope
172.30.250.30 yes up 10/10 IPv4 none
Append 'registration history' to see the registration history for ethernet EID

Note: This command is very useful when devices roam in the fabric to see where and when the MAC address has been registered
CP_BN_2071#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet server registration-history
Map-Server registration history
Roam = Did host move to a new location?
WLC = Did registration come from a Wireless Controller?
Prefix qualifier: + = Register Event, - = Deregister Event, * = AR register event
Timestamp (UTC) Instance Proto Roam WLC Source
EID prefix / Locator
*Mar 24 20:47:10.291 8191 TCP Yes No 172.30.250.44
+ 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:10.296 8191 TCP No No 172.30.250.30
- 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:18.644 8191 TCP Yes No 172.30.250.30
+ 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:18.647 8191 TCP No No 172.30.250.44
- 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:20.700 8191 TCP Yes No 172.30.250.44
+ 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:20.702 8191 TCP No No 172.30.250.30
- 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:31.914 8191 TCP Yes No 172.30.250.30
+ 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:31.918 8191 TCP No No 172.30.250.44
- 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:40.206 8191 TCP Yes No 172.30.250.44
+ 0019.3052.6d7f/48
*Mar 24 20:47:40.210 8191 TCP No No 172.30.250.30
- 0019.3052.6d7f/48
To see the registered Address Resolution information on the Control Plane node the command is appended with address-resolution.
- This only shows the mappings between the MAC Address and their Layer 3 information and is to be used primarily for the Fabric Edges to rewrite the layer 2 destination MAC addresses from broadcast/multicast to unicast.
- The RLOC that corresponds to that Layer 2 MAC address would be resolved separately .
Append 'address-resolution' to see registered Address Resolution information on the Control Plane node
CP_BN_2071#sh lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet server address-resolution
Address-resolution data for router lisp 0 instance-id 8191
L3 InstID Host Address Hardware Address
4099 172.24.1.3/32 0050.5693.8930
4099 172.24.1.4/32 0050.5693.f1b2
4099 2001:DB8::E70B:E8E1:E368:BDB7/128 0050.5693.8930
4099 2001:DB8::F304:BCCD:6BF3:BFAF/128 0050.5693.f1b2
4099 FE80::3EE:5111:BA77:E37D/128 0050.5693.f1b2
4099 FE80::1AE4:8804:5B8F:50F6/128 0050.5693.8930

Note: Even though the link local IPv6 Addresses do not match the IPv6 Dynamic EID they are to be learned for Address resolution and would this show up on the Control Plane node. These would not be registered themselves under the Layer 3 Instance ID, but are available for Address Resolution.
Resolve Remote Destinations
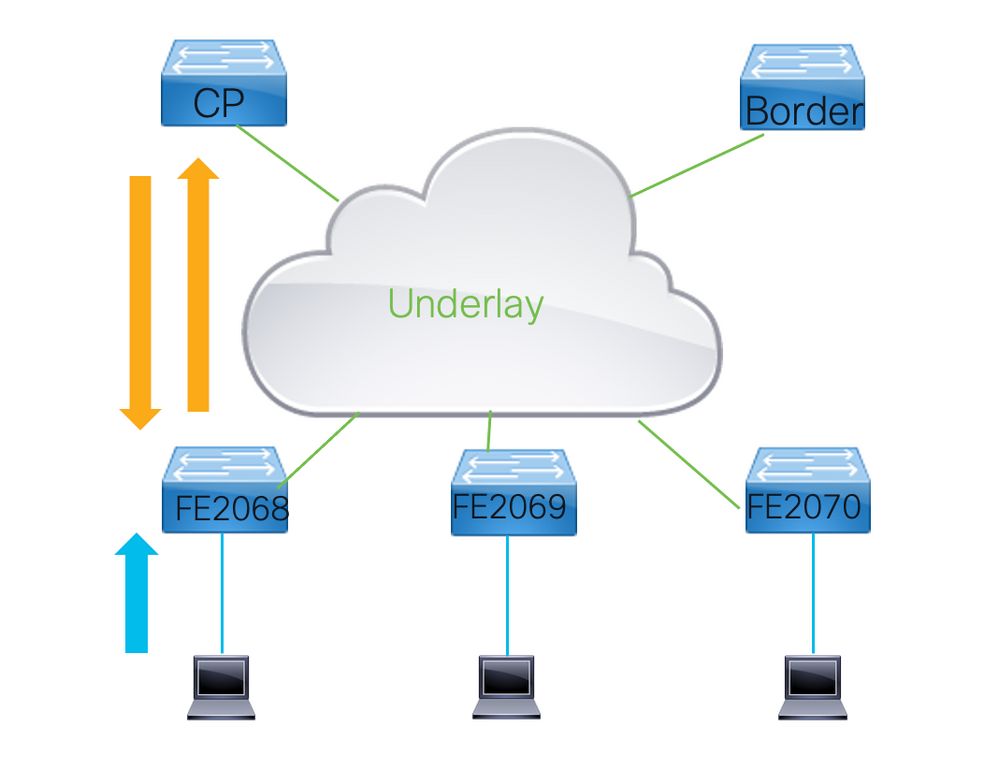
For traffic to be forwarded through a LISP VXLAN fabric the RLOC of a destination needs to be resolved. Within an LISP VXLAN fabric this is done with the use of a map-cache from which information is put into the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) of the Fabric device.
With LISP VXLAN fabrics map-caches are to be triggered due to data signals.
- This means traffic is forwarded to the CPU and the CPU creates a map-request towards the Control Plane node to query for the RLOC information to which frames towards that EID would need to be sent.
- The control plan when it receives a map-request would either provide the Routing Locator information associated with this EID or it would send back a negative map-reply.
- When it sends a negative map-reply the control plane node would not just indicate that the requested EID is not known, it would offer the entire block of EIDs that this EID would belong to that it would not have any registration for.
With the the information inside the map-reply from the control plane node the map-cache is updated.
- The TTL for map-replies is typically 24 hours. (For negative map-replies it typically only 15 minutes).
- For Ethernet EID the negative map-replies are not put into the map-cache. (This is only done for Layer 3 Instances).
2.1 Ethernet map-cache
Display the Ethernet map-cache with command show lisp instance-id <instance> map-cache
FE2067#show lisp instance-id 8191 ethernet map-cache
LISP MAC Mapping Cache for LISP 0 EID-table Vlan 150 (IID 8191), 1 entries
0019.3052.6d7f/48, uptime: 00:00:07, expires: 23:59:52, via map-reply, complete
Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID
172.30.250.44 00:00:07 up 10/10 -
This command shows the remote MAC address entry that would have been resolved.
- To trigger a map-cache entry for an Ethernet instance traffic needs to be send to a unknown destination.
- That would result in the Fabric Device to try and resolve it through LISP.
- Once it is learned via a map-reply it would be put in the map-cache and subsequent frames towards that layer 2 destination would be send directly to the Routing Locator learned.
Optionally in Layer 2 Instances is the use of flood of BUM traffic .
- LISP/VXLAN does not flood traffic by default as it uses an overlay technology but an IP Multicast group can be configured in the underlay network (GRT) through which layer 2 frames could be flooded.
Display the broadcast underlay group address
FE2068#sh run | sec instance-id 8191
instance-id 8191
remote-rloc-probe on-route-change
service ethernet
eid-table vlan 150
broadcast-underlay 239.0.1.19
database-mapping mac locator-set rloc_hosts
exit-service-ethernet
!
exit-instance-id
2.2 IP Map Cache
For Layer 3 instances the map-cache information is similar to ethernet build by traffic send to the CPU to signal causes a map-request to be sent.
- However, for Layer 3 packets only get punted to CPU to signal when this is to be setup. This is done by the map-cache command that is configured. For IPv4 this is 0.0.0.0/0 and ::0/0 for IPv6.
- Configuration of this map-cache entry on border nodes must be done with care. If a border node is configured with this map-cache 0.0.0.0/0 or ::0/0 map-cache entry it tries to resolve unknown destinations though the fabric in stead of routing it outside the fabric.
Display the map-cache configuration
FE2068#sh run | sec instance-id 4099
instance-id 4099
remote-rloc-probe on-route-change
dynamic-eid Fabric_VN_Subnet_1_IPv4
database-mapping 172.24.1.0/24 locator-set rloc_hosts
exit-dynamic-eid
!
dynamic-eid Fabric_VN_Subnet_1_IPv6
database-mapping 2001:DB8::/64 locator-set rloc_hosts
exit-dynamic-eid
!
service ipv4
eid-table vrf Fabric_VN_1
map-cache 0.0.0.0/0 map-request
exit-service-ipv4
!
service ipv6
eid-table vrf Fabric_VN_1
map-cache ::/0 map-request
exit-service-ipv6
!
exit-instance-id
The map-cache 0.0.0.0/0 and ::/0 map-request cause a map-cache entry be configured in the map-cache with the "send-map-request" actions. Traffic that hits this triggers map-requests. As the map-cache entries are to be put into the FIB which works based on longest-match this is applied to all routed IP traffic that does not hit any of the more specific entries.
- On supported platforms to avoid the first packet to be dropped the action shown is send-map-request + encapsulate to proxy ETR.
This results in the first packet to an unknown destination trigger a map-request as well that the packet is forwarded to the proxy-etr if present.
FE2067#show lisp instance-id 4099 ipv4 map-cache
LISP IPv4 Mapping Cache for LISP 0 EID-table vrf Fabric_VN_1 (IID 4099), 6 entries
0.0.0.0/0, uptime: 22:28:18, expires: 00:13:41, via map-reply, unknown-eid-forward
action: send-map-request + Encapsulating to proxy ETR
PETR Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID Metric
172.30.250.19 22:28:18 up 10/10 - 0
10.48.13.0/24, uptime: 02:31:26, expires: 21:28:34, via map-reply, complete
Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID
172.30.250.19 02:31:26 up 10/10 -
172.24.1.0/24, uptime: 22:31:34, expires: never, via dynamic-EID, send-map-request
Negative cache entry, action: send-map-request
172.24.2.0/24, uptime: 22:31:34, expires: never, via dynamic-EID, send-map-request
Negative cache entry, action: send-map-request
172.24.2.2/32, uptime: 00:00:21, expires: 23:59:38, via map-reply, complete
Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID
172.30.250.44 00:00:21 up 10/10 -
172.28.0.0/14, uptime: 22:28:22, expires: 00:13:39, via map-reply, unknown-eid-forward
PETR Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID Metric
172.30.250.19 22:28:19 up 10/10 - 0
In this output a few entries are shown.
- 10.48.13.0/24 and 172.24.2.2/32 in this output is learned via map-reply and are completed. Traffic to those destinations is to be encapsulated and forwarded to the respective locators.
- The 172.28.0.0/14 is an example of a negative map reply that been received and a block of IP addresses that has been returned. Traffic towards this subnet does not trigger a map-request for as long as this entry is in the map-cache.
Traffic Forwarding Through the Fabric
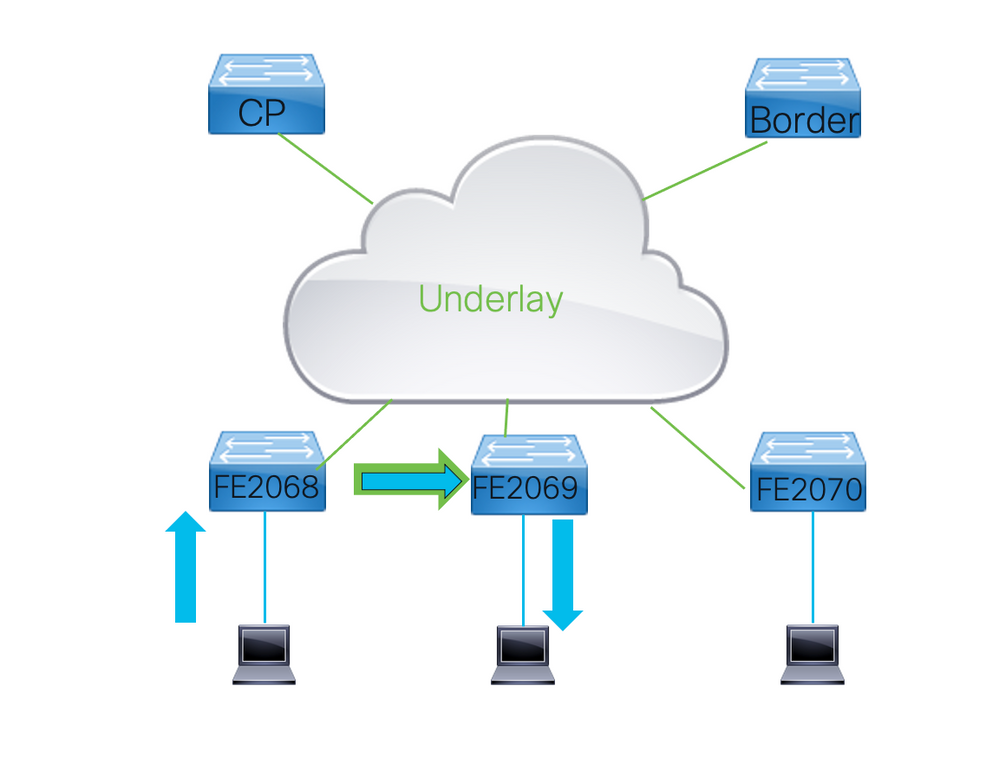
3.1 Layer 2 or Layer 3 Forwarding
Traffic in an LISP/VXLAN fabric can be forwarded through Layer 2 or Layer Instances.
- The determination which instance is used depends on thev destination MAC address of the frames.
- Frames that are send to any MAC address other then the one that is registered with the switch the frame is to be forwarded is to use Layer 2. If the destination of the packet is the switch it is forwarded through Layer 3.
- This is the same logic that would apply to normal forwarding through a Catalyst 9000 series switch.
3.2 Layer 2 Forwarding
Layer 2 forwarding through a LISP VXLAN fabric is done based upon the Layer 2 destination MAC address. Remote destination are inserted into the MAC address table with egress interface L2LI0.
Display the local and remote layer 2 interfaces
FE2068#show mac address-table vlan 150
Mac Address Table
-------------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports
---- ----------- -------- -----
150 0000.0c9f.f18e STATIC Vl150
150 0050.5693.8930 DYNAMIC Gi1/0/1
150 2416.9db4.33fd STATIC Vl150 <- Local
150 0019.3052.6d7f CP_LEARN L2LI0 <- Remote
Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 3
Total Mac Addresses installed by LISP: REMOTE: 1
For unknown destinations, if configured, traffic is send through the configured IP Multicast group in the underlay.
- To ensure correct flood of Broadcast, Unknown Unicast and Multicast (Selective Multicast flood only) traffic a correctly operational multicast environment in the underlay is needed.
- Trafffic that would be send through this multicast-underlay group is to be encapsulated in VXLAN.
- All other edges must join the multicast group and receive traffic and de-encapsulate the traffic for known Layer 2 Instances.
Display the underlay IP Multicast group
FE2068#sh ip mroute 239.0.19.1
IP Multicast Routing Table
Flags: D - Dense, S - Sparse, B - Bidir Group, s - SSM Group, C - Connected,
L - Local, P - Pruned, R - RP-bit set, F - Register flag,
T - SPT-bit set, J - Join SPT, M - MSDP created entry, E - Extranet,
X - Proxy Join Timer Running, A - Candidate for MSDP Advertisement,
U - URD, I - Received Source Specific Host Report,
Z - Multicast Tunnel, z - MDT-data group sender,
Y - Joined MDT-data group, y - Sending to MDT-data group,
G - Received BGP C-Mroute, g - Sent BGP C-Mroute,
N - Received BGP Shared-Tree Prune, n - BGP C-Mroute suppressed,
Q - Received BGP S-A Route, q - Sent BGP S-A Route,
V - RD & Vector, v - Vector, p - PIM Joins on route,
x - VxLAN group, c - PFP-SA cache created entry,
* - determined by Assert, # - iif-starg configured on rpf intf,
e - encap-helper tunnel flag, l - LISP decap ref count contributor
Outgoing interface flags: H - Hardware switched, A - Assert winner, p - PIM Join
t - LISP transit group
Timers: Uptime/Expires
Interface state: Interface, Next-Hop or VCD, State/Mode
(*, 239.0.1.19), 00:02:36/stopped, RP 172.31.255.1, flags: SJCF
Incoming interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/23, RPF nbr 172.30.250.42
Outgoing interface list:
L2LISP0.8191, Forward/Sparse-Dense, 00:02:35/00:00:24, flags:
(172.30.250.44, 239.0.1.19), 00:02:03/00:00:56, flags: FT
Incoming interface: Null0, RPF nbr 0.0.0.0
Outgoing interface list:
GigabitEthernet1/0/23, Forward/Sparse, 00:02:03/00:03:23, flags:
(172.30.250.30, 239.0.1.19), 00:02:29/00:00:30, flags: JT
Incoming interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/23, RPF nbr 172.30.250.42
Outgoing interface list:
L2LISP0.8191, Forward/Sparse-Dense, 00:02:29/00:00:30, flags:
This output shows an S,G entry for all other Edges in the fabric where clients are configured that would send flooded traffic. It also shows one S,G entry with the Loopback0 of this Edge device as the source.
For the receiver side of the traffic through the underlay multicast group the show ip mroute command also shows the L2LISP0.<instance>
this would indicate for which Layer 2 Instances this edge device would be de-encapsulate flooded traffic and forwarding it to its
relevant interfaces.
3.3 Layer 3 forwarding information
To determine how traffic is forwarded when a LISP VXLAN fabric is deployed it important to verify CEF.
- LISP unlike traditional routing protocols inserts the routing direction not in the Routing Table but interacts directly with CEF to update the FIB.
For a given remote destination the map-cache information contains the locator information that is to be used.
Display the locator information
FE2067#sh lisp instance-id 4099 ipv4 map-cache 172.24.2.2
LISP IPv4 Mapping Cache for LISP 0 EID-table vrf Fabric_VN_1 (IID 4099), 1 entries
172.24.2.2/32, uptime: 11:19:02, expires: 12:40:57, via map-reply, complete
Sources: map-reply
State: complete, last modified: 11:19:02, map-source: 172.30.250.44
Idle, Packets out: 2(1152 bytes), counters are not accurate (~ 11:18:35 ago)
Encapsulating dynamic-EID traffic
Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt Encap-IID
172.30.250.44 11:19:02 up 10/10 -
Last up-down state change: 11:19:02, state change count: 1
Last route reachability change: 11:19:02, state change count: 1
Last priority / weight change: never/never
RLOC-probing loc-status algorithm:
Last RLOC-probe sent: 11:19:02 (rtt 2ms)
From the map-cache the Locator to be used for this EID is 172.30.250.44. So traffic towards this destination is to be encapsulated and the outer IP header has an IP Destination Address of 172.30.250.44.
In the routing table for the VRF used for this instance this entry is not shown.
FE2067#show ip route vrf Fabric_VN_1
Routing Table: Fabric_VN_1
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, m - OMP
n - NAT, Ni - NAT inside, No - NAT outside, Nd - NAT DIA
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
H - NHRP, G - NHRP registered, g - NHRP registration summary
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
& - replicated local route overrides by connected
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.24.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.24.1.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan150
l 172.24.1.4/32 [10/1] via 172.24.1.4, 06:11:02, Vlan150
L 172.24.1.254/32 is directly connected, Vlan150
C 172.24.2.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan151
L 172.24.2.254/32 is directly connected, Vlan151
CEF outputs give more information about the forwarding through the LISP VXLAN fabric.
