ESA Centralizing Policy, Virus, and Outbreak Quarantine (PVO) Cannot be Enabled
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes a problem encountered where the Centralizing Policy, Virus, and Outbreak Quarantine (PVO) cannot be enabled on the Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA) because the Enable button is grayed out and offers a solution to the problem.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- How to enable PVO on the Security Management Appliance (SMA).
- How to add the PVO Service to each managed ESA.
- How to configure migration of PVO.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- SMA Version 8.1 and later
- ESA Version 8.0 and later
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
Messages processed by certain filters, policies, and scanning operations on an ESA can be placed into quarantines to temporarily hold them for further action. In some cases, it appears that the PVO cannot be enabled on the ESA although it was properly configured on the SMA and the Migration Wizard was used. The button to enable this feature on the ESA is usually still grayed out because the ESA is not able to connect to the SMA on Port 7025.
Problem
On the ESA, the Enable button is grayed out.
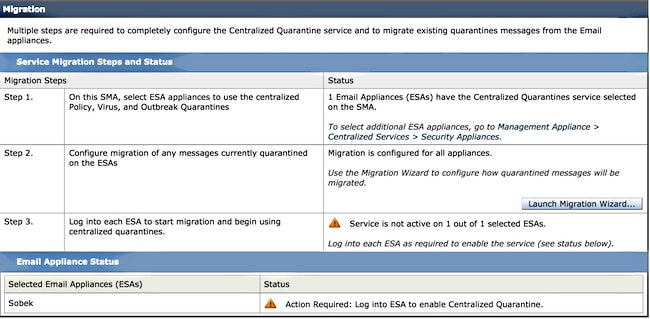
The SMA shows service not active and action required
Solution
There are several scenarios, which are described here.
Scenario 1
On the SMA, run the status command on the CLI in order to ensure the appliance is in an online state. If the SMA is offline, the PVO cannot be enabled on the ESA because the connection fails.
sma.example.com> status
Enter "status detail" for more information.
Status as of: Mon Jul 21 11:57:38 2014 GMT
Up since: Mon Jul 21 11:07:04 2014 GMT (50m 34s)
Last counter reset: Never
System status: Offline
Oldest Message: No Messages
If the SMA is offline, run the resume command in order to bring it back online, which starts the cpq_listener.
sma.example.com> resume
Receiving resumed for euq_listener, cpq_listener.
Scenario 2
After you use the Migration Wizard on the SMA, it is important to commit the changes. The [Enable...] button on the ESA remains grayed out if you do not commit changes.
- Log into the SMA and ESA with the Administrator account, not the Operator (or other account types) or the setup can be performed but the [Enable...] button will be grayed out on the ESA side.
- On the SMA , choose Management Appliance > Centralized Services > Policy, Virus, and Outbreak Quarantines.
- Click Launch Migration Wizard and choose a migration method.
- Submit and commit your changes.
Scenario 3
If the ESA has been configured with a default delivery interface via the deliveryconfig command and if that default interface has no connectivity towards the SMA because it resides in a different subnet or there is no route, the PVO cannot be enabled on the ESA.
Here is an ESA with default delivery interface configured to interface In:
mx.example.com> deliveryconfig
Default interface to deliver mail: In
Here is an ESA connectivity test from interface In to SMA Port 7025:
mx.example.com> telnet
Please select which interface you want to telnet from.
1. Auto
2. In (192.168.1.1/24: mx.example.com)
3. Management (10.172.12.18/24: mgmt.example.com)
[1]> 2
Enter the remote hostname or IP address.
[]> 10.172.12.17
Enter the remote port.
[25]> 7025
Trying 10.172.12.17...
telnet: connect to address 10.172.12.17: Operation timed out
telnet: Unable to connect to remote host
In order to solve this problem, configure the default interace to Auto where the ESA uses the correct interface automatically.
mx.example.com> deliveryconfig
Default interface to deliver mail: In
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- SETUP - Configure mail delivery.
[]> setup
Choose the default interface to deliver mail.
