IPsec LAN-to-LAN Tunnel Between a Catalyst 6500 with the VPN Service Module and a Cisco IOS Router Configuration Example
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to create an IPsec LAN-to-LAN tunnel between a Cisco Catalyst 6500 series switch with the VPN Acceleration service module and a Cisco IOS® router.
Prerequisites
Requirements
There are no specific requirements for this document.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(14)SY2 for the Catalyst 6000 Supervisor Engine, with the IPsec VPN service module
-
Cisco 3640 router that runs Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(4)T
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
For more information on document conventions, refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Background Information
The Catalyst 6500 VPN service module has two Gigabit Ethernet (GE) ports with no externally visible connectors. These ports are addressable for configuration purposes only. Port 1 is always the inside port. This port handles all traffic from and to the inside network. The second port (port 2) handles all traffic from and to the WAN or outside networks. These two ports are always configured in 802.1Q trunking mode. The VPN service module uses a technique called Bump In The Wire (BITW) for packet flow.
Packets are processed by a pair of VLANs, one Layer 3 inside VLAN and one Layer 2 outside VLAN. The packets, from the inside to the outside, are routed through a method called Encoded Address Recognition Logic (EARL) to the inside VLAN. After it encrypts the packets, the VPN service module uses the corresponding outside VLAN. In the decryption process, the packets from the outside to the inside are bridged to the VPN service module using the outside VLAN. After the VPN service module decrypts the packet and maps the VLAN to the corresponding inside VLAN, EARL routes the packet to the appropriate LAN port. The Layer 3 inside VLAN and the Layer 2 outside VLANs are joined together by issuing the crypto connect vlan command. There are three types of ports in the Catalyst 6500 series switches:
-
Routed ports—By default, all Ethernet ports are routed ports. These ports have a hidden VLAN associated with them.
-
Access ports—These ports have an external or VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) VLAN associated with them. You can associate more than one port to a defined VLAN.
-
Trunk ports—These ports carry many external or VTP VLANs, on which all packets are encapsulated with an 802.1Q header.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to find more information on the commands used in this document.
Network Diagram
This document uses the network setup shown in this diagram:
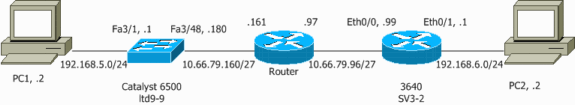
Configuration for IPsec Using a Layer 2 Access or Trunk Port
Perform these steps to configure IPsec with the help of a Layer 2 access or trunk port for the outside physical interface.
-
Add the inside VLANs to the inside port of the VPN service module.
Assume that the VPN service module is on slot 4. Use VLAN 100 as the inside VLAN and VLAN 209 as the outside VLAN. Configure the VPN service module GE ports like this:
interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk
-
Add the VLAN 100 interface and the interface where the tunnel is terminated (which, in this case, is interface Vlan 209, as shown here).
interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 interface Vlan209 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100
-
Configure the outside physical port as an access or trunk port (which, in this case, is FastEthernet 3/48, as shown here).
!--- This is the configuration that uses an access port. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport access vlan 209 switchport mode access !--- This is the configuration that uses a trunk port. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk
-
Create the Bypass NAT. Add these entries to the no nat statement in order to exempt the nating between these networks:
access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
-
Create your crypto configuration and the access control list (ACL) that defines the traffic to be encrypted.
-
Create an ACL (in this case, ACL 100) that defines the traffic from the inside network 192.168.5.0/24 to the remote network 192.168.6.0/24, like this:
access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
-
Define your Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) policy proposals, like this:
crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
-
Issue this command (in this example) to use and define pre-shared keys.
crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99
-
Define your IPsec proposals, like this:
crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
-
Create your crypto map statement, like this:
crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100
-
-
Apply the crypto map to the VLAN 100 interface, like this:
interface vlan100 crypto map cisco
These configurations are used.
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
!--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. !--- This indicates that Internet Key Exchange (IKE) !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- security associations (SAs) to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! no spanning-tree vlan 100 ! ! ! interface FastEthernet3/1 ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 ! !--- This is the outside Layer 2 port that allows VLAN !--- 209 traffic to enter. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk ! interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- VLAN 100 is defined as the Interface VLAN (IVLAN). switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable ! interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- The Port VLAN (PVLAN) configuration is handled transparently by !--- the VPN service module without user configuration !--- or involvement. It also is not shown in the configuration. !--- Note: For every IVLAN, a corresponding PVLAN exists. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IVLAN that is configured to intercept the traffic !--- destined to the secure port on which the inside port !--- of the VPN service module is the only port present. interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 crypto map cisco !--- This is the secure port that is a virtual Layer 3 interface. !--- This interface purposely does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. interface Vlan209 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100 ! ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.161 global (outside) 1 interface !--- NAT 0 prevents NAT for networks specified in the ACL inside_nat0_outbound. nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 !--- This access list (inside_nat0_outbound) is used with the nat zero command. !--- This prevents traffic which matches the access list from undergoing !--- network address translation (NAT). The traffic specified by this ACL is !--- traffic that is to be encrypted and !--- sent across the VPN tunnel. This ACL is intentionally !--- the same as (100). !--- Two separate access lists should always be used in this configuration. access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 |
| Cisco IOS Router |
|---|
SV3-2#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1268 bytes ! version 12.3 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname SV3-2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ip ssh break-string no ftp-server write-enable ! !--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.180 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. This indicates that IKE !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.180 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! !--- Apply the crypto map to the interface. interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.66.79.99 255.255.255.224 half-duplex crypto map cisco ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 half-duplex no keepalive ! ! ip http server no ip http secure-server ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.97 ! ! !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Configuration for IPsec Using a Routed Port
Perform these steps to configure IPsec with the help of a Layer 3 routed port for the outside physical interface.
-
Add the inside VLANs to the inside port of the VPN service module.
Assume that the VPN service module is on slot 4. Use VLAN 100 as the inside VLAN and VLAN 209 as the outside VLAN. Configure the VPN service module GE ports like this:
interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk
-
Add the VLAN 100 interface and the interface where the tunnel is terminated (which, in this case, is FastEthernet3/48, as shown here).
interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100
-
Create the Bypass NAT. Add these entries to the no nat statement in order to exempt the nating between these networks:
access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
-
Create your crypto configuration and the ACL that defines the traffic to be encrypted.
-
Create an ACL (in this case, ACL 100) that defines the traffic from the inside network 192.168.5.0/24 to the remote network 192.168.6.0/24, like this:
access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
-
Define your ISAKMP policy proposals, like this:
crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
-
Issue this command (in this example) to use and define pre-shared keys:
crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99
-
Define your IPsec proposals, like this:
crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
-
Create your crypto map statement, like this:
crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100
-
-
Apply the crypto map to the VLAN 100 interface, like this:
interface vlan100 crypto map cisco
These configurations are used.
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
!--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. This indicates that IKE !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! no spanning-tree vlan 100 ! ! ! interface FastEthernet3/1 ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 !--- This is the secure port that is configured in routed port mode. !--- This routed port mode does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to the VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. This is the Layer 2 port VLAN on which the !--- outside port of the VPN service module also belongs. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100 ! interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- VLAN 100 is defined as the IVLAN. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable ! interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- The PVLAN configuration is handled transparently by the !--- VPN service module without user configuration !--- or involvement. It also is not shown in the configuration. !--- Note: For every IVLAN, a corresponding PVLAN exists. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IVLAN that is configured to intercept the traffic !--- destined to the secure port on which the inside port of the !--- VPN service module is the only port present. interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 crypto map cisco ! ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.161 ! global (outside) 1 interface !--- NAT 0 prevents NAT for networks specified in the ACL inside_nat0_outbound. nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 !--- This access list (inside_nat0_outbound) is used with the nat zero command. !--- This prevents traffic which matches the access list from undergoing !--- network address translation (NAT). The traffic specified by this ACL is !--- traffic that is to be encrypted and !--- sent across the VPN tunnel. This ACL is intentionally !--- the same as (100). !--- Two separate access lists should always be used in this configuration. access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 |
| Cisco IOS Router |
|---|
SV3-2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1268 bytes ! version 12.3 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname SV3-2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ip ssh break-string no ftp-server write-enable ! !--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.180 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. This indicates that IKE !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.180 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! !--- Apply the crypto map to the interface. interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.66.79.99 255.255.255.224 half-duplex crypto map cisco ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 half-duplex no keepalive ! ! ip http server no ip http secure-server ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.97 ! ! !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Verify
This section provides the information to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
-
show crypto ipsec sa—Shows the settings used by the current IPsec SAs.
-
show crypto isakmp sa—Shows all the current IKE SAs at a peer.
-
show crypto vlan—Shows the VLAN associated with the crypto configuration.
-
show crypto eli—Shows the VPN service module statistics.
For additional information on verifying and troubleshooting IPsec, refer to IP Security Troubleshooting - Understanding and Using debug Commands.
Troubleshoot
This section provides the information to troubleshoot your configuration.
Troubleshooting Commands
Note: Before you issue debug commands, refer to Important Information on Debug Commands.
-
debug crypto ipsec—Shows the IPsec negotiations of Phase 2.
-
debug crypto isakmp—Shows the ISAKMP negotiations of Phase 1.
-
debug crypto engine—Shows the traffic that is encrypted.
-
clear crypto isakmp—Clears the SAs related to Phase 1.
-
clear crypto sa—Clears the SAs related to Phase 2.
For additional information on verifying and troubleshooting IPsec, refer to IP Security Troubleshooting - Understanding and Using debug Commands.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback