PIX/ASA 7.x/FWSM 3.x: Translate Multiple Global IP Addresses to a Single Local IP Address using Static Policy NAT
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration for mapping one local IP address to two or more global IP addresses through policy-based static Network Address Translation (NAT) on the PIX/Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) 7.x software.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Ensure that you meet this requirement before you attempt this configuration:
-
Ensure that you have a working knowledge of the PIX/ASA 7.x CLI and prior experience configuring access-lists and static NAT.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
This specific example uses an ASA 5520. However the policy NAT configurations work on any PIX or ASA appliance that runs 7.x.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure
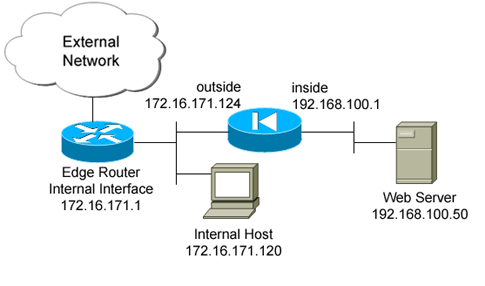
This configuration example has an internal web server at 192.168.100.50, located behind the ASA. The requirement is that the server needs to be accessible to the outside network interface by its internal IP address of 192.168.100.50 and its external address of 172.16.171.125. There is also a security policy requirement that the private IP address of 192.168.100.50 can only be accessed by the 172.16.171.0/24 network. Additionally, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and port 80 traffic are the only protocols allowed inbound to the internal web server. Since there are two global IP addresses mapped to one local IP address, you need to use policy NAT. Otherwise, the PIX/ASA rejects the two one-to-one statics with an overlapping address error.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to obtain more information on the commands used in this section.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup
Configuration
This document uses this configuration.
ciscoasa(config)#show run : Saved : ASA Version 7.2(2) ! hostname ciscoasa enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted names ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 nameif outside security-level 0 ip address 172.16.171.124 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 nameif inside security-level 100 ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 shutdown no nameif no security-level no ip address ! interface Management0/0 nameif management security-level 100 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 management-only ! passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted ftp mode passive !--- policy_nat_web1 and policy_nat_web2 are two access-lists that match the source !--- address we want to translate on. Two access-lists are required, though they !--- can be exactly the same. access-list policy_nat_web1 extended permit ip host 192.168.100.50 any access-list policy_nat_web2 extended permit ip host 192.168.100.50 any !--- The inbound_outside access-list defines the security policy, as previously described. !--- This access-list is applied inbound to the outside interface. access-list inbound_outside extended permit tcp 172.16.171.0 255.255.255.0 host 192.168.100.50 eq www access-list inbound_outside extended permit icmp 172.16.171.0 255.255.255.0 host 192.168.100.50 echo-reply access-list inbound_outside extended permit icmp 172.16.171.0 255.255.255.0 host 192.168.100.50 echo access-list inbound_outside extended permit tcp any host 172.16.171.125 eq www access-list inbound_outside extended permit icmp any host 172.16.171.125 echo-reply access-list inbound_outside extended permit icmp any host 172.16.171.125 echo pager lines 24 logging asdm informational mtu management 1500 mtu inside 1500 mtu outside 1500 no failover icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1 no asdm history enable arp timeout 14400 !--- This first static allows users to reach the translated global IP address of the !--- web server. Since this static appears first in the configuration, for connections !--- initiated outbound from the internal web server, the ASA translates the source !--- address to 172.16.171.125. static (inside,outside) 172.16.171.125 access-list policy_nat_web1 !--- The second static allows networks to access the web server by its private !--- IP address of 192.168.100.50. static (inside,outside) 192.168.100.50 access-list policy_nat_web2 !--- Apply the inbound_outside access-list to the outside interface. access-group inbound_outside in interface outside route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.171.1 1 timeout xlate 3:00:00 timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02 timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00 timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00 timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute http server enable http 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 management no snmp-server location no snmp-server contact snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart telnet timeout 5 ssh timeout 5 console timeout 0 ! class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters message-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy class inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map inspect ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect rsh inspect rtsp inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect skinny inspect sunrpc inspect xdmcp inspect sip inspect netbios inspect tftp ! service-policy global_policy global prompt hostname context |
Verify
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
-
On upstream IOS® router 172.16.171.1, verify you can reach both global IP addresses of the web server via the ping command.
router#ping 172.16.171.125 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.171.125, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms router#ping 192.168.100.50 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.100.50, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
-
On the ASA, verify that you see the translations that are built in the translation (xlate) table.
ciscoasa(config)#show xlate global 192.168.100.50 2 in use, 28 most used Global 192.168.100.50 Local 192.168.100.50 ciscoasa(config)#show xlate global 172.16.171.125 2 in use, 28 most used Global 172.16.171.125 Local 192.168.100.50
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
If your ping or connection is unsuccessful, attempt to use syslogs to determine if there are any problems with the translation configuration. On a lightly used network (such as a lab environment), the logging buffer size is usually sufficient for troubleshooting the problem. Otherwise, you need to send the syslogs to an external syslog server. Enable logging to the buffer at level 6 in order to see if the configuration is correct in these syslog entries.
ciscoasa(config)#logging buffered 6
ciscoasa(config)#logging on
!--- From 172.16.171.120, initiate a TCP connection to port 80 to both the external !--- (172.16.171.125) and internal addresses (192.168.100.50).
ciscoasa(config)#show log
Syslog logging: enabled
Facility: 20
Timestamp logging: disabled
Standby logging: disabled
Deny Conn when Queue Full: disabled
Console logging: disabled
Monitor logging: disabled
Buffer logging: level debugging, 4223 messages logged
Trap logging: disabled
History logging: disabled
Device ID: disabled
Mail logging: disabled
ASDM logging: level informational, 4032 messages logged
%ASA-5-111008: User 'enable_15' executed the 'clear logging buffer' command.
%ASA-7-609001: Built local-host outside:172.16.171.120
%ASA-7-609001: Built local-host inside:192.168.100.50
%ASA-6-302013: Built inbound TCP connection 67 for outside:172.16.171.120/33687
(172.16.171.120/33687) to inside:192.168.100.50/80 (172.16.171.125/80)
%ASA-6-302013: Built inbound TCP connection 72 for outside:172.16.171.120/33689
(172.16.171.120/33689) to inside:192.168.100.50/80 (192.168.100.50/80)
If you see translation errors in the log, double check your NAT configurations. If you do not observe any syslogs, use the capture function on the ASA to attempt to capture the traffic on the interface. In order to set up a capture, you must first specify an access-list to match on a specific type of traffic or TCP flow. Next, you must apply this capture to one or more interfaces in order to start to capture packets.
!--- Create a capture access-list to match on port 80 traffic to !--- the external IP address of 172.16.171.125. !--- Note: These commands are over two lines due to spatial reasons.
ciscoasa(config)#access-list acl_capout permit tcp host 172.16.171.120
host 172.16.171.125 eq 80
ciscoasa(config)#access-list acl_capout permit tcp host 172.16.171.125
eq 80 host 172.16.171.120
ciscoasa(config)#
!--- Apply the capture to the outside interface.
ciscoasa(config)#capture capout access-list acl_capout interface outside
!--- After you initiate the traffic, you see output similar to this when you view !--- the capture. Note that packet 1 is the SYN packet from the client, while packet !--- 2 is the SYN-ACK reply packet from the internal server. If you apply a capture !--- on the inside interface, in packet 2 you should see the server reply with !--- 192.168.100.50 as its source address.
ciscoasa(config)#show capture capout
4 packets captured
1: 13:17:59.157859 172.16.171.120.21505 > 172.16.171.125.80: S
2696120951:2696120951(0) win 4128 <mss 1460>
2: 13:17:59.159446 172.16.171.125.80 > 172.16.171.120.21505: S
1512093091:1512093091(0) ack 2696120952 win 4128 <mss 536>
3: 13:17:59.159629 172.16.171.120.21505 > 172.16.171.125.80: .
ack 1512093092 win 4128
4: 13:17:59.159873 172.16.171.120.21505 > 172.16.171.125.80: .
ack 1512093092 win 4128
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
27-Dec-2006 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback