Introduction
This document describes how to deploy L3 Ethernet VPN (EVPN) over Segment Routing (SR) Multiprotocol Label Switching on Nexus 9300 with external BGP.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- L3VPN
- EVPN
- SR
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- SPINE Hardware - 9336C-FX that runs Release 10.2(2)
- LEAF Hardware - 93240YC-FX2 that runs Release 10.2(2)
- CLIENT - 92160YC-X (Host-1), Catlyst-3850 (Host-2)
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
MPLS L3VPN Recap
A VPN is:
-
An IP-based network that delivers private network services over a public infrastructure.
-
A set of sites that are allowed to communicate with each other privately over the Internet or other public or private networks.
Conventional VPNs are created by the configuration of a full mesh of tunnels or permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) to all sites in a VPN. This type of VPN is not easy to maintain or expand, as the addition of a new site requires a change to each edge device in the VPN.
MPLS-based VPNs are created in Layer 3 and are based on the peer model. The peer model enables the service provider and the CE to exchange Layer 3 routing information. The service provider relays the data between the CE sites without CE involvement.
MPLS VPNs are easier to manage and expand than conventional VPNs. When a new site is added to an MPLS VPN, only the edge router of the service provider that provides services to the customer site needs to be updated.
These are the components of the MPLS VPN:
-
Provider (P) router- Router in the core of the provider network. PE routers run MPLS switching and do not attach VPN labels to routed packets. VPN labels are used to direct data packets to the correct private network or CE edge router.
-
Provider Edge (PE) router- Router that attaches the VPN label to incoming packets based on the interface or subinterface on which they are received, and also attaches the MPLS core labels. A PE router attaches directly to a router.
-
Customer (C) router- Router in the Internet service provider (ISP) or enterprise network.
-
Customer Edge (CE) router- Edge router on the network of the ISP that connects to the PE router on the network. A CE router must interface with a PE router.
Overview of EVPN with L3VPN (MPLS SR)
Data Center (DC) deployments have adopted Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) EVPN or MPLS EVPN for its benefits such as EVPN control-plane learning, multitenancy, seamless mobility, redundancy, and easier POD additions. Similarly, the CORE is either a Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)-based MPLS L3VPN network or a transition from the traditional MPLS L3VPN LDP-based underlay to a more sophisticated solution like SR.
SR is adopted for its benefits such as:
-
Unified interior gateway protocol (IGP) and MPLS control planes
-
Simpler traffic engineering methods
-
Easier configuration
-
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) adoption
EVPN (RFC 7432) is BGP MPLS-based solution that has been used for next-generation Ethernet services in a virtualized data center network. It uses several blocks such as Route.
Distinguisher (RD), Route Target (RT), and Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) from MPLS technologies that exist.
L3 EVPN over SR which was introduced in NXOS 7.0(3)I6(1) release uses the EVPN Type-5 route with MPLS encapsulation. It offers Multi-tenant, Scalability, and High Performance for evolved data center services.
Note: In DC, the data plane can be VXLAN or MPLS.
| Traditional MPLS L3 VPN |
MPLS L3 VPN over SR |
| Main build blocks: RD, RT, and VRF |
Main build blocks: RD, RT, and VRF |
| Underlay Layer for Transport: IGP, LDP, and RSVP-TE |
Underlay Layer for Transport: IGP/BGP-LU and SR-TE |
| Overlay Layer for Service: VPNv4 and VPNv6 |
Overlay Layer for Service: EVPN |
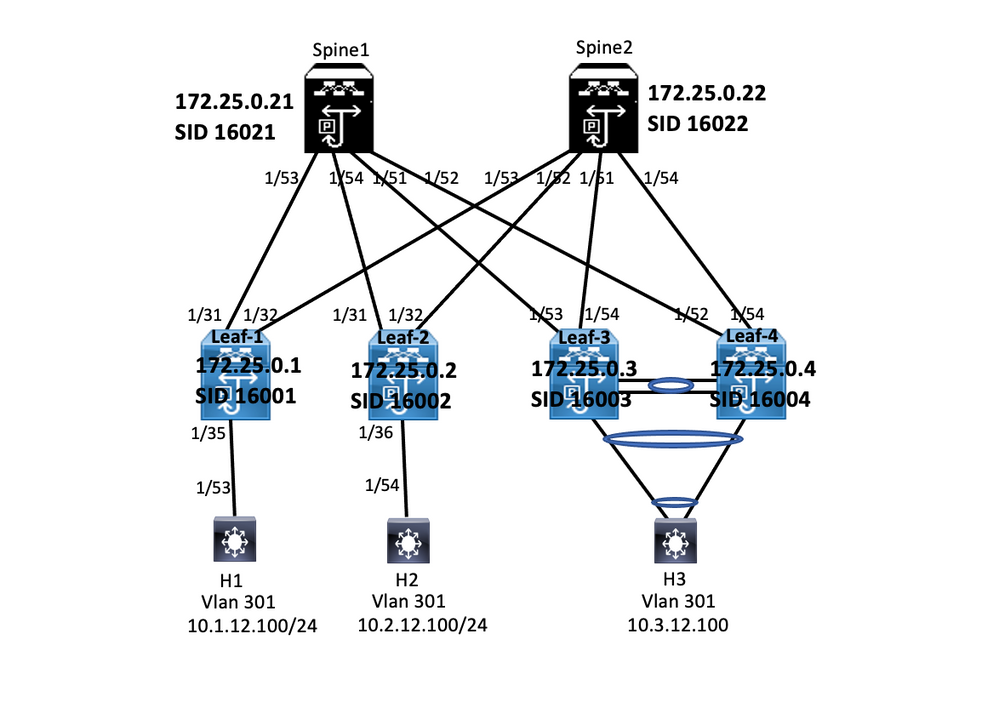
Network Diagram
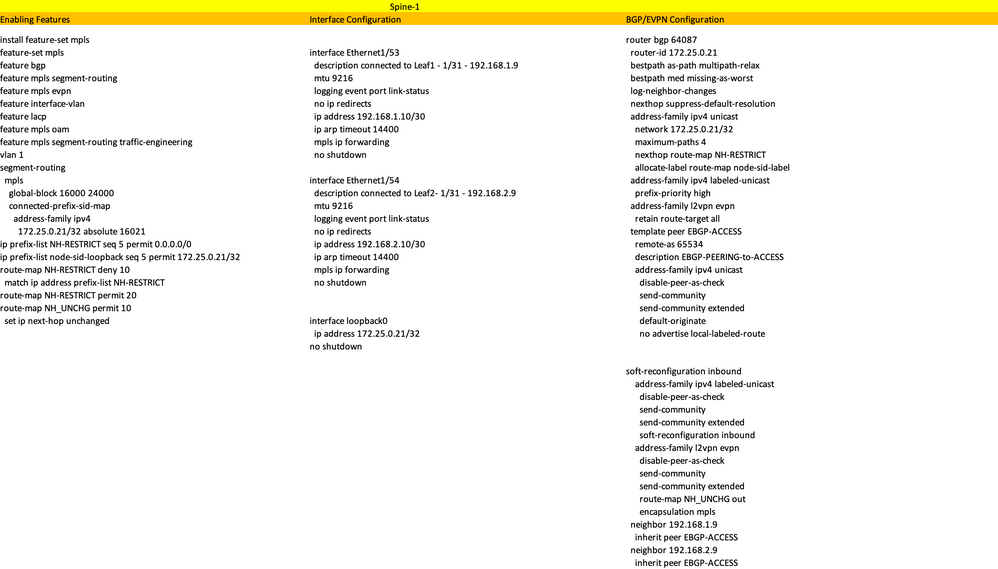
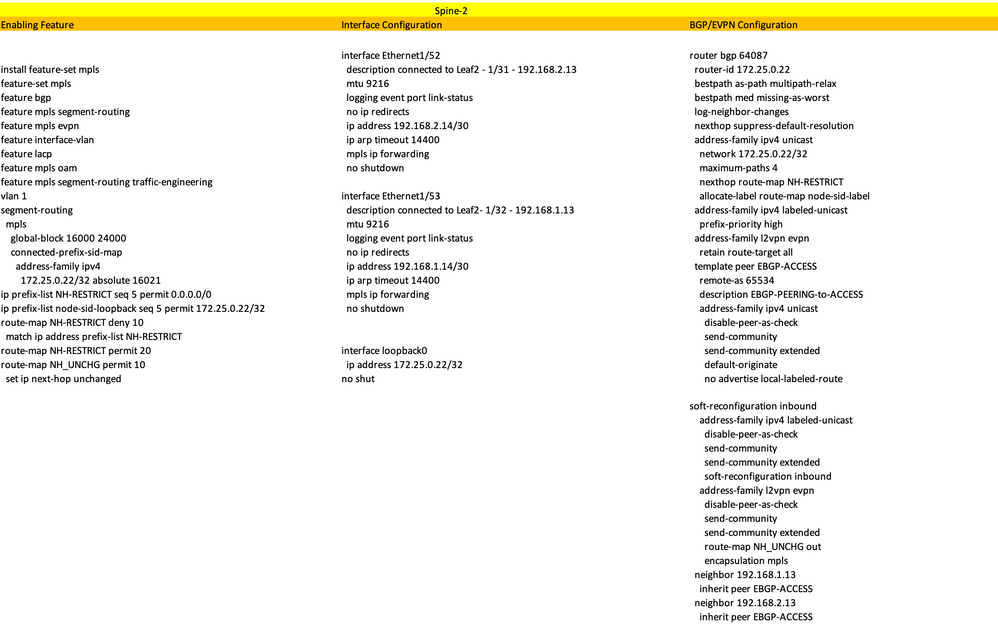
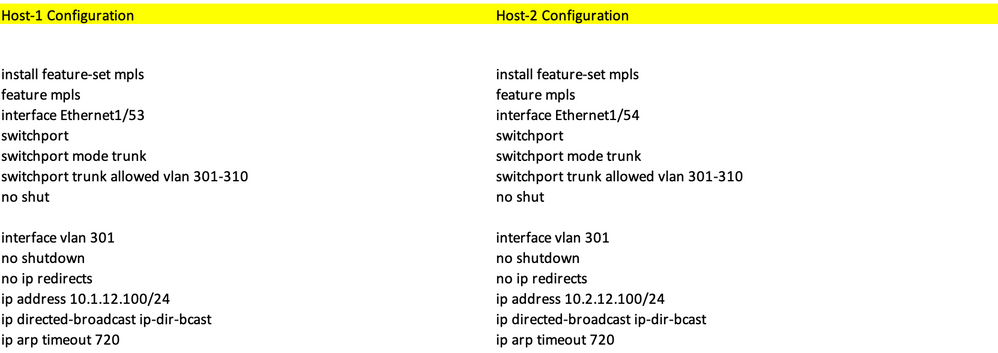
High-Level Configuration
- Install Features
- Configure IP address - Underlay
- Configure IGP/MP - BGP
- Configure VLAN and EVPN Overlay
- Configure e-BGP between Hosts and LEAFs


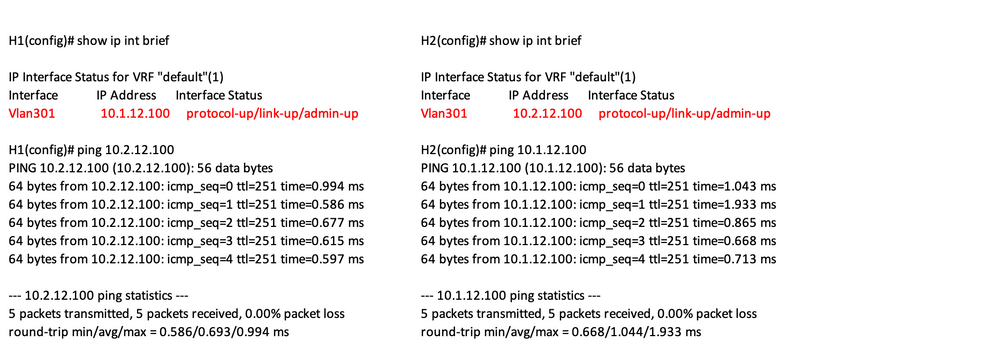
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.












 Feedback
Feedback