Configure IPv6 Black-Holing through Interface Null0
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document describes how to configure Black-Holing in IPv6 through interface Null0. Black Hole Routing is a method that allows the administrator to block undesirable traffic, such as traffic from illegal sources or traffic generated by a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, by dynamically routing the traffic to a dead interface or to a host designed to collect information for investigation, which mitigates the impact of the attack on the network.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Make sure that you meet these requirements before you attempt this configuration:
-
Have an understanding of BGP routing protocol and its operation
-
Have an understanding of the IPv6 Addressing scheme
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the Cisco 7200 Series Router with Cisco IOS® Software Release 15.0(1).
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) in order to find more information on the commands used in this document.
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
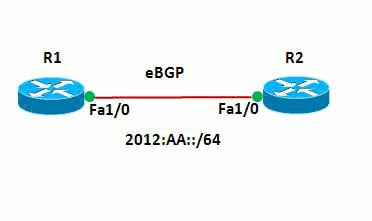
In this network, the routers and R1 and R2 forms an eBGP relationship with each other. The routers use OSPFv3 in order to communicate internally. In router R1, Black-holing is achieved by the configuration of Null0 in such a way that any packets with source address 20:20::20/128 are directed to Null0. In other words all traffic routed to Null0 are dropped.
Sample Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
| Router R1 |
|---|
! hostname R1 ! no ip domain lookup ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ipv6 address AA::1/128 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! interface Loopback10 no ip address ipv6 address AA:10::10/128 ipv6 enable ! interface FastEthernet1/0 no ip address speed auto duplex auto ipv6 address 2012:AA::1/64 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! router bgp 6501 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor BB::1 remote-as 6502 neighbor BB::1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor BB::1 update-source Loopback1 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 redistribute static network AA:10::10/128 neighbor BB::1 activate exit-address-family ! ipv6 route 20:20::20/128 Null0 ipv6 router ospf 10 router-id 1.1.1.1 ! end |
| Router R2 |
|---|
! hostname R2 ! ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef ! ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ipv6 address BB::1/128 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! interface Loopback20 no ip address ipv6 address 20:20::20/128 ipv6 enable ! interface FastEthernet1/0 no ip address speed auto duplex auto ipv6 address 2012:AA::2/64 ipv6 enable ipv6 ospf 10 area 0 ! router bgp 6502 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes no bgp default ipv4-unicast neighbor AA::1 remote-as 6501 neighbor AA::1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor AA::1 update-source Loopback1 ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 network 20:20::20/128 neighbor AA::1 activate exit-address-family ! ipv6 router ospf 10 router-id 2.2.2.2 ! end |
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
In order to verify the eBGP configuration, use the show ipv6 route bgp and show bgp ipv6 unicast commands in router R1.
| Router R1 |
|---|
show ipv6 route R1#show ipv6 route bgp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 7 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, HA - Home Agent, MR - Mobile Router, R - RIP
I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, ND - Neighbor Discovery
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
!--- The router R2 advertises the network 20:20::20/128, !--- but still the routing table is empty.
To check what are the routes received by BGP use the show bgp ipv6 unicast command. R1#show bgp ipv6 unicast
BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 20:20::20/128 BB::1 0 0 6502 I
*> :: 0 32768 ?
*> AA:10::10/128 :: 0 32768 I
!--- Note that the route 20:20::20/128 is received, !--- but it is not installed in the routing table.
|
Use the source as loopback interface 20 in order to try to ping router R1 from the router R2.
R2#ping ipv6 AA:10::10 source lo20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to AA:10::10, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 20:20::20 ..... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) !--- The reason is the ICMP packet reaches !--- router R1 with source address as !--- 20:20::20/128 and therefore gets dropped.
Try ping router R1 from router R2 without the use of the loopback interface as source.
R2#ping AA:10::10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to AA:10::10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/61/180 ms !--- In this case, the ICMP packet has !--- the source address as BB::1.
If the ipv6 route 20:20::20/128 Null0 statement is removed from the router R1, the route 20:20::20/128 advertised by router R2 gets installed in the routing table of router R1. This is the sample output:
| In router R1 |
|---|
R1(config)#no ipv6 route 20:20::20/128 Null0
!--- The Null0 command in removed from router R1.
R1#show bgp ipv6 unicast
BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 20:20::20/128 :: 0 32768 ?
* BB::1 0 0 6502 I
*> AA:10::10/128 :: 0 32768 I
!--- After the removal of the statement, !--- the route 20:20::20/128 is shown as best route.
R1#show ipv6 route bgp
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 7 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, HA - Home Agent, MR - Mobile Router, R - RIP
I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2, IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, ND - Neighbor Discovery
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
B 20:20::20/128 [20/0]
via BB::1
!--- You can see that the route is displayed in routing table.
|
Now try to ping the router R1 from router R2 with the source as loopback interface Lo 20.
R2#ping ipv6 AA:10::10 source lo20 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to AA:10::10, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 20:20::20 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/54/140 ms !--- You can see that the ping is successful.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
30-Jul-2012 |
Initial Release |
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback