EtherChannel zwischen Catalyst Switches der Serien 3550/3560/3750 und Catalyst Switches mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware - Konfigurationsbeispiel
Inhalt
Einführung
Dieses Dokument enthält eine Beispielkonfiguration zum Einrichten eines EtherChannels zwischen einem Catalyst 3550 und einem Catalyst 6500/6000 mit Cisco IOS® Systemsoftware. EtherChannel kann je nach Geschwindigkeit der Schnittstellen oder Ports, die zum Erstellen des EtherChannels verwendet werden, auch als Fast EtherChannel oder Gigabit EtherChannel bezeichnet werden.
Hinweis: Die in diesem Dokument auf den Catalyst 3550-Switch angewendeten EtherChannel-Befehle können auch auf Catalyst Switches der Serie 3750 angewendet werden.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Für dieses Dokument bestehen keine speziellen Anforderungen.
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf den folgenden Software- und Hardwareversionen:
-
Catalyst 3550-Switch mit Cisco IOS-Software, Version 12.1(14)EA
-
Catalyst 6500/6000-Switch mit Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(13)E1
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument wurden von den Geräten in einer bestimmten Laborumgebung erstellt. Alle in diesem Dokument verwendeten Geräte haben mit einer leeren (Standard-)Konfiguration begonnen. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die potenziellen Auswirkungen eines Befehls verstehen.
Konventionen
Weitere Informationen zu Dokumentkonventionen finden Sie unter Cisco Technical Tips Conventions (Technische Tipps zu Konventionen von Cisco).
Hintergrundtheorie
In diesem Dokument wurden zwei Gigabit Ethernet-Schnittstellen auf einem Catalyst 3550-Switch - die GigabitEthernet-Schnittstelle des 3500 ist eine 10/100/1000-handelte Ethernet-Schnittstelle - in einem Fast EtherChannel mit zwei Fast Ethernet-Schnittstellen eines Catalyst 6500/600-Switches mit Cisco gebündelt. IOS-Systemsoftware zur Erstellung eines Layer-2-EtherChannels (L2).
Hinweis: In diesem Dokument werden Fast EtherChannel, Gigabit EtherChannel, Port-Channel und Channel-Gruppen alle als EtherChannel bezeichnet.
Die Catalyst Switch-Konfiguration in diesem Dokument gilt für alle Catalyst Switches der Serien 6500/6000 oder 4500/4000 mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware.
In diesem Dokument werden nur Konfigurationsdateien für die Switches sowie die Ausgabe der entsprechenden Beispiel-show-Befehle angezeigt. Weitere Informationen zum Konfigurieren eines EtherChannels finden Sie in den folgenden Dokumenten:
-
Konfigurieren des Layer-2-EtherChannels-Abschnitts zur Konfiguration des EtherChannels (Catalyst 3550-Switch)
-
Konfigurieren des Layer-3-EtherChannels-Abschnitts zur Konfiguration des EtherChannels (Catalyst 3560-Switch)
-
Konfigurieren des Layer-2-EtherChannels-Abschnitts zur Konfiguration des EtherChannels (Catalyst 3750-Switch)
-
Konfigurieren von Layer 3 und Layer 2 EtherChannel (Catalyst 6500/6000 mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware)
-
Konfigurieren des Layer-2-EtherChannel-Abschnitts Grundlegendes und Konfigurieren des EtherChannels (Catalyst 4500/4000 mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware)
Wichtige Hinweise
Der EtherChannel kann manuell mit den entsprechenden Befehlen konfiguriert werden. Sie können den EtherChannel auch automatisch mit PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol) konfigurieren, damit der Switch den Kanal mit der anderen Seite aushandeln kann. Einzelheiten zu PAgP finden Sie in folgenden Dokumenten:
-
Informationen zum Port Aggregation Protocol-Abschnitt zur Konfiguration von EtherChannel (Catalyst 3550-Switch)
-
Informationen zum Port Aggregation Protocol-Abschnitt zur Konfiguration von EtherChannel (Catalyst 3560-Switch)
-
Port Aggregation Protocol Abschnitt zur Konfiguration von EtherChannels (Catalyst 3750-Switch)
-
Informationen zum Port Aggregation Protocol Abschnitt zur Konfiguration von EtherChannel (Catalyst 6500/6000 mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware)
-
Informationen zum Abschnitt "Port Aggregation Protocol" (Port-Aggregation-Protokoll) zum Verständnis und Konfigurieren von EtherChannel (Catalyst 4500/4000 mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware)
Die Konfigurationen in diesem Dokument werden mithilfe des erwünschten Modus implementiert. Wenn Sie planen, den EtherChannel manuell zu konfigurieren, verwenden Sie die bereitgestellten Schritte, um einen Port-Channel zu erstellen. Dadurch werden Probleme mit dem Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) während des Konfigurationsprozesses vermieden. STP kann einige Ports mit dem Portstatus "error-disabled" [errdisable] schließen, wenn eine Seite als Kanal konfiguriert ist, bevor die andere Seite als Kanal konfiguriert werden kann.
Führen Sie die folgenden Schritte aus, um einen Port-Channel zu erstellen:
-
Lassen Sie die Schnittstellen für die Port-Channeling-Funktion beim administrativen Herunterfahren verwendet.
-
Erstellen Sie den Port-Channel (Kanalgruppe) auf dem Catalyst 6500/6000-Switch.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie den Channel-Modus auf ein einstellen, z. B. Kanal-Gruppe-1-Modus aktiviert.
-
Erstellen Sie Port-Channels auf dem Catalyst 3550-, 3560- oder 3750-Switch.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass der Kanalmodus aktiviert ist.
-
Aktivieren Sie die Schnittstellen, die zuvor auf dem Catalyst 6500/6000-Switch deaktiviert wurden, mit dem Befehl no shut erneut.
Konfigurieren
In diesem Abschnitt erhalten Sie Informationen zum Konfigurieren der in diesem Dokument beschriebenen Funktionen.
Hinweis: Um weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Dokument verwendeten Befehlen zu erhalten, verwenden Sie das Command Lookup Tool ![]() (nur registrierte Kunden).
(nur registrierte Kunden).
Netzwerkdiagramm
In diesem Dokument wird die in diesem Diagramm dargestellte Netzwerkeinrichtung verwendet:
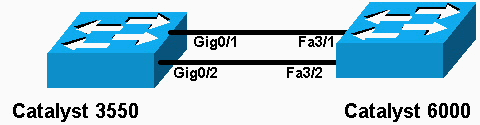
Hinweis: Die Gigabit Ethernet-Schnittstelle des Catalyst 3550 ist eine Ethernet-Schnittstelle mit 10/100/1000 Mbit/s, die ausgehandelt wird. Der Gigabit-Port des Catalyst 3550 kann auch mit einem FastEthernet-Port (100 Mbit/s) eines Catalyst 6500/6000 verbunden werden.
Hinweis: Die Catalyst Switches der Serie 3750 unterstützen stapelübergreifende EtherChannels, sodass Schnittstellen verschiedener Stack-Switches der gleichen EtherChannel-Gruppe angehören können. Weitere Informationen zu EtherChannel in einer Stack-Switch-Umgebung finden Sie im Abschnitt EtherChannel und Switch-Stacks in der Konfiguration von EtherChannels-Dokumentation für Catalyst Switches der Serie 3750.
Konfigurationen
In diesem Dokument werden folgende Konfigurationen verwendet:
| Catalyst 3550 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 1610 bytes ! version 12.1 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname Cat3550 ! enable password ww ! ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! ! ! ! !--- A logical port-channel interface is automatically created !--- when ports are grouped into a channel group. interface Port-channel 1 !--- In this example, the L2 EtherChannel is configured. !--- A Layer 3 (L3) EtherChannel can also be configured on the Catalyst 3550 switches. !--- For more information, refer to the document Configuring EtherChannel. switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status! !--- Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Catalyst 3550 is a !--- 10/100/1000 Mbps negotiated Ethernet interface. The Gigabit port on the Catalyst 3550 is !--- connected to a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port on the Catalyst 6500/6000. !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status channel-group 1 mode desirable ! !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status ! !--- Output suppressed. interface GigabitEthernet0/12 switchport mode access no ip address snmp trap link-status !--- Interface VLAN1 is required for management purposes. interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless ip http server ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 5 15 ! end |
| Catalyst 6500/6000 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 5869 bytes ! version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname cat6500 ! boot buffersize 126968 boot bootldr bootflash:c6msfc-boot-mz.121-4.E1 enable password ww ! redundancy main-cpu auto-sync standard ip subnet-zero ! ! no ip finger ! ! ! ! !--- A logical port-channel interface is automatically created !--- when ports are grouped into a channel group. interface Port-channel 1 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! interface GigabitEthernet1/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet1/2 no ip address shutdown ! !--- Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interface on the Catalyst 3550 is a !--- 10/100/1000 Mbps negotiated Ethernet interface. The Gigabit port on the Catalyst 3550 is !--- connected to a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port on the Catalyst 6500/6000. interface FastEthernet3/1 no ip address !--- In this example, the L2 EtherChannel is configured. !--- An L3 EtherChannel can also be configured on the Catalyst 6500/6000 running !--- Cisco IOS System Software. For more details, refer to the document !--- Configuring EtherChannel. !--- On a Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport !--- command once, without any keywords, in order to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default; !--- no additional command is required. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet3/2 no ip address !--- On a Catalyst 6500/6000, you must issue the switchport !--- command once, without any keywords, in order to configure the interface as an L2 port. !--- By default, all the ports are router ports (L3 ports). !--- On a Catalyst 4500/4000 switch, all ports are L2 ports by default; !--- no additional command is required. switchport !--- This command puts the interface in VLAN1, by default. switchport mode access !--- The port is a member of channel group 1. channel-group 1 mode desirable ! interface FastEthernet3/3 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! !--- Output suppressed. ! interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport mode access ! !--- Interface VLAN1 is required for management purposes. interface Vlan1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip classless no ip http server ! ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 ! end |
Hinweis: Dieses Konfigurationsbeispiel zeigt eine EtherChannel-Konfiguration mit Zugriffs-Links. Die gleiche Konfiguration gilt für EtherChannel-Trunk-Verbindungen. Geben Sie den Befehl switchport mode trunk ein, oder lassen Sie den Switches die Aushandlung des Modus mit dem Modus dynamisch wünschenswert zu. Weitere Informationen zum Konfigurieren von Trunking finden Sie im Abschnitt Konfigurieren von VLAN-Trunks im Dokument Konfigurieren von VLANs.
Port-Channel-Subschnittstellenkonfiguration
Ein weiteres Beispiel für die Konfiguration von Port-Channel mit Subschnittstelle im Catalyst 3560-Switch mit Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(25).
| Catalyst 3560 |
|---|
Building configuration... Current configuration : 2480 bytes ! version 12.2 ! interface Port-channel5 no switchport no ip address ! interface Port-channel5.690 ! interface Port-channel10 no switchport no ip address ! interface Port-channel10.1 ! interface Port-channel10.690 ! interface Port-channel11 no switchport no ip address |
Überprüfen
Bestimmte show-Befehle werden vom Output Interpreter Tool ![]() (nur registrierte Kunden) unterstützt, mit dem Sie eine Analyse der show-Befehlsausgabe anzeigen können.
(nur registrierte Kunden) unterstützt, mit dem Sie eine Analyse der show-Befehlsausgabe anzeigen können.
Führen Sie folgende Befehle aus, um den Port-Channel in Catalyst 6500/6000- und Catalyst 3500-Switches mit Cisco IOS System Software zu überprüfen:
Führen Sie folgenden Befehl aus, um den STP-Status in Catalyst 6500/6000- und Catalyst 3500-Switches mit Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware zu überprüfen:
Catalyst 3550
Cat3550#show interface port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0002.4b28.db02 (bia 0002.4b28.db02)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 1000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
input flow-control is off, output flow-control is off
Members in this channel: Gi0/1 Gi0/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:03:27, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
26 packets input, 5344 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 17 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
59 packets output, 5050 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat3550#show spanning-tree vlan 1 detail
VLAN1 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
We are the root of the spanning tree
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 1 last change occurred 00:00:38 ago
from Port-channel1
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 0
Port 65 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated port id is 128.65, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 34, received 0
Cat3550# show etherchannel 1 summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
U - port-channel in use
Group Port-channel Ports
-----+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Gi0/1(P) Gi0/2(P)
Cat3550# ping 10.1.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Catalyst 6500/6000
Cat6500# show interface port-channel 1
Port-channel1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is EtherChannel, address is 0002.7ef1.36e1 (bia 0002.7ef1.36e1)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 200000 Kbit, DLY 100 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Full-duplex, 100Mb/s
Members in this channel: Fa3/1 Fa3/2
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/2000, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 1000 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
407 packets input, 34994 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 311 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
93 packets output, 16598 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Cat6500# show spanning-tree vlan 1 detail
VLAN1 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 00d0.024f.6001
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Current root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Root port is 833 (Port-channel1), cost of root path is 12
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:02:13 ago
Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300
Port 833 (Port-channel1) of VLAN1 is forwarding
Port path cost 12, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 131.65.
Designated root has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0002.4b28.db01
Designated port id is 128.65, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 1, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
BPDU: sent 0, received 66
Cat6500# show etherchannel 1 summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
Group Port-channel Ports
-----+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Fa3/1(P) Fa3/2(P)
Cat6500# ping 10.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Fehlerbehebung
Status Deaktiviert
Ein häufiges Problem bei der EtherChannel-Konfiguration besteht darin, dass die Schnittstellen in den Error-Disable-Modus wechseln. Dies ist erkennbar, wenn Etherchannel in einem Switch in den ON-Modus geschaltet wird und der andere Switch nicht sofort konfiguriert wird. Wenn in diesem Zustand eine Minute lang verbleibt, denkt STP auf dem Switch, auf dem der EtherChannel aktiviert ist, an eine Schleife. Dies bewirkt, dass die Channeling-Ports in den Status "errdisable" gesetzt werden. In diesem Beispiel finden Sie weitere Informationen dazu, wie Sie bestimmen können, ob sich Ihre EtherChannel-Schnittstellen im Zustand err-disable befinden:
%SPANTREE-2-CHNL_MISCFG: Detected loop due to etherchannel misconfiguration of Gi0/9 %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po10, putting Gi0/9 in err-disable state %PM-4-ERR_DISABLE: channel-misconfig error detected on Po10, putting Gi0/10 in err-disable state
Switch1#show etherchannel summary
Flags: D - down P - in port-channel
I - stand-alone s - suspended
H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
R - Layer3 S - Layer2
u - unsuitable for bundling
U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator
d - default port
Number of channel-groups in use: 1
Number of aggregators: 1
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
------+-------------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------
10 Po10(SD) - Gi0/9(D) Gi0/10(D)
Switch1#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/9 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi0/9 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
Switch1#show interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/10 status
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
Gi0/10 err-disabled 1 auto auto 10/100/1000BaseTX
In der Fehlermeldung wird angegeben, dass der EtherChannel auf eine Spanning Tree-Schleife gestoßen ist. Um das Problem zu beheben, setzen Sie den Kanalmodus auf beiden Seiten der Verbindung auf wünschenswert, und aktivieren Sie dann die Schnittstellen erneut:
Switch1#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch1(config)#interface gi0/9 Switch1(config-if)#channel-group 10 mode desirable
Dies führt dazu, dass jede Seite nur dann einen Channel bildet, wenn beide dem Channel zustimmen. Wenn sie dem Channel nicht zustimmen, funktionieren sie weiterhin wie normale Ports.
Nachdem der Channel-Modus auf beiden Seiten der Verbindung auf wünschenswert gesetzt wurde, führen Sie die Befehle Shutdown und no Shutdown für die zugeordnete Schnittstelle aus, um die Ports manuell erneut zu aktivieren:
Switch1(config-if)#shutdown Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown
Der Befehl "speed nonegotiate" wird in der aktuellen Konfiguration nicht angezeigt.
Der auf einem Port-Channel konfigurierte Befehl speed nonegotiate (Geschwindigkeit ungerechnet) wird nicht immer in der aktuellen Konfiguration angezeigt. Dies geschieht, weil die Aushandlung für die Port-Channel-Schnittstelle von der der gebündelten Ports abhängt. Sie wird eingefügt, wenn der Port-Channel aktiv ist und die Konfiguration der einzelnen Channel-Ports zugrunde liegt.
Zugehörige Informationen
- Systemanforderungen für die Implementierung von EtherChannel auf Catalyst Switches
- Beispielkonfiguration: EtherChannel zwischen Catalyst-Switches mit CatOS- und Cisco IOS-Systemsoftware
- Produktsupport für Switches
- Unterstützung der LAN Switching-Technologie
- Technischer Support und Dokumentation - Cisco Systems
 Feedback
Feedback