Introduction
This document describes the process for deleting network access devices (NADs) on ISE via ERS API using PostMan as the REST Client.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- ISE (Identity Services Engine)
- ERS (External RESTful Services)
- REST clients like Postman, RESTED, Insomnia, and so on.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software versions:
- Cisco ISE (Identity Services Engine) 3.1 patch 6
- Postman REST client v10.16

Note: The procedure is similar or identical for other ISE versions and REST Clients. You can use these steps on all 2.x and 3.x ISE Software Releases unless stated otherwise.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Configure
Enable ERS (Port 9060)
ERS APIs are HTTPS-only REST APIs that operate over port 443 and port 9060. Port 9060 is closed by default, so it needs to be opened first. A timeout from the server is presented if clients trying to access this port do not enable ERS first. Therefore, the first requirement is to enable ERS from the Cisco ISE admin UI.
Navigate to Administration > Settings > API Settings and enable the ERS (Read/Write) toggle button.
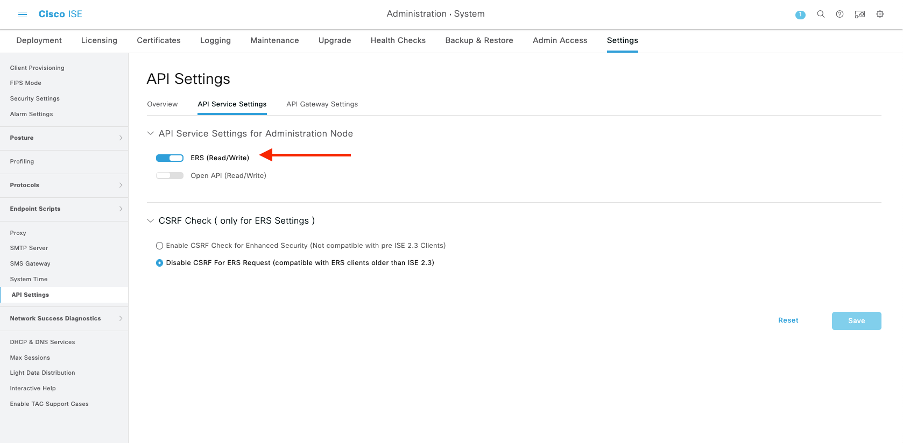

Note: The ERS APIs support TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2. ERS APIs do not support TLS 1.0 regardless of enabling TLS 1.0 in the Security Settings window of the Cisco ISE GUI (Administration > System > Settings > Security Settings). Enabling TLS 1.0 in the Security Settings window is related to the EAP protocol only and does not impact ERS APIs.

Note: Bulk Delete operations are not supported by ISE. NAD deletion has to be performed one at a time.
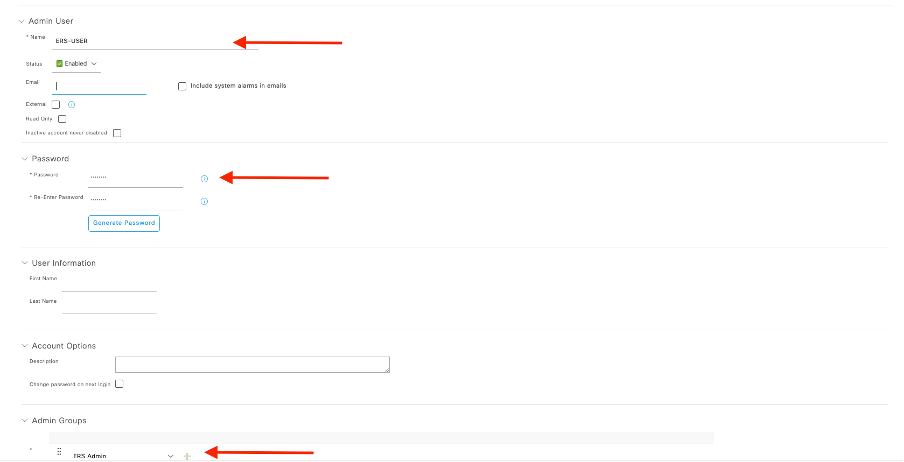
Create ERS Admin
Create a Cisco ISE Administrator, assign a password, and then add a user to the admin group as ERS Admin. You can leave the rest of the configuration empty.
Set up Postman
Download or use the the online version of Postman .
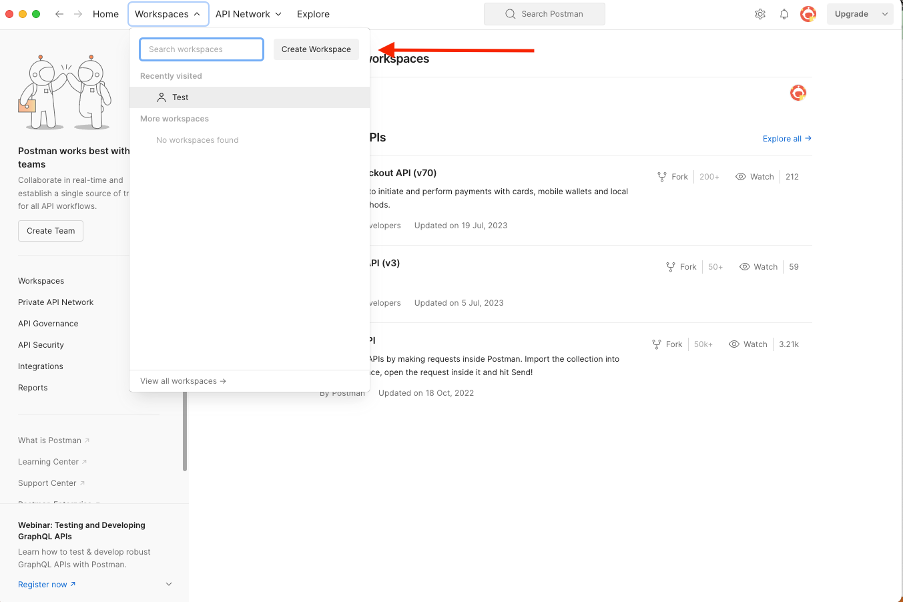
- Create a user and create a workspace by clicking Create Workspace under the Workspaces tab.
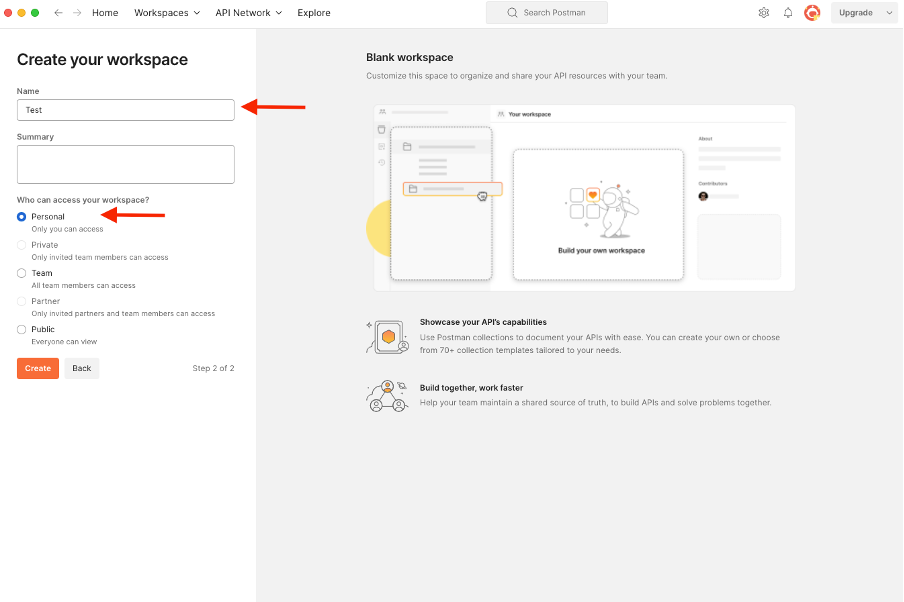
2. Select Blank Workspace and assign a name to the workspace. You can add a description and make it public. For this example Personal is selected.
Once you have created the workspace, you can now configure our API calls.
Get NAD Name and ID
Before you start deleting NADs you must first know either the Name or the ID of the NAD. The NAD name is easily obtained from the NAD list on ISE but the ID is only obtainable from a GET API call. The same API call not only returns the NAD ID but also the name as well as the description if any was added during the NAD configuration.
To configure the GET call, first access the ISE ERS SDK (Software Developer Kit). This tool compiles the whole list of API calls ISE can perform:
- Navigate to https://{ise-ip}/ers/sdk
- Login using your ISE Admin credentials.
- Now expand the API Documentation
- Scroll down until you find Network Device and click on it.
- Under this option you can now find all the available operations you can perform for Network Devices on ISE. Select Get-All
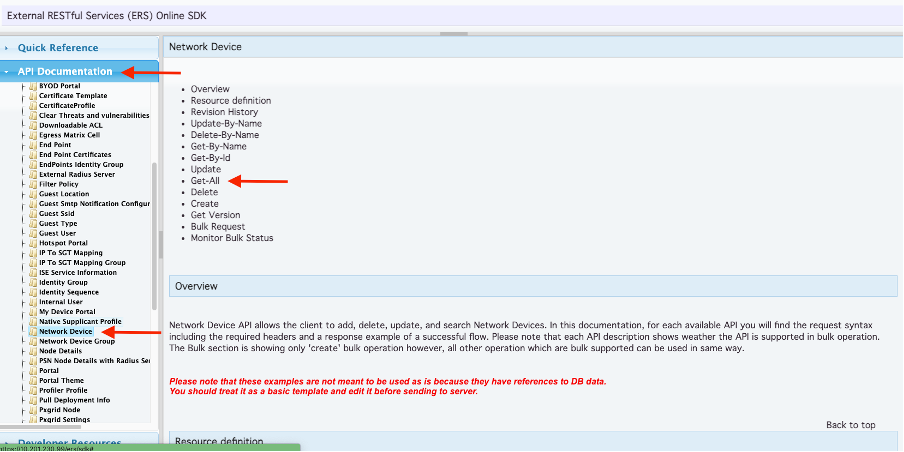
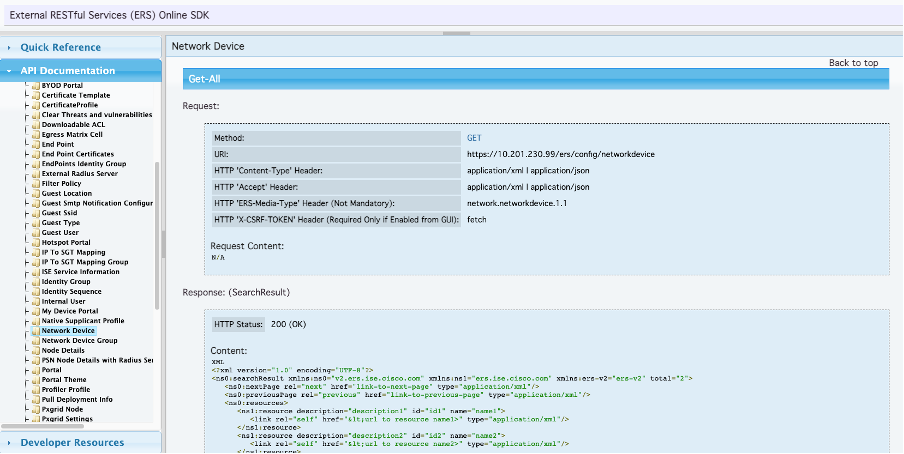
6. You can now see the configuration required to perform the API call on any Rest Client as well as an expected response example.
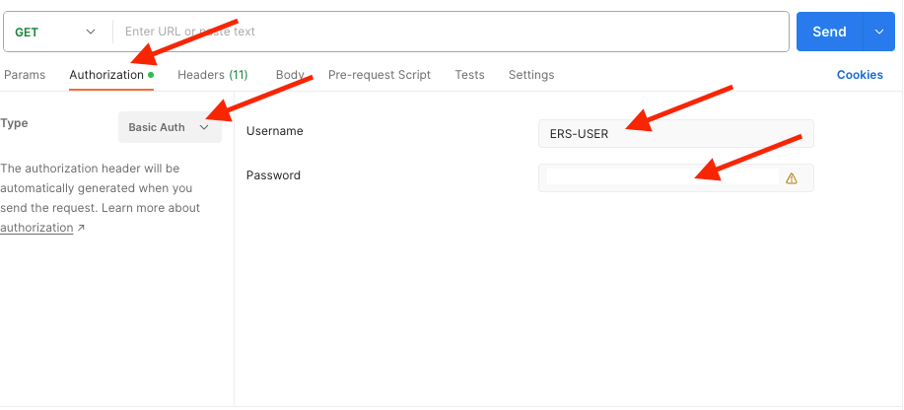
7. Back to Postman, configure basic authentication to ISE. Under the Authorization tab, select Basic Auth as the authentication type and add the ISE ERS User credentials previously created on ISE.

Note: The password are shown as clear text unless variables are configured on Postman
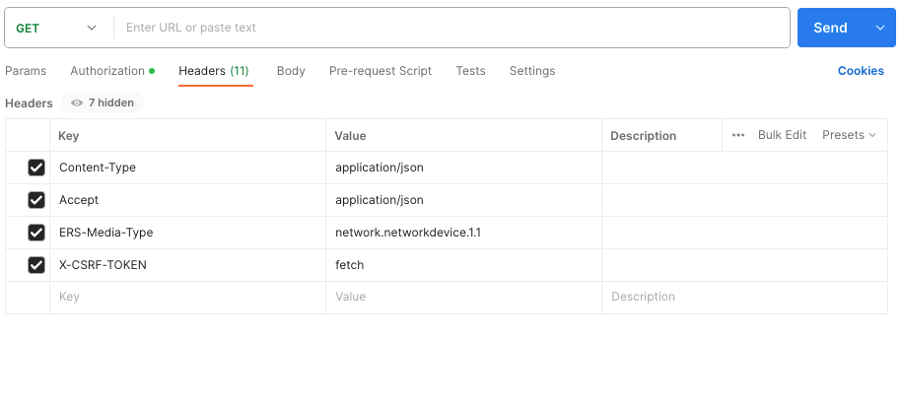
8. Move to the Headers tab and configure the needed headers for the API call as seen in the SDK. For this example JSON is used but xml can be also used. For this example, the header configuration must look like the following:
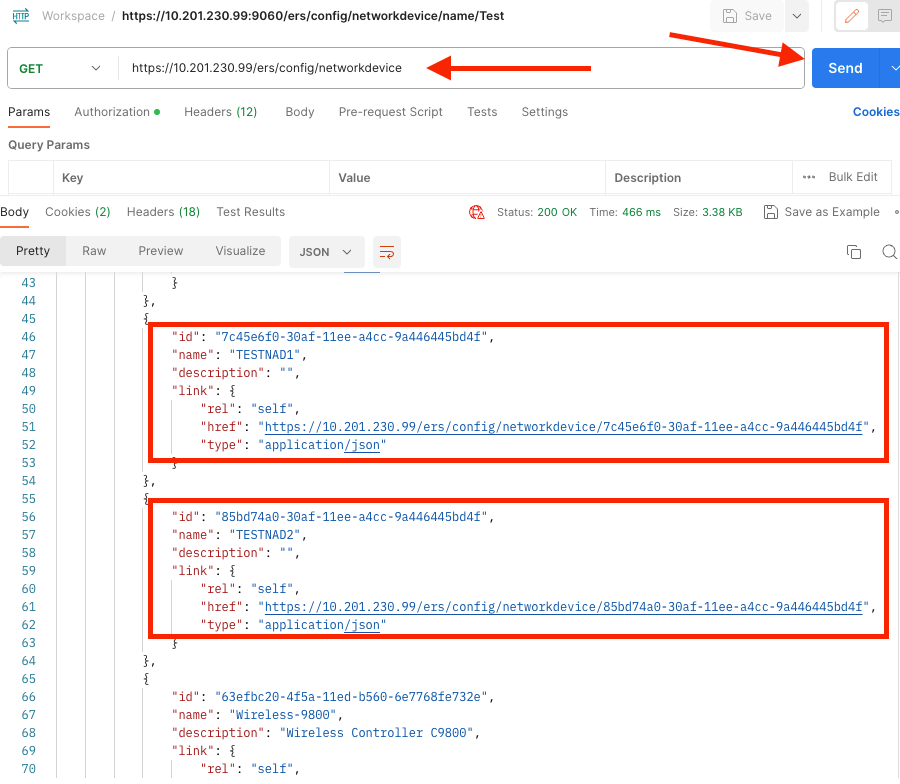
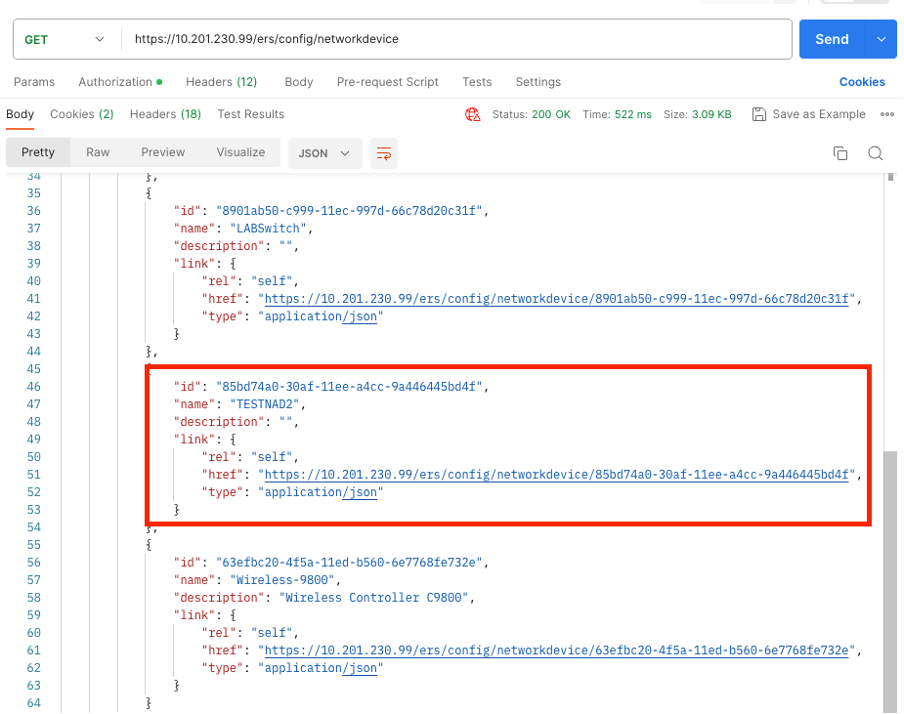
9. Perform the GET call. Select GET as the method. Paste https://{ISE-ip}/ers/config/networkdevice in the field and click Send. If everything was correctly configured, you must see a 200 Ok message and the result.
TESTNAD1 and TESTNAD2 can be deleted using 2 different delete calls.
Delete NAD by ID
Delete TESTNAD1 using the ID collected from the GET Call.
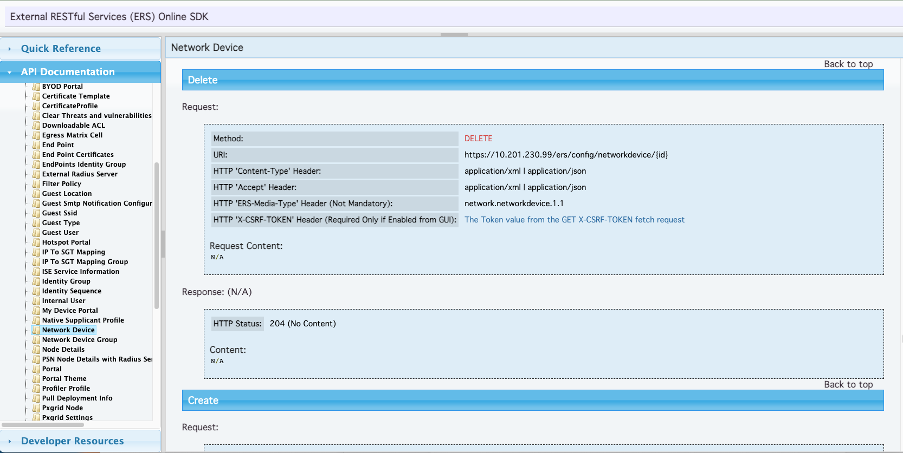
1. On the SDK under the Network Device tab select Delete. As seen before here are the headers required to perform the call as well as the expected response
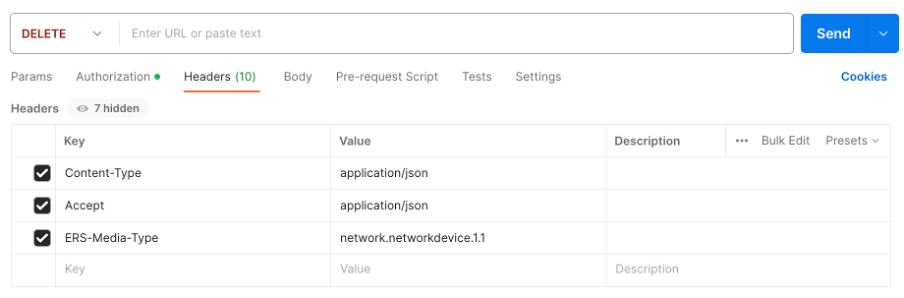
2.Given that the headers are similar to the GET call and that you are performing the DELETE call on the same ISE, duplicate the previous call and change the needed variables. At the end, the header configuration must look like this:
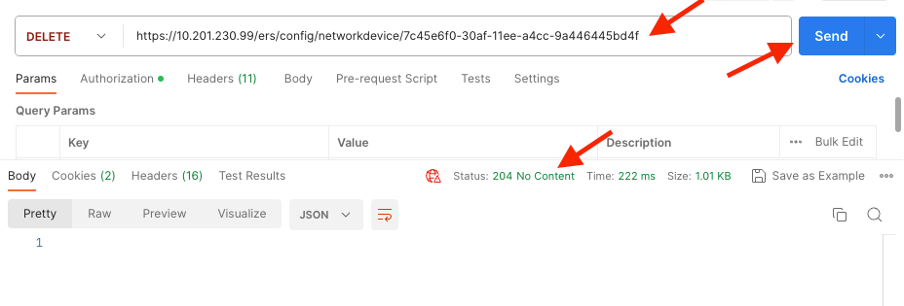
3. Now, delete TESTNAD1. Select DELETE as the method. Paste https://{ISE-ip}/ers/config/networkdevice/{id} in the field, replace {id} by the actual ID of the NAD seen from the GET call, and click Send. If everything was correctly configured, you must see a 204 No Content message and the result empty.
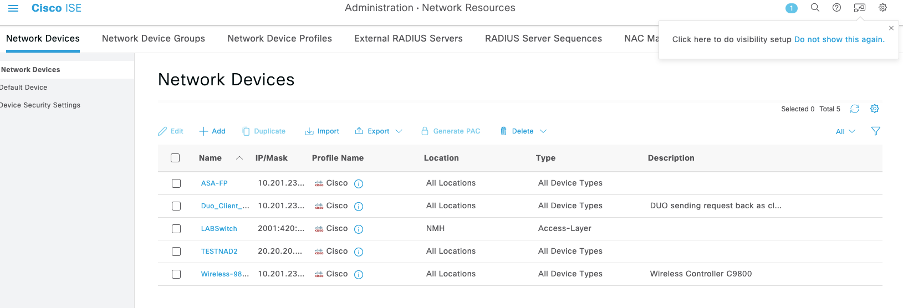
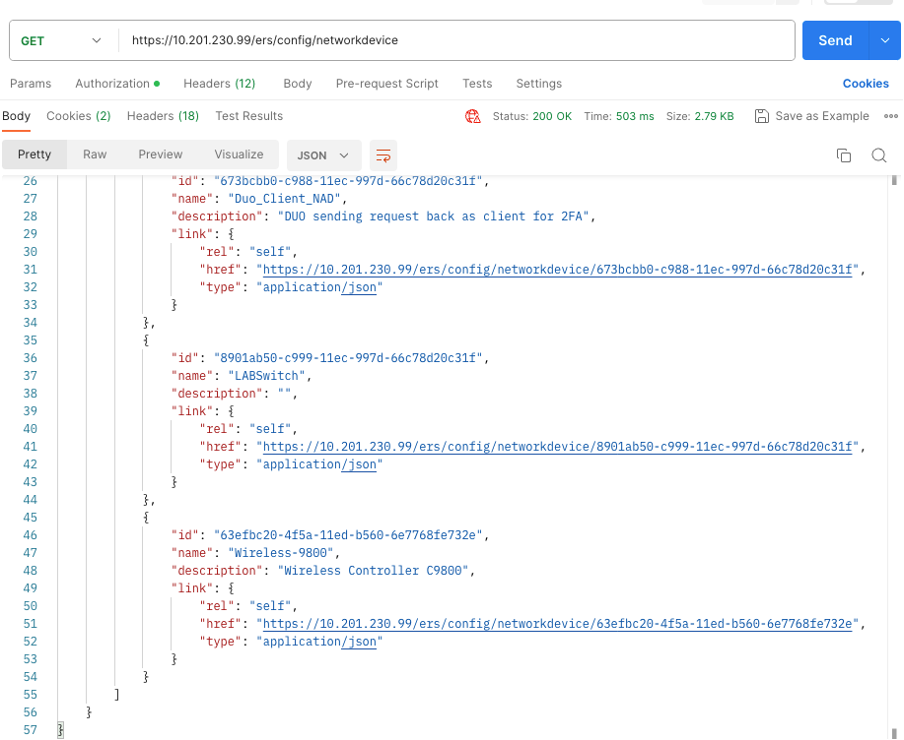
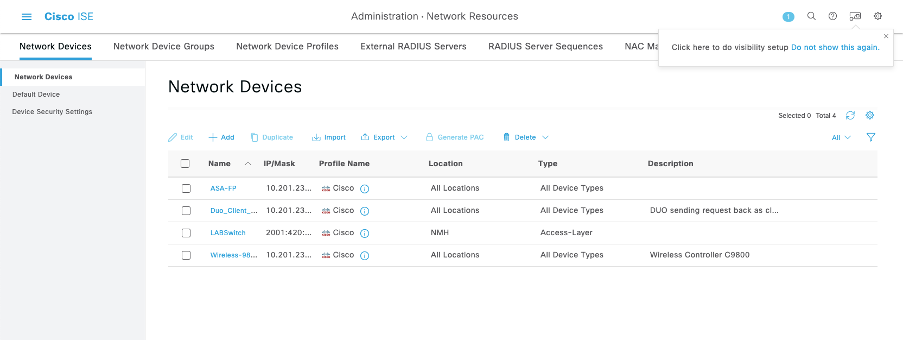
4. Confirm if the NAD was deleted by performing the GET call again or by checking the ISE NAD list. Note that TESTNAD1 no longer exists.
Delete NAD by Name
Delete TESTNAD2 using the name collected from the GET Call or from the NAD list of the ISE GUI.
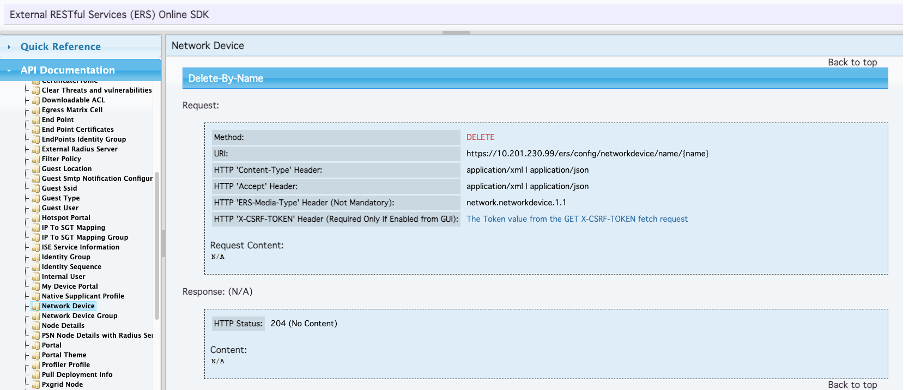
- On the SDK under the Network Device tab select Delete-by-Name. As seen before here are the headers required to perform the call as well as the expected response.
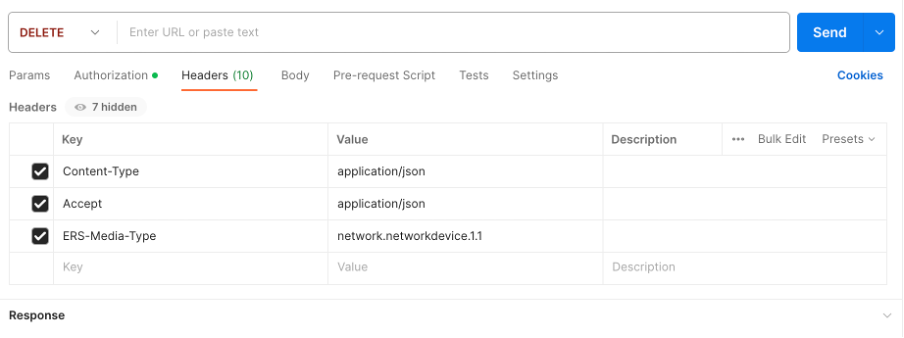
2. Given that the headers are similar to the GET call and that you are performing the DELETE call on the same ISE, duplicate the previous call and change the needed variables. At the end, the header configuration must look like this:
3. Delete TESTNAD2. Select DELETE as the method. Paste https://{ISE-ip}/ers/config/networkdevice/name/{name} in the field, replace {name} by the actual name of the NAD seen from the GET call or from the ISE GUI, and click Send. If everything was correctly configured, you must see a 204 No Content message and the result empty.
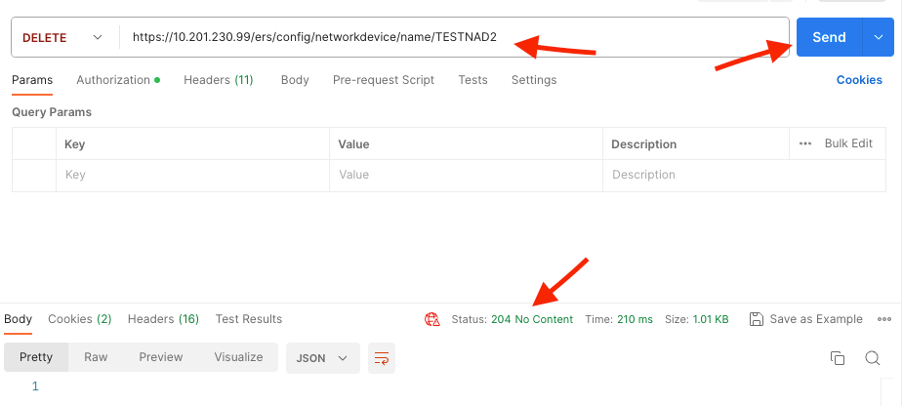
4. Confirm if the NAD was deleted by performing the GET call again or by checking the ISE NAD list. Note that TESTNAD2 no longer exists.
Verify
If you are able to access the API service GUI page, for example, https://{iseip}:{port}/api/swagger-ui/index.html or https://{iseip}:9060/ers/sdk, it means the API service is working as expected.
Troubleshoot
- All REST operations are audited and the logs are logged in the system logs.
- To troubleshoot issues that are related to the Open APIs, set the Log Level for the apiservice component to DEBUG in the Debug Log Configuration window.
- To troubleshoot issues relating to the ERS APIs, set the Log Level for the ers component to DEBUG in the Debug Log Configuration window. To view this window, navigate to the Cisco ISE GUI, click the Menu icon and choose Operations > Troubleshoot > Debug Wizard > Debug Log Configuration.
- You can download the logs from the Download Logs window. To view this window, navigate to the Cisco ISE GUI, click the Menu icon and choose Operations > Troubleshoot > Download Logs.
- You can choose to download either a support bundle from the Support Bundle tab by clicking the Download button under the tab, or download the api-service debug logs from the Debug Logs tab by clicking the Log File value for the api-service debug log.





















 Feedback
Feedback