1. Auto
2. In (192.168.1.1/24: mx.example.com)
3. Management (10.172.12.18/24: mgmt.example.com)
[1]> 1
Scenario 4
Connections to the centralized quarantine are Transport Layer Security (TLS)-encrypted by default. If you review the mail log file on the ESA and search for Delivery Connection IDs (DCIDs) to Port 7025 on the SMA, you might see TLS failed errors such as this:
Mon Apr 7 15:48:42 2014 Info: New SMTP DCID 3385734 interface 172.16.0.179
address 172.16.0.94 port 7025
Mon Apr 7 15:48:42 2014 Info: DCID 3385734 TLS failed: verify error: no certificate
from server
Mon Apr 7 15:48:42 2014 Info: DCID 3385734 TLS was required but could not be
successfully negotiated
When you run a tlsverify on the ESA CLI, you see the same.
mx.example.com> tlsverify
Enter the TLS domain to verify against:
[]> the.cpq.host
Enter the destination host to connect to. Append the port (example.com:26) if you are not
connecting on port 25:
[the.cpq.host]> 10.172.12.18:7025
Connecting to 10.172.12.18 on port 7025.
Connected to 10.172.12.18 from interface 10.172.12.17.
Checking TLS connection.
TLS connection established: protocol TLSv1, cipher ADH-CAMELLIA256-SHA.
Verifying peer certificate.
Certificate verification failed: no certificate from server.
TLS connection to 10.172.12.18 failed: verify error.
TLS was required but could not be successfully negotiated.
Failed to connect to [10.172.12.18].
TLS verification completed.
Based on this, the ADH-CAMELLIA256-SHA cipher used in order to negotiate with the SMA causes the SMA to fail to present a peer certificate. Further investigation reveals that all ADH ciphers use anonymous authentication, which does not provide a peer certificate. The fix here is to eliminate anonymous ciphers. In order to do this, change the outgoing cipher list to HIGH:MEDIUM:ALL:-aNULL:-SSLv2.
mx.example.com> sslconfig
sslconfig settings:
GUI HTTPS method: sslv3tlsv1
GUI HTTPS ciphers: RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5:ALL
Inbound SMTP method: sslv3tlsv1
Inbound SMTP ciphers: RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5:ALL
Outbound SMTP method: sslv3tlsv1
Outbound SMTP ciphers: RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5:ALL
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- GUI - Edit GUI HTTPS ssl settings.
- INBOUND - Edit Inbound SMTP ssl settings.
- OUTBOUND - Edit Outbound SMTP ssl settings.
- VERIFY - Verify and show ssl cipher list.
[]> OUTBOUND
Enter the outbound SMTP ssl method you want to use.
1. SSL v2.
2. SSL v3
3. TLS v1
4. SSL v2 and v3
5. SSL v3 and TLS v1
6. SSL v2, v3 and TLS v1
[5]>
Enter the outbound SMTP ssl cipher you want to use.
[RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5:ALL]> HIGH:MEDIUM:ALL:-aNULL:-SSLv2
sslconfig settings:
GUI HTTPS method: sslv3tlsv1
GUI HTTPS ciphers: RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5:ALL
Inbound SMTP method: sslv3tlsv1
Inbound SMTP ciphers: RC4-SHA:RC4-MD5:ALL
Outbound SMTP method: sslv3tlsv1
Outbound SMTP ciphers: HIGH:MEDIUM:ALL:-aNULL:-SSLv2
Choose the operation you want to perform:
- GUI - Edit GUI HTTPS ssl settings.
- INBOUND - Edit Inbound SMTP ssl settings.
- OUTBOUND - Edit Outbound SMTP ssl settings.
- VERIFY - Verify and show ssl cipher list.
[]>
mx.example.com> commit
Scenario 5
The PVO cannot be enabled and shows this type of error message.
Unable to proceed with Centralized Policy, Virus and Outbreak Quarantines
configuration as host1 and host2 in Cluster have content filters / DLP actions
available at a level different from the cluster Level.
The error message can indicate that one of the hosts does not have a DLP feature key applied and DLP is disabled. The solution is to add the missing feature key and apply DLP settings identical as on the host that has the feature key applied. This feature key inconsistency might have the same effect with Outbreak Filters, Sophos Antivirus, and other feature keys.
Scenario 6
The enable button for the PVO will be grayed out if, in a cluster configuration there is machine or group-level configuration for content, message filters, DLP, and DMARC settings. In order to solve this problem, all message and content filters must be moved from machine- or group-level to cluster-level as well as DLP and DMARC settings. Alternatively, you can entirely remove the machine that has machine level configuration from the cluster. Enter the CLI command clusterconfig > removemachine and then join it back to the cluster in order to inherit the cluster configuration.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
23-Jul-2014 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback