Quality of Service on Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL Series Switches Frequently Asked Questions
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document addresses the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on the Quality of Service (QoS) features of the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches. This document does not address the QoS features of newer Catalyst 2940, 2955/2950, 2970, 3550, 3560, and 3750 series switches.
For information on configuring these switches, refer to:
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Q. Which QoS features do the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches support?
A. The Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL switches with 8 MB of DRAM provide QoS based on IEEE 802.1p Class of Service (CoS) values. They support input classification and output scheduling. The Catalyst 3524-PWR XL and 3548 XL switches also support the port-based input re-classification feature. The original Catalyst 2900 XL with 4 MB DRAM and WS-X2914-XL and WS-X2922-XL modules do not support any QoS features. GigaStack daisy-chained configurations cannot provide guaranteed voice QoS because they are shared media access models.
Q. What is the software version requirement for the QoS features on Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches?
A. Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches need to at least run Cisco IOS® Software Release12.0(5)XP. The input re-classification feature of remarking Class of Service (CoS) values is available only on Catalyst 3524-PWR XL and 3548 XL switches after Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(5)XU.
Q. Do the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches support rate-limiting or policing on ports or VLANs?
A. Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches do not provide rate-limiting or policing features. The bandwidth interface command is not related to QoS. It is an unsupported command on these switches.
Q. Can the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches switch-mark or re-write IP precedence (ToS) bits in an IP packet?
A. Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches do not provide Layer 3 marking or re-writing, as they are Layer 2 switches. They cannot convert Layer 2 Class of Service (CoS) values into Layer 3 Type of Service (ToS) information. Packets with ToS/Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) already set coming into the switch are retained through the switch. They are available for downstream switches to act on them.
Q. What is 802.1p prioritization and how does it support IP Telephony?
A. The 802.1Q/p standard defines the use of the three-bit Class of Service (CoS) field in the 802.1Q tag to prioritize frames with eight classes (priorities) of traffic. The Cisco InterSwitch Link (ISL) trunk mode, which is also similar, provides the CoS field (least three significant bits in a four-bit user field). The Cisco IP phones, such as the Cisco 7960, tag the voice packets with a CoS value of five. These tagged packets are used by the Catalyst XL switches to prioritize the voice traffic by queuing them in the priority queue in the egress port. This guarantees top priority to the time critical voice packets.
Q. Do the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches provide priority scheduling in the input/ingress port?
A. Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches do not provide any priority scheduling in the input side. However, they do provide priority scheduling in the output/egress port.
Q. Do the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches honor the incoming Class of Service (CoS) values in dot1p tags from IP phones?
A. Yes, Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches honor the incoming Class of Service (CoS) value in the dot1q tag. All the ports are considered trusted ports by default. Since dot1q does not tag the native VLAN traffic, issue the switchport priority default <0-7> interface level configuration command to classify the incoming untagged packet as desired. The switchport priority default <0-7> command is issued to provide CoS equivalent egress scheduling. If the egress port is a trunk port, the ingress CoS or port default priority configuration is marked in the outgoing frames as CoS values for the far-end device to treat them with the desired higher priority.
Q. My server/IP phone/device cannot tag Class of Service (CoS) values. Can the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches tag the traffic from the server/device for a specific CoS value?
A. If the server/IP phones/any other device connected to the switch do not support dot1p tagging, issue the switchport priority default <0-7> interface command to make the switch preferentially treat the traffic on that interface as if the device had set the CoS values. This feature is called port-based prioritization. For example, a port priority of four makes the switch queue the packet in the high priority queue as it would a packet tagged with a CoS value of four. The packet is tagged with the configured ingress port priority value if the outgoing port is a trunk port. As a result, these packets are used for classification and preferential treatment in the connected switch.
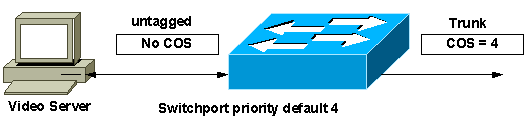
Q. Can I override the incoming Class of Service (CoS) to a specific CoS value?
A. Yes, you can override the CoS value set by the PC attached to the Cisco IP phone and use the configured port priority instead. This feature is called port-based re-classification. The switchport priority extend cos <0-7> interface command is issued to achieve this. This feature is supported only on Catalyst 3524-PWR XL and 3548 XL switches. This command was introduced after Cisco IOS® Software Release12.0(5)XU. This feature is complementary to the port prioritization available on supported Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches for untagged packets.
Q. Can I re-classify Class of Service (CoS) value of data generated from a PC connected to an IP phone which is attached to the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches?
A. Yes, you can configure the interface level switchport priority extend trust command. This feature instructs the first Cisco IP phone to trust the dot1p tag received from the phone or any device connected to it on the phone's secondary port. This command needs to be used with caution. If the user connects a workstation which sets the tag to the IP phone, the data traffic from the user gets the user set priority. It has a negative impact on the quality of the voice.
Q. Can I trust the traffic on data VLANs or native VLANs on ports configured for IP phones?
A. Yes, you can override the Class of Service (CoS) value set by the connected device and use the default port priority configured on the port instead. The switchport priority override interface command is issued to achieve this. Configure a default port priority. Otherwise the switch overrides to default port priority of zero. This results in all traffic on the port being treated with a low priority. This command is supported on WS-C3524-PWR and WS-C3548-XL switches after Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.0(5)XU.
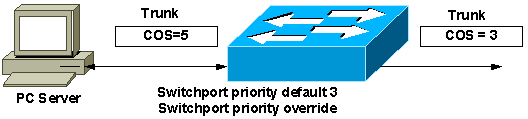
Q. What kind of output scheduling do the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches provide?
A. Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches support two queues per port on the 10/100 and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. Port priority value or Class of Service (CoS) value 0-3 maps to a low priority queue on the egress port. Port priority value or CoS value 4-7 maps to the high priority queue on the egress port(s).
CoS/Port Priority Queue Selected 0-3 Q1 (Lower priority) 4-7 Q2 (Higher priority) Priority scheduling is applied between the queues. This assures that the high priority queue is always serviced before scheduling the low priority traffic. These features enable to prioritize mission critical traffic, such as IP Telephony, over regular traffic, such as FTP or generic Web. The low priority queues experience tail drop during congestion when there is traffic in the high priority queue.
Q. Is it possible to use Access-Lists (ACLs) to define traffic for which QoS features can be applied?
A. No. The Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches do not support ACL or class-maps to define interesting traffic. The classification is per port. The switchport priority extend COs <0-7> interface level command is issued to provide the same CoS value for traffic on data VLANs as the voice VLAN. The switchport priority extend COs <0-7> interface level command is issued to assign a default CoS for all untagged traffic.
Q. How do I configure the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches with voice VLANs for Cisco IP phone connections?
A. To view example configuration, refer to Configuring Voice Ports section of the document Configuring the Switch Ports.
Q. What is the general recommendation for configuring QoS on Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches?
A. The overall objective of QoS is to prioritize the voice/video traffic at the uplink port/router port so that those packets are not delayed. In order to achieve this objective, these guidelines are used:
Configure the PC ports as access ports. The default priority on a port is zero. If needed, you can explicitly configure the port by issuing the switchport priority default <0-3> command so that the traffic that comes from those ports are queued in a lower priority queue.
Configure ports which receive tagged low-priority traffic by issuing the switch priority override command and the switchport priority default <0-3> command so that this traffic is queued in a low priority queue. The override option is available only on WS-X3524-PWR-XL and WS-X3548-XL with Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.0(5)XU and later.
Configure the ports connected to Cisco IP phones for 802.1Q trunking so that the switch acts on the dot1q/p priority from the phones. As a result, the switch queues these packets in the high priority queue. Configure InterSwitch Link (ISL) trunks to Cisco devices/server network interface cards (NICs), which support the encapsulation. The switch acts on the Class of Service (CoS) value present in the ISL frame.
Configure the ports connected to Cisco IP phones with a PC attached to the secondary port by issuing the extended trust configuration switchport priority extend COs <0-3> command so that these frames are queued in the low priority queue.
Configure the ports connected to Cisco IP phones with another Cisco IP phone attached to the secondary port by issuing the extended trust configuration switchport priority extend trust command so that these packets are queued to the high priority queue as well.
Configure the ports connected to non-Cisco IP phones (which cannot tag the dot1p value) by issuing the switch priority default <4-7> command so that these frames are queued in the high priority queue. All traffic received on this port is prioritized. Therefore, do not connect PC or other data traffic devices on this port.
Q. How do I verify the QoS configuration on the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches?
A. The exec mode show interface <interface> switchport command provides the current configuration on the port. This configuration is used to verify whether you have configured the interface according to the requirement.
3548XL#show running-config interface FastEthernet 0/20 Building configuration... Current configuration: ! interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk switchport priority default 5 spanning-tree portfast end 3548XL#show interfaces FastEthernet 0/20 switchport Name: Fa0/20 Switchport: Enabled Administrative mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: Disabled Access Mode VLAN: 0 ((Inactive)) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Trunking VLANs Active: 1-22,29,231,651 Pruning VLANs Enabled: 2-1001 Priority for untagged frames: 5 Override vlan tag priority: FALSE Voice VLAN: none Appliance trust: noneThere is no command available which provides information on egress scheduling or queuing statistics. The scheduling, as explained earlier in this document, is priority scheduling. This means that if a packet exists in the Q2, it is scheduled ahead of any packet in Q1. To verify whether packets are being tagged as expected on a trunk egress port, use an inline sniffer to capture the frames coming from the egress port or capture the frame on the switch downstream.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)


 Feedback
Feedback