Einleitung
In diesem Dokument wird die Behebung von CPU- oder Speicherproblemen auf der Cloud Native Deployment Platform (CNDP) als Session Management Function (SMF) oder Policy Control Function (PCF) beschrieben.
1. Problem Warnhinweis: Hohe CPU/Speicher auf Pod
Das Verständnis der Warnmeldung ist wichtig, um einen guten Anfang bei der Fehlerbehebung zu haben. Unter diesem Link werden alle vorkonfigurierten Standardwarnungen erläutert.
1.1. Warnung für CPU
In diesem Fall wird eine aktive Standardwarnung ausgelöst. Sie heißt k8s-pod-cpu-usage-high .
Wie Sie sehen, ist das mit einem Pod namens verbunden: smf-udp-proxy-0 und es handelt sich um einen Container: k8s_smf-udp-proxy_smf-udp-proxy-0_smf
Sie sehen, dass sich dieser Container im Namespace befindet: smf
alerts active detail k8s-pod-cpu-usage-high 36fbd5e0bbce
severity major
type "Processing Error Alarm"
startsAt 2024-02-23T12:45:44.558Z
source smf-udp-proxy-0
summary "Container: k8s_smf-udp-proxy_smf-udp-proxy-0_smf of pod: smf-udp-proxy-0 in namespace: smf has CPU usage more than 80% for 5min -- VALUE = 131.79654468989753"
labels [ "name: k8s_smf-udp-proxy_smf-udp-proxy-0_smf" "namespace: smf" "pod: smf-udp-proxy-0" ]
Suchen Sie auf Kubernetes master den betroffenen Pod, indem Sie den folgenden Befehl eingeben:
master $ kubectl get pods smf-udp-proxy-0 -n smf
1.2. Erinnerung
In diesem Fall wird eine aktive Standardwarnung ausgelöst. Sie heißt container-memory-usage-high .
Sie können sehen, dass sich auf einen Pod mit dem Namen bezieht: grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct und es handelt sich um einen Container: k8s_istio-proxy_grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct_smf_389290ee-77d1-4ff3-981d-58ea1c8eabdb_0
Dieser Container befindet sich im Namespace:smf
alerts active detail container-memory-usage-high 9065cb8256ba
severity critical
type "Processing Error Alarm"
startsAt 2024-04-25T10:17:38.196Z
source grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct
summary "Pod grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct/k8s_istio-proxy_grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct_smf_389290ee-77d1-4ff3-981d-58ea1c8eabdb_0 uses high memory 94.53%."
labels [ "alertname: container-memory-usage-high" "beta_kubernetes_io_arch: amd64" "beta_kubernetes_io_os: linux" "cluster: smf" "container: istio-proxy" "id: /kubepods/burstable/pod389290ee-77d1-4ff3-981d-58ea1c8eabdb/e127400d9925e841ebfb731ba3b2e13b5ed903caef001448f93489fc6f697ce1" "image: sha256:716ac2efc7d3e3c811564170c48c51fbe97ab4e50824109c11132dc053276ff8" "instance: alcp0200-smf-ims-master-3" "job: kubernetes-cadvisor" "kubernetes_io_arch: amd64" "kubernetes_io_hostname: alcp0200-smf-ims-master-3" "kubernetes_io_os: linux" "monitor: prometheus" "name: k8s_istio-proxy_grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct_smf_389290ee-77d1-4ff3-981d-58ea1c8eabdb_0" "namespace: smf" "pod: grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct" "replica: smf" "severity: critical" "smi_cisco_com_node_type: oam" "smi_cisco_com_node_type_2: service" "smi_cisco_com_node_type_3: session" ]
annotations [ "summary: Pod grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct/k8s_istio-proxy_grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct_smf_389290ee-77d1-4ff3-981d-58ea1c8eabdb_0 uses high memory 94.53%." "type: Processing Error Alarm" ]
Suchen Sie auf Kubernetes master den betroffenen Pod, indem Sie den folgenden Befehl eingeben:
master $ kubectl get pods grafana-dashboard-sgw-765664b864-zwxct -n smf
2. Kubernetes Profiling pro Prozess
2.1. CPU-Profilerstellung (/debug/pprof/profile)
Die CPU-Profilerstellung dient als Technik zur Erfassung und Analyse der CPU-Auslastung eines laufenden Go-Programms.
Es entnimmt regelmäßig eine Stichprobe der Aufrufliste und zeichnet die Informationen auf, sodass Sie analysieren können, wo das Programm die meiste Zeit verbringt.
2.2. Speicherprofilierung (/debug/pprof/heap)
Die Speicherprofilierung bietet Einblicke in die Speicherzuweisungs- und Nutzungsmuster in Ihrer Go-Anwendung.
Es kann Ihnen helfen, Speicherlecks zu identifizieren und die Speichernutzung zu optimieren.
2.3. Goroutine Profiling (/debug/pprof/goroutine)
Goroutine Profiling bietet Einblicke in das Verhalten aller aktuellen Goroutines durch Anzeige ihrer Stapelspuren. Diese Analyse hilft bei der Identifizierung von festsitzenden oder undichten Goroutinen, die die Leistung des Programms beeinflussen können.
2.4. Prof. Port auf einem Kubernetes Pod finden
Command:
master:~$ kubectl describe pod <POD NAME> -n <NAMESPACE> | grep -i pprof
Beispiel:
master:~$ kubectl describe pod udp-proxy-0 -n smf-rcdn | grep -i pprof
PPROF_EP_PORT: 8851
master:~$
3. Vom System zu erfassende Daten
Sammeln Sie während der Problemphase und während der aktiven Warnmeldung in der Common Execution Environment (CEE) die Daten, die die Zeit vor und während/nach der Problemstellung abdecken:
MOE:
cee# show alerts active detail
cee# show alerts history detail
cee# tac-debug-pkg create from yyyy-mm-dd_hh:mm:ss to yyyy-mm-dd_hh:mm:ss
CNDP-Master-Knoten:
General information:
master-1:~$ kubectl get pods <POD> -n <NAMESPACE>
master-1:~$ kubectl pods describe <POD> -n <NAMESPACE>
master-1:~$ kubectl logs <POD> -n <NAMESPACE> -c <CONTAINER>
Login to impacted pod and check top tool:
master-1:~$ kubectl exec -it <POD> -n <NAMESPACE> bash
root@protocol-n0-0:/opt/workspace# top
If pprof socket is enabeled on pod:
master-1:~$ kubectl describe pod <POD NAME> -n <NAMESPACE> | grep -i pprof
master-1:~$ curl http://<POD IP>:<PPROF PORT>/debug/pprof/goroutine?debug=1
master-1:~$ curl http://<POD IP>:<PPROF PORT>/debug/pprof/heap
master-1:~$ curl http://<POD IP>:<PPROF PORT>/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=30
4. Grundlegendes zu den erfassten Prof-Protokollausgaben
4.1. Lesen der Ausgabe von Speicherprofilen (/debug/pprof/heap)
This line indicates that a total of 1549 goroutines were captured in the profile. The top frame (0x9207a9) shows that the function google.golang.org/grpc.(*addrConn).resetTransport is being executed, and the line number in the source code is clientconn.go:1164 .
Jeder Abschnitt, der mit einer Zahl beginnt (z. B. 200), stellt eine Stapelspur eines Goroutine dar.
goroutine profile: total 1549
200 @ 0x4416c0 0x415d68 0x415d3e 0x415a2b 0x9207aa 0x46f5e1
# 0x9207a9 google.golang.org/grpc.(*addrConn).resetTransport+0x6e9 /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/clientconn.go:1164
The first line in each section shows the number of goroutines with the same stack trace. For example, there are 200 goroutines with the same stack trace represented by memory addresses (0x4416c0 , 0x415d68, and more.). The lines that start with # represent the individual frames of the stack trace. Each frame shows the memory address, function name, and the source code location (file path and line number) where the function is defined.
200 @ 0x4416c0 0x45121b 0x873ee2 0x874803 0x89674b 0x46f5e1
# 0x873ee1 google.golang.org/grpc/internal/transport.(*controlBuffer).get+0x121 /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/internal/transport/controlbuf.go:395
# 0x874802 google.golang.org/grpc/internal/transport.(*loopyWriter).run+0x1e2 /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/internal/transport/controlbuf.go:513
# 0x89674a google.golang.org/grpc/internal/transport.newHTTP2Client.func3+0x7a /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/internal/transport/http2_client.go:346
92 @ 0x4416c0 0x45121b 0x873ee2 0x874803 0x897b2b 0x46f5e1
# 0x873ee1 google.golang.org/grpc/internal/transport.(*controlBuffer).get+0x121 /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/internal/transport/controlbuf.go:395
# 0x874802 google.golang.org/grpc/internal/transport.(*loopyWriter).run+0x1e2 /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/internal/transport/controlbuf.go:513
# 0x897b2a google.golang.org/grpc/internal/transport.newHTTP2Server.func2+0xca /opt/workspace/gtpc-ep/pkg/mod/google.golang.org/grpc@v1.26.0/internal/transport/http2_server.go:296
5. Grafana
5.1. CPU-Abfrage
sum(cpu_percent{service_name=~"[[microservice]]"}) by (service_name,instance_id)
Beispiel:
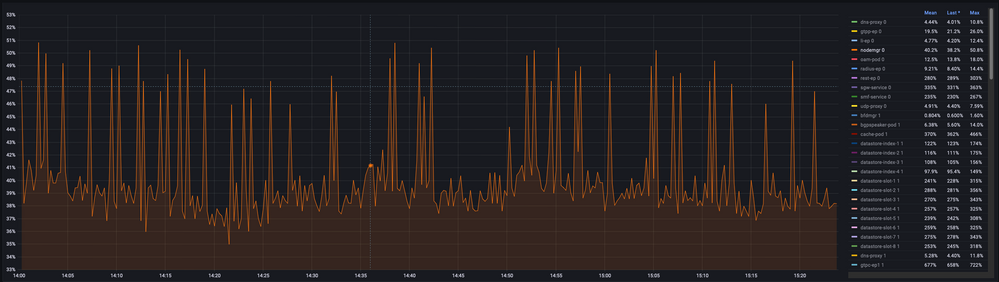
5.2. Speicherabfrage
sum(increase(mem_usage_kb{service_name=~"[[microservice]]"}[15m])) by (service_name,instance_id)
Beispiel:
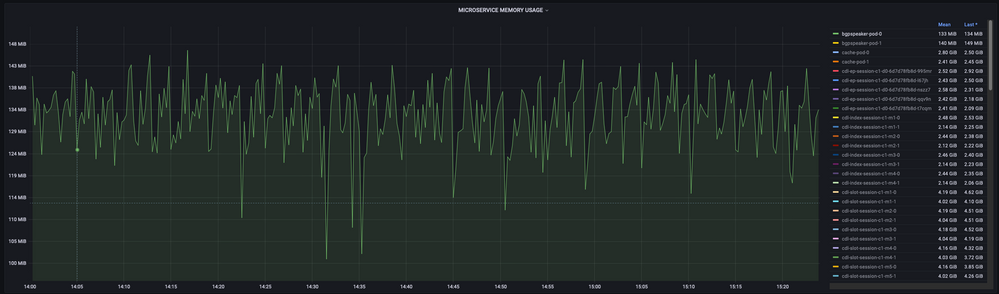


 Feedback
Feedback