- When the detail keyword to the show ip cef command is added it does not just give the destination for the encapsulated frame to be send.
- The Egress interface with this output is LISP 0.<instance> indicates that the traffic is send encapsulated.
FE2067#sh ip cef vrf Fabric_VN_1 172.24.2.2 detail
172.24.2.2/32, epoch 1, flags [subtree context, check lisp eligibility]
SC owned,sourced: LISP remote EID - locator status bits 0x00000001
LISP remote EID: 2 packets 1152 bytes fwd action encap, dynamic EID need encap
SC inherited: LISP cfg dyn-EID - LISP configured dynamic-EID
LISP EID attributes: localEID No, c-dynEID Yes, d-dynEID No, a-dynEID No
SC inherited: LISP generalised SMR - [enabled, inheriting, 0x7FF95B3E0BE8 locks: 5]
LISP source path list
nexthop 172.30.250.44 LISP0.4099
2 IPL sources [no flags]
nexthop 172.30.250.44 LISP0.4099
As traffic would be sent encapsulated towards the next hop, the next step is to run a show ip cef <next hop> to see the egress interface where the packet would be routed out too.
Run to see the egress interface
FE2067#sh ip cef 172.30.250.44
172.30.250.44/32
nexthop 172.30.250.38 GigabitEthernet1/0/23

Note: There are 2 different levels of equal cost multiple path(ECMP) routing are possible.
- Traffic could be load balanced in the overlay in case there are 2 advertised RLOCs and can be load balanced in the underlay network if redundant paths exist to reach a RLOC IP address.
- As the UDP destination port is fixed to 4789 and the source and destination IP addresses for all flows between two fabric devices are the same some form of anti-polarization mechanisme needs to occur to avoid all packets routed over the same path.
- With LISP VXLAN this is the UDP source port in the outer header that would be different for different flows in the overflow network.
3.4 Packet Format
- Within LISP VXLAN fabrics all traffic is completly encapsulated in VXLAN. This includes the entire Layer 2 frame to be able to support both Layer 2 and Layer 3 overlays.
For Layer 2 frames the original header is encapsulated. For frames send through an Layer 3 instance a dummy Layer 2 header is used.
Ethernet II, Src: 24:16:9d:3d:56:67 (24:16:9d:3d:56:67), Dst: 6c:31:0e:f6:21:c7 (6c:31:0e:f6:21:c7)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 172.30.250.30, Dst: 172.30.250.44
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: 65288, Dst Port: 4789
Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network
Flags: 0x8800, GBP Extension, VXLAN Network ID (VNI)
1... .... .... .... = GBP Extension: Defined
.... .... .0.. .... = Don't Learn: False
.... 1... .... .... = VXLAN Network ID (VNI): True
.... .... .... 0... = Policy Applied: False
.000 .000 0.00 .000 = Reserved(R): 0x0000
Group Policy ID: 16
VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI): 4099
Reserved: 0
Ethernet II, Src: 00:00:00:00:80:a3 (00:00:00:00:80:a3), Dst: ba:25:cd:f4:ad:38 (ba:25:cd:f4:ad:38)
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 172.24.1.4, Dst: 172.24.2.2
Internet Control Message Protocol
As seen by the sample capture of a frame carried through a LISP VXLAN fabric there is the fully encapsulated frame inside the vxlan packet. As its a layer 3 frame the ethernet header is a dummy header.
In the VXLAN header the VLAN Network Identifier field carries the LISP instance id the frame belongs too.
- Through the Group Policy ID field the frames SGT tag is carried.
- This is set on ingress in the fabric and carried through towards the fabric until group based policy enforcement is to be done.
Authentication and Security Enforcement
4.1 Switch Port Authentication
To dynamically assign endpoints to their respective VLANs and assign them an SGT tag authentication can be used.
- Authentication protocols as Dot1x/MAB/central webauth can be deployed authenticate and authorize users and endpoints on a Radius server that sends attributes back to the switch to allow network access to the client/endpoint in the correct pool and with the correct network access authorization.
For LISP VXLAN fabric there are few common radius attributes:
- Vlan Assignment: This attributes is set to Vlan ID or name from the radius server to the switches an endpoint can be assigned to a specific Layer 2/Layer 3 LISP instance.
- SGT Value: This attribute sets an SGT assigns an endpoint to this SGT. This would be used for group based policies towards this endpoint as well as assigns an SGT value to all frames send through the fabric that are originated by this endpoint.
