Configure IPv4 and IPv6 on a Wireless Access Point
Available Languages
Objective
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the commonly used form of IP addressing used to identify hosts on a network and uses a 32-bit format. Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the next-generation IP address standard intended to replace the IPv4 format. IPv6 solves the address scarcity problem with the use of 128-bit addressing instead of 32-bit addressing which was used in IPv4.
This configuration helps to assign an IP address via Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or manually. By default, the WAP automatically requests for network information through a broadcast. In the absence of a DHCP server on the network, it uses its default IP address. If you want to use a static IP address, you must disable the DHCP client and manually assign the IP address and other network information.
The objective of this document is to configure IPv4 and IPv6 settings on the Wireless Access Point device.
Applicable Devices
- WAP100 Series
- WAP300 Series
- WAP500 Series
Software Version
- 1.0.1.4 – WAP131, WAP351
- 1.0.6.2 – WAP121, WAP321
- 1.2.1.3 – WAP371, WAP551, WAP561
- 1.0.1.2 – WAP150, WAP361
- 1.0.0.17 – WAP571, WAP571E
Configure IPv4
Configure IPv4 DHCP
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility and choose LAN > IPv4 Settingor LAN > VLAN and IPv4 Address depending on the WAP model you have.
|
WAP131, WAP150, WAP351, WAP361, WAP571, WAP571E
|
WAP121, WAP321, WAP371, WAP551, WAP561 |
|---|---|
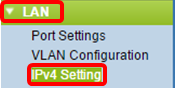 |
 |
Step 2. In the Connection Type area, click DHCP radio button to automatically obtain an IP address. This setting is chosen by default.

Step 3. Choose your preferred DNS configuration from the Domain Name Servers radio buttons. DNS is a protocol that helps the devices reach other computers and private networks over the Internet by translating domain names into their respective IP addresses.
Note: If DHCP is enabled, the DNS configuration is optional.

The available options are defined as follows:
-
Dynamic — WAP acquires the Domain Name Server (DNS) addresses from a DHCP server on the Local Area Network (LAN). If you choose this option, skip to Step 4.
-
Manual — Allows you to manually configure one or more DNS server addresses in the Domain Name Servers fields.
Step 4. Click Save.
Configure Static IPv4 Address
Step 1. Click the radio button for Static IP.

Step 2. Enter an IP address for the access point in the Static IP Address field. The IP address should be unique and has not been assigned to any other devices in the same network.

Step 3. Enter the subnet mask of the network in the Subnet Mask field. The default mask is based on either the class of IP address you choose, or how many subnets you use for the network.
Note: The default mask is 255.255.255.0

Step 4. Enter the default gateway IP address in the Default Gateway field. A default gateway is a node on the computer that is used when an IP address does not match a route in the routing table. It then forwards the traffic appropriately. This device is usually a router. To learn how to find your connected device’s default gateway IP address using a Windows command prompt, click here.

Step 5. Enter the IP address of the DNS in the Domain Name Server fields. DNS is a protocol that helps the devices reach other computers and private networks over the Internet by translating domain names into their respective IP addresses.
Note: You can also add another DNS server IP address in the other field provided, but it is optional. Having two DNS servers can be helpful in the event that one of the servers goes down or becomes unavailable.

Step 6. Click Save.

Step 7. If you have pre-configured settings before, a pop-up window will appear confirming the wireless settings are about to be updated and that possible disconnections may happen. Click OK.

You should now have statically configured the IPv4 address.
Configure IPv6
Configure IPv6 DHCP
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility and choose LAN > IPv6 Setting or LAN > IPv6 Addresses.
|
WAP131, WAP150, WAP351, WAP361, WAP571, and WAP571E
|
WAP121, WAP321, WAP371, WAP551, and WAP561 |
|---|---|
 |
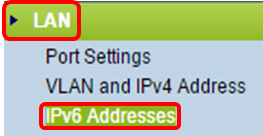 |
Step 2. Click DHCPv6 as the IPv6 Connection Type. The IPv6 connection type tells the device how to obtain IPv6 address.
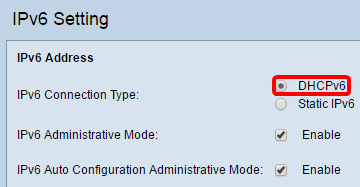
Step 3. To permit IPv6 management access to the access point, check the Enable IPv6 Administrative Mode check box.

Step 4. To learn its IPv6 addresses and gateway through router advertisements received on the LAN port, check the Enable IPv6Auto Configuration Administrative Mode check box. Access points can have multiple auto-configured IPv6 addresses.

Step 5. Click Save.
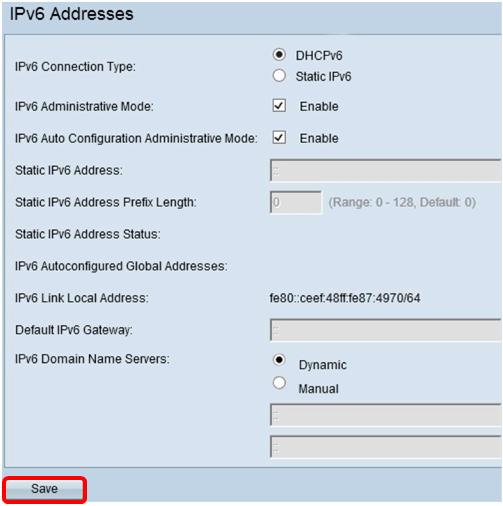
Configure Static IPv6 Address
Step 1. Click Static IPv6 as the IPv6 Connection Type to assign an IPv6 address manually to the access point.

Step 2. Check the IPv6 Administrative Mode check box to enable IPv6 management access. This allows the device management interface to be accessed via an IPv6 address.

Step 3. Check the IPv6 Auto Configuration Administrative Mode check box to enable IPv6 automatic address configuration on the device. This is enabled by default.

Step 4. Enter the IPv6 address of the access point in the Static IPv6 Address field. This is a unique IPv6 address, and no other device in the network should use it. This is a global routable IPv6 address.

Step 5. Enter the prefix length of the static address in the Static IPv6 Address Prefix Length field. The prefix length is an integer in the range of 0 to 128 which specifies the network portion of the IPv6 IP address. For this example, 48 is used.
Note: This is similar to the subnet mask in IPv4. The default prefix length is 0.

Step 6. Enter the IPv6 address of the default gateway in the Default IPv6 Gateway field.
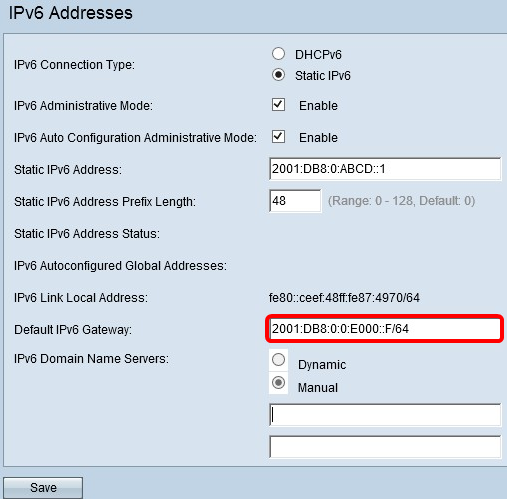
Step 7. Enter the IPv6 DNS server address in the IPv6 Domain Name Servers fields.

Step 8. Click Save.

You should now have configured the Static IPv6 settings.
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
13-Dec-2018 |
Initial Release |
 Feedback
Feedback