- Voice Authorization: Voice devices operate on the voice vlan. This sets voice authorization the endpoint would be allowed to send and receive traffic in the voice vlan configured on a port. This to separate voice and data traffic in their respective VLANs
- Session timeout: Various end points have their own timeouts for the sessions. A timeout can be send from the radius server to indicate how often a client needs to re-authenticate
- Template: For some endpoints a different template needs to be applied on a port to correctly operate. A template name could be send from the Radius server that would indicate what needs to be applied to the port
Check the result of Authentication on a port use the command show access-session
FE2067#show access-session interface Gi1/0/1 details
Interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1
IIF-ID: 0x1FF97CF7
MAC Address: 0050.5693.f1b2
IPv6 Address: FE80::3EE:5111:BA77:E37D
IPv4 Address: 172.24.1.4
User-Name: 00-50-56-93-F1-B2
Device-type: Microsoft-Workstation
Device-name: W7180-PC
Status: Authorized
Domain: DATA
Oper host mode: multi-auth
Oper control dir: both
Session timeout: N/A
Acct update timeout: 172800s (local), Remaining: 172678s
Common Session ID: 9256300A000057B8376D924C
Acct Session ID: 0x00016d77
Handle: 0x85000594
Current Policy: PMAP_DefaultWiredDot1xClosedAuth_1X_MAB
Local Policies:
Server Policies:
Vlan Group: Vlan: 150
SGT Value: 16
Method status list:
Method State
dot1x Stopped
mab Authc Success
Note these key fields:
- IPv4 and IPv6 addresses: Typicaly learned through device-tracking.
- Username: This the username used for authentication.
- For Dot1x this would typically be the user that authenticates.
- When MAB is used this is the MAC address of the station that is send to Radius as username and password for authentication.
- Status: This indicates the status of the Authentication and the Authentication result.
- Domain: For normal endpoints this would be the Data domain, so traffic would be send/received untagged on the port. (For voice devices this can be set to Voice)
- Server policies: This is the where the information from the Radius server like Vlan assignment and SGT assignment
- Method status list: This shows an overview of the methods run.
- Standard dot1x runs before MAB.
- If an endpoint would not respond to EAPOL frames the method would fail over to mab.
- This would then show dot1x to have failed.
- MAB shows authc success indicates it managed to authenticate, it does not reflect if the authentication result would be an access-accept or reject.
4.2 Traffic Policies & Group Based Policies (CTS)
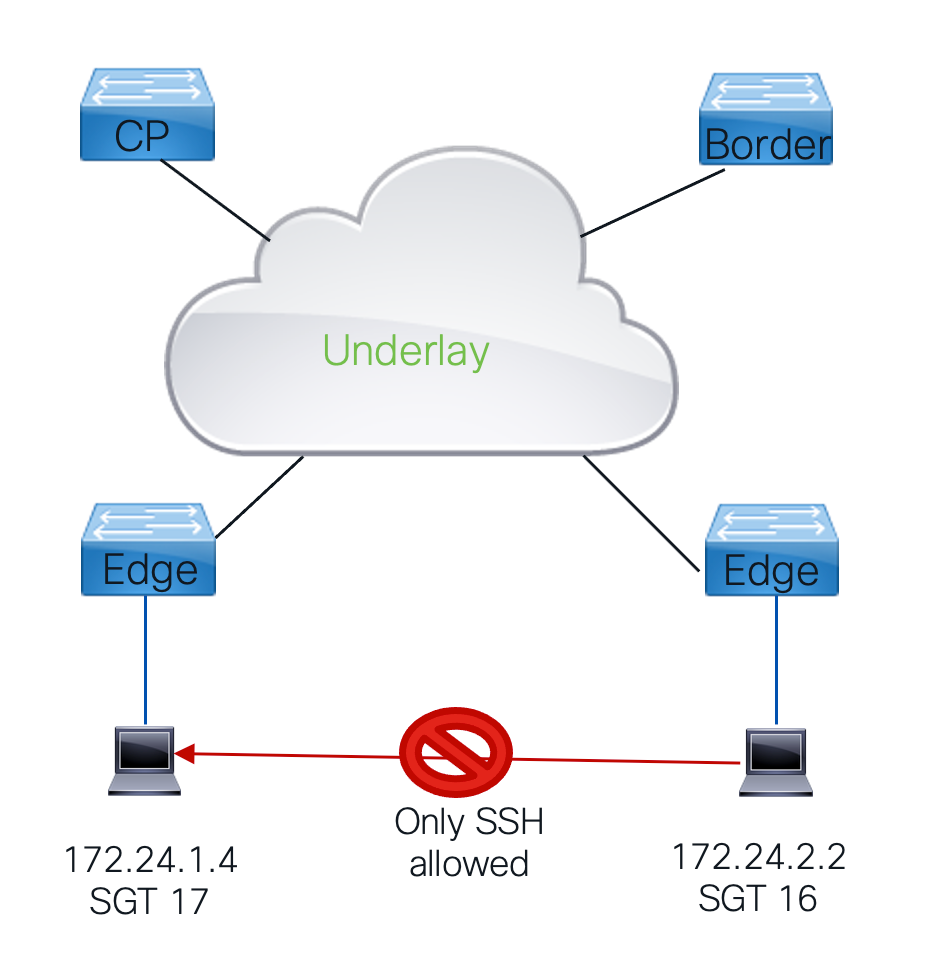
Within an LISP VXLAN fabric CTS is used to enforce traffic policies:
- The Group Based Policy architecture is based upon Secure Group Tags.
- All traffic inside the fabric is assigned on ingress and SGT tag which is carried through the fabric in every frame.
- When this traffic would leave the fabric the trafffic policies are enforced.
- This is done in Group Based Policies that checks the source and destination group tags of the packet against the matrix that consists of Source-Destination SGTs where the result is an SGACL that defines what traffic would or would not be permitted.
- When there no specific match inside the matrix for the Source-Destination SGT the default action that is defined is to be applied.
4.3 CTS Enviroment
To operate with group based policies the first thing that is needed for an Fabric devices is to get a CTS pac.
- This pac is to be used inside radius frames to authorize the RADIUS frames on Cisco ISE. This is used to set the cts-pac-opaque field inside the Radius frames.
Display the CTS pac information
FE2067#sh cts pacs
AID: C7105D0DA108B6AE0FB00499233B9C6A
PAC-Info:
PAC-type = Cisco Trustsec
AID: C7105D0DA108B6AE0FB00499233B9C6A
I-ID: FOC2410L1ZZ
A-ID-Info: Identity Services Engine
Credential Lifetime: 18:05:51 UTC Sat Jun 24 2023
PAC-Opaque: 000200B80003000100040010C7105D0DA108B6AE0FB00499233B9C6A0006009C00030100C5C0B998FB5E8C106F6882A088D5041300000013641F061A00093A80BA05A1608225843FBAAFD6C3BCD673353B18A6C68149AFAE24A060CBCAFC783E1E6C483AA1A32ADDB8C8EA5E739FB65DB7747ABAEDA59C48F4D1A4F9C8342C36E6D28725A440C1FE4BDB34207081E93CD79367AB19811E323F5882FE20EF831B7A5C2F339C3F35EFC0DBF346C77404F206F5B2171A4C0AAC187F74C5
Refresh timer is set for 12w0d
It important to ensure that the CTS pac is configured and valid. This gets refreshed by the Fabric device automatically.

Note: To manually trigger a refresh the command "cts refresh pac" can be issued.
For group based policies to operate it downloads environment data as wel as it downloads the required policy information.
- This enviroment data contains both the CTS tag the switch itself uses as well as download the table of all group based policy groups that are known on the Radius server.
Display cts environment data
FE2067#sh cts environment-data
CTS Environment Data
====================
Current state = COMPLETE
Last status = Successful
Service Info Table:
Local Device SGT:
SGT tag = 2-00:TrustSec_Devices
Server List Info:
Installed list: CTSServerList1-0001, 1 server(s):
*Server: 10.48.13.221, port 1812, A-ID C7105D0DA108B6AE0FB00499233B9C6A
Status = ALIVE
auto-test = TRUE, keywrap-enable = FALSE, idle-time = 60 mins, deadtime = 20 secs
Security Group Name Table:
0-00:Unknown
2-00:TrustSec_Devices
3-00:Network_Services
4-00:Employees
5-00:Contractors
6-00:Guests
7-00:Production_Users
8-00:Developers
9-00:Auditors
10-00:Point_of_Sale_Systems
11-00:Production_Servers
12-00:Development_Servers
13-00:Test_Servers
14-00:PCI_Servers
15-00:BYOD
16-00:Fabric_Client_1
17-00:Fabric_Client_2
255-00:Quarantined_Systems
Environment Data Lifetime = 86400 secs
Last update time = 11:46:41 UTC Fri Mar 31 2023
Env-data expires in 0:19:17:04 (dd:hr:mm:sec)
Env-data refreshes in 0:19:17:04 (dd:hr:mm:sec)
Cache data applied = NONE
State Machine is running
Retry_timer (60 secs) is not running
When group based policies are used the only policies that gets downloaded are the CTS tags the device has local endpoints with that it needs to enforce.
- To be able to check the mapping from IP address (or subnet) to a group based policy group the command "show cts role-based sgt-map vrf <vrf> all" can be used.
Display all known IP to SGT information for a VRF
FE2067#sh cts role-based sgt-map vrf Fabric_VN_1 all
Active IPv4-SGT Bindings Information
IP Address SGT Source
============================================
172.24.1.4 17 LOCAL
172.24.1.254 2 INTERNAL
172.24.2.254 2 INTERNAL
IP-SGT Active Bindings Summary
============================================
Total number of LOCAL bindings = 1
Total number of INTERNAL bindings = 2
Total number of active bindings = 3
Active IPv6-SGT Bindings Information
IP Address SGT Source
================================================================
2001:DB8::1 2 INTERNAL
2001:DB8::F304:BCCD:6BF3:BFAF 17 LOCAL
IP-SGT Active Bindings Summary
============================================
Total number of LOCAL bindings = 1
Total number of INTERNAL bindings = 1
Total number of active bindings = 2
This output shows all the known IP addresses (and subnets) for a given VRF and their group based policy associations.
- As can be seen there one IP address of an endpoint that is assigned group based policies group 17 and that is sourced local.
- This is the result of authentication that occurs on the port and where the results indicated that the tag associated with that endpoint.
- It also highlights the switches own IP addresses which are assigned the device-sgt tag as sourced internal.
- Group based policy tags could also be assigned through configuration or via an SXP session towards ISE.
When a device learns of an SGT tag it tries to download the policies associated with it from the ISE server.
- The command show cts authorization entries gives an overview when those were attempted to be downloaded and if they were or were not successively downloaded.

Note: Policies are to be refreshed periodically in case of any changes in policies. ISE can also push an CoA command for the switch to be triggered to download new policies when changes are made. To manually refresh the policies the command "cts refresh policy" is issued.
Display an overview of the policies attempted to be downloaded and if they were or were not successively downloaded
FE2067#show cts authorization entries
Authorization Entries Info
==========================
Peer name = Unknown-0
Peer SGT = 0-00:Unknown
Entry State = COMPLETE
Entry last refresh = 22:14:46 UTC Thu Mar 30 2023
SGT policy last refresh = 22:14:46 UTC Thu Mar 30 2023
SGT policy refresh time = 86400
Policy expires in 0:05:23:44 (dd:hr:mm:sec)
Policy refreshes in 0:05:23:44 (dd:hr:mm:sec)
Retry_timer = not running
Cache data applied = NONE
Entry status = SUCCEEDED
AAA Unique-ID = 11
Peer name = Unknown-17
Peer SGT = 17-01:Fabric_Client_2
Entry State = COMPLETE
Entry last refresh = 11:47:31 UTC Fri Mar 31 2023
SGT policy last refresh = 11:47:31 UTC Fri Mar 31 2023
SGT policy refresh time = 86400
Policy expires in 0:18:56:29 (dd:hr:mm:sec)
Policy refreshes in 0:18:56:29 (dd:hr:mm:sec)
Retry_timer = not running
Cache data applied = NONE
Entry status = SUCCEEDED
AAA Unique-ID = 4031
If there are any policies downloaded they can be displayed with the command "show cts rolebased policies".
FE2067#sh cts role-based permissions
IPv4 Role-based permissions default:
Permit IP-00
IPv4 Role-based permissions from group 17:Fabric_Client_2 to group 16:Fabric_Client_1:
PermitWeb-02
RBACL Monitor All for Dynamic Policies : FALSE
RBACL Monitor All for Configured Policies : FALSE
This command shows all policies the device has learned. On the ISE server there are potentially more policies present for different groups but the device only attempts to download policies for which it knows endpoints for. This conserves valuable hardware resources.
This command also shows the default action that is to be applied to traffic no more specific entry is known for. In this case its Permit IP, so all traffic that does not match a specific entry in the table is to be allowed to pass through.
Run show cts rbacl <name>to get more detail on the exact content of the RBACL that has been downloaded
FE2067#sh cts rbacl permitssh
CTS RBACL Policy
================
RBACL IP Version Supported: IPv4 & IPv6
name = permitssh-03
IP protocol version = IPV4
refcnt = 2
flag = 0x41000000
stale = FALSE
RBACL ACEs:
permit tcp dst eq 22
permit tcp dst eq 23
deny ip
In this case the only traffic allowed to be sent to the endpoint with this RBACL applied to it are tcp packets towards 22 (SSH) and 23(Telnet).

Note: RBACL only works in one direction. Unless there is a policy in the return traffic it gets enforced with the default policy. Traffic that ingresses the fabric is not enforced, it send through the fabric with the SGT tag known on the ingress node. It only gets enforced when it leaves the fabric and it is to be enforced on the policies that are present on that device. Typically those policies would be the same, but it is possible to extend the CTS domain for example with a firewall where other policies could have been defined depends on the security policies deployed.
Run 'show cts role-based counters' to validate if frames are or are not dropped
- This command shows the cumulative counters for the entire switch. There is no equivelant command for per interface.
FE2067#sh cts role-based counters
Role-based IPv4 counters
From To SW-Denied HW-Denied SW-Permitt HW-Permitt SW-Monitor HW-Monitor
* * 0 0 3565235 7777106 0 0
17 16 0 3 0 3412 0 0
16 17 0 5812 0 871231 0 0
This overview shows all the known entries that the switch knows about in this case to be able to match traffic from 17 to 16 and from 16 to 17.
- Any other match that falls under the * * and gets the default action applied so if any traffic for example from 18 to 16 would come it doesnt match the matrix known on the switch and have the default action applied.
Even though the counters are cumulative they do give a good indication if traffic is dropped.
- To determine what traffic would hit an entry the log keyword could be added on the ISE server to the respective policies, which results in the switch provide log messages when this entry is hit.
- This can be done for both the default action (* *) or one of the more specific entries in the matrix.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
06-Apr-2023 |
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Michel PetersCat Eng CEAD Switching Escalation